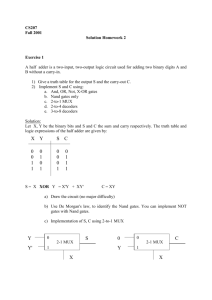
Solution - Electrical and Computer Engineering
advertisement

The University of British Columbia
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
EECE-256 Fall 2000 (Dr. Saif Zahir)
Solutions to Assignment No. 2
(Issued October 3, 2000)
Problem 1.
Draw a K-map for the following Boolean expressions:
(i) X’Y’Z’ + XY’Z’ + X’YZ’
XY
Z
00
01
11
10
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
YZ
X
OR
00
01
11
10
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
00
01
11
10
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
00
01
11
10
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
(ii) X’YZ’ + X’Y’
XY
Z
00
01
11
10
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
YZ
X
OR
(iii) X’Y’ + Y’Z’
XY
Z
00
01
11
10
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
YZ
X
OR
Problem 2. Using K-map, simplify the following Boolean algebraic expressions using
Sum-of-Products:
(i) A’B’C’ + AB’C’ + ABC + A’BC’ + A’B’C (Terms 3, 4, and 5 are Don’t Care)
AB
C
00
01
11
10
0
1
d
0
1
1
d
0
d
0
BC
A
OR
00
01
11
10
0
1
d
0
d
1
1
0
d
0
B'C'
B'C'
The “don’t cares” did not help to provide simpler expressions.
(ii) ABC + AB’C’ + ABC’ + AB’C (Terms 3 and 4 are Don’t Care)
AB
C
00
01
11
10
0
0
0
d
1
1
0
0
1
d
BC
A
OR
00
01
11
10
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
d
1
d
A
The “don’t cares” were all very useful in this exercise.
A
(iii) ABCD + A’B’C’D + A’BCD + AB’CD + A’B’CD + ABCD’ (Terms 4,5, and 6
are Don’t Care)
AB
CD
00
01
11
10
00
0
0
0
0
01
1
0
0
0
11
d
1
1
10
0
0
d
CD
AB
00
01
11
10
00
0
1
d
0
01
0
0
1
0
d
11
0
0
1
d
0
10
0
0
d
0
OR
A'B'D + CD
Two of the “don’t cares” were useful in this exercise.
A'B'D + CD
2
Problem 3. Using K-map, determine the minimal Product-of-Sums expression for the
following minterms:
(i) m1 + m3 + m5 + m7 + m12 + m13 + m8 + m9
Truth table for this expression:
m1
m3
m5
m7
m8
m9
m12
m13
AB
CD
A
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
00
01
11
10
00
0
0
1
1
01
1
1
1
1
11
1
1
0
10
0
0
0
B
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
C
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
D
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
F
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
CD
AB
00
01
11
10
00
0
1
1
0
01
0
1
1
0
0
11
1
1
0
0
0
10
1
1
0
0
OR
F = (A' + C' + D')(A + C)(C + D')
F = (A' + C' + D')(A + C)(C + D')
The 0’s in the K-map are used to obtain the Product-of-Sum expressions.
3
(ii) m0 + m5 + m7 + m8 + m11 + m13 + m15
Truth table for this expression:
m15
A
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
m0
m5
m7
m8
m11
m13
AB
CD
00
01
11
10
00
1
0
0
1
01
0
1
1
0
11
0
1
1
10
0
0
0
B
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
C
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
D
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
F
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
CD
AB
00
01
11
10
00
1
0
0
0
01
0
1
1
0
1
11
0
1
1
0
0
10
1
0
1
0
OR
F = (B + C' + D')(B' + C' + D)(A' + B' + D)(C + D')
The 0’s in the K-map are used to obtain the Product-of-Sum expressions.
4
Problem 4. (logic design) Consider a five-input Boolean function that is asserted
whenever exactly two of its inputs are asserted :
(i) construct the Truth Table for the function
A
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
B
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
C
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
D
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
E
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
F
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
(ii) What is the function in sum-of-products
Write out the expression for each 1 occurring in the truth table:
F = A'B'C'DE + A'B'CD'E + A'B'CDE' + A'BC'D'E + A'BC'DE' +
A'BCD'E' + AB'C'D'E + AB'C'DE' + AB'CD'E' + ABC'D'E'
5
(iii) what is the function in product-of-sums
Write out the expression for each 0 occurring in the truth table:
F = (A + B + C + D + E) (A + B + C + D + E') (A + B + C + D' + E)
(A + B + C' + D + E) (A + B + C' + D' + E') (A + B' + C + D + E)
(A + B' + C + D' + E') (A + B' + C' + D + E') (A + B' + C' + D' + E)
(A + B' + C' + D' + E') (A' + B + C + D + E) (A' + B + C + D' + E')
(A' + B + C' + D + E') (A' + B + C' + D' + E) (A' + B + C' + D' + E')
(A' + B' + C + D + E') (A' + B' + C + D' + E) (A' + B' + C + D' + E')
(A' + B' + C' + D + E) (A' + B' + C' + D + E')(A' + B' + C' + D' + E)
(A' + B' + C' + D' + E')
(iv) using K-map, simplify the function in sum-of-products form
F = A'B'C'DE + A'B'CD'E + A'B'CDE' + A'BC'D'E + A'BC'DE' +
A'BCD'E' + AB'C'D'E + AB'C'DE' + AB'CD'E' + ABC'D'E'
CD
00 01 11 10
AB
0
00
0
01
E=0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
11
10
0
0
0
1
CD
00 01 11 10
AB
0
00
1
01
E=1
1
0
0
0
11
10
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
The expression is in the simplest form already.
6
Problem 5 (Logic design): Consider a four-input function that outputs a 1 whenever an
odd number of its inputs are 1.
(i) construct the Truth Table
A
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
B
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
C
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
D
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
F
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
(ii) generate the K-map for the expression
AB
CD
00
01
11
10
00
0
1
0
1
01
1
0
1
0
11
0
1
0
10
1
0
1
CD
AB
00
01
11
10
00
0
1
0
1
01
1
0
1
0
1
11
0
1
0
1
0
10
1
0
1
0
OR
(iii) find minimal sum-of-product. can you simplify it using K-map?
Write a term for each 1 in the truth table.
F = A'B'C'D + A'B'CD' + A'BC'D' + A'BCD + AB'C'D' + AB'CD + ABC'D + ABCD'
It is not possible to simplify the expression using K-map.
7
(iv) Can you provide a more economic solution given that XOR gates are
available is in your inventory ?…
F = A'B'C'D + A'B'CD' + A'BC'D' + A'BCD + AB'C'D' + AB'CD + ABC'D + ABCD'
F = A' (B'C'D + B'CD' + BC'D' + BCD) + A(B'C'D' + B'CD + BC'D + BCD' )
F = A' {B'(C'D + CD') + B(C'D' + CD)} + A{B'(C'D' + CD) + B(C'D + CD')}
Recall:
X'Y + XY' = X XOR Y = X Y
and
XY + X'Y' = X XNOR Y = (X Y)'
F = A' {B'(C D) + B(C D)'} + A{B'(C D)' + B(C D)}
Let
CD = Z
Then
F = A' {B'Z + BZ'} + A{B'Z' + BZ}
= A' {B Z} + A{B Z}'
= A' {B (C D)} + A{B (C D)}'
Let
B (C D) = W
Then
F = A' W + AW'
= AW
= A {B (C D)}
So, if we have XOR gates in our inventory, we can provide a more economic
solution.
Problem 6. Solve the following:
(i) Problem 5.2 in the textbook (Milo).
a.
E(x, y, z) = m(1,5,7)
m1
m5
m7
x
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
y
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
z
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
E
1
1
1
8
xy
z
00
01
11
10
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
yz
x
OR
b.
E(w, x, y, z) = w'x'y + y'z + xz'
wx
yz
00
01
11
10
00
0
1
1
0
01
1
1
1
1
11
1
0
0
10
1
1
1
00
01
11
10
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
yz
wx
00
01
11
10
00
0
1
1
1
01
1
1
0
1
0
11
1
1
0
1
0
10
0
1
0
0
OR
(ii) Problem 5.8 in the textbook (Milo).
A combinatorial system have four input a, b, c, d and one output y. The output y
is 1 if and only if the number represented by (a, b, c, d) in binary code is prime.
Design a minimal two-level network to implement this system. (0 and 1 are not
prime).
Draw the truth table:
a
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
b
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
c
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
d
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
y
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
9
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
Write the expression for y:
y = a'b'cd' + a'b'cd + a'bc'd + a'bcd + ab'cd + abc'd
Simplify the expression:
y = a'b'cd' + a'b'cd + a'bc'd + a'bcd + a'b'cd + ab'cd + a'bc'd + abc'd
= a'b'c(d' + d) + a'bd(c' + c) + b'cd(a' + a) + bc'd(a' + a)
= a'b'c + a'bd + b'cd + bc'd
= a'b'c + a'bd + b'cd + bc'd
Implement the logic circuit.
a
b
a'
c
b
'
d
c
'
d
'
a'b'c
a'bd
y
b'cd
bc'd
10