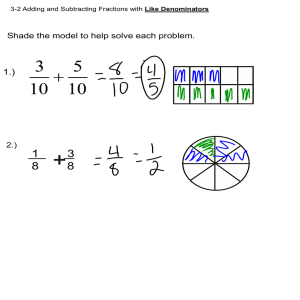
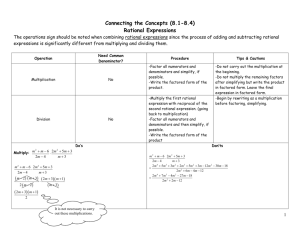
Module 3: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
advertisement
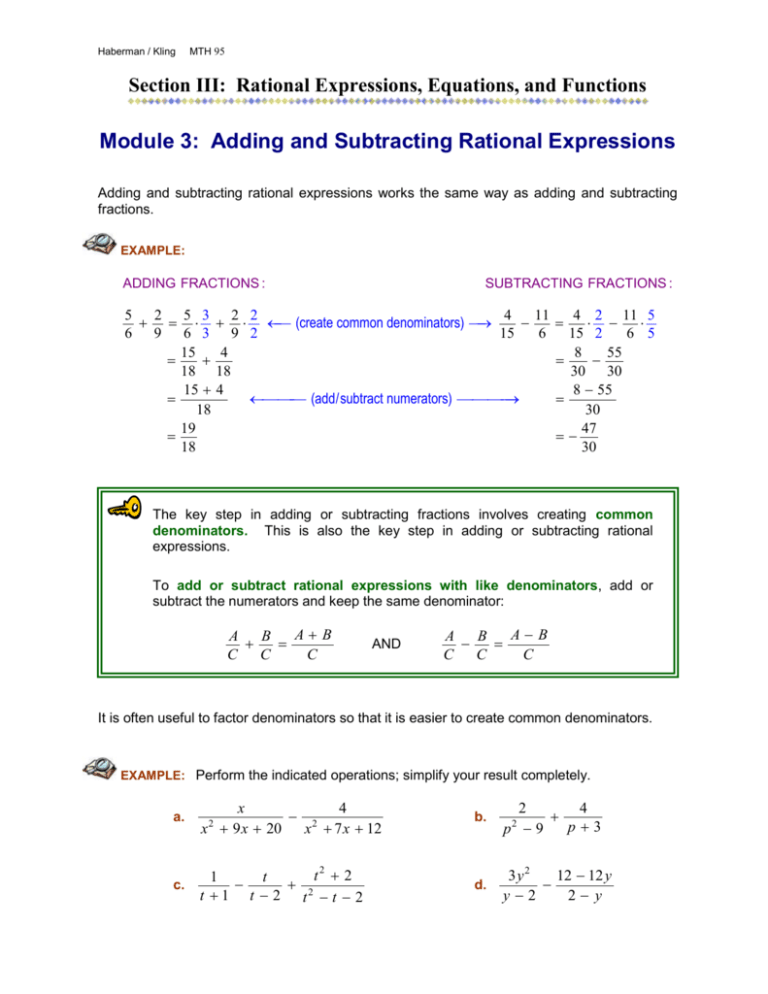
Haberman / Kling MTH 95 Section III: Rational Expressions, Equations, and Functions Module 3: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions Adding and subtracting rational expressions works the same way as adding and subtracting fractions. EXAMPLE: ADDING FRACTIONS : 5 2 5 3 6 9 6 3 15 18 15 18 19 18 SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS : 2 2 4 11 4 2 11 5 (create common denominators) 9 2 15 6 15 2 6 5 4 8 55 18 30 30 4 8 55 (add/subtract numerators) 30 47 30 The key step in adding or subtracting fractions involves creating common denominators. This is also the key step in adding or subtracting rational expressions. To add or subtract rational expressions with like denominators, add or subtract the numerators and keep the same denominator: AB A B C C C AND AB A B C C C It is often useful to factor denominators so that it is easier to create common denominators. EXAMPLE: Perform the indicated operations; simplify your result completely. a. x 4 2 x 9 x 20 x 7 x 12 b. 2 4 p 3 p 9 c. t2 2 1 t 2 t 1 t 2 t t 2 d. 3 y2 12 12 y y2 2 y 2 2 2 SOLUTIONS: a. x 4 x 4 2 (factor denominators) x 9 x 20 x 7 x 12 ( x 5)( x 4) ( x 4)( x 3) x x3 4 x5 ( x 5)( x 4) x 3 ( x 4)( x 3) x 5 x( x 3) 4( x 5) ( x 5)( x 4)( x 3) ( x 4)( x 3)( x 5) x( x 3) 4( x 5) (subtract numerators) ( x 5)( x 4)( x 3) 2 b. x 2 x 20 ( x 5)( x 4)( x 3) ( x 5) ( x 4) ( x 5) ( x 4) ( x 3) x5 , for x 4 ( x 5)( x 3) 2 4 2 4 (factor denominators) p 3 ( p 3)( p 3) p3 p 9 p3 2 4 (create common denominators) ( p 3)( p 3) p3 p3 2 4 ( p 3) (add numerators) ( p 3)( p 3) 2 4 p 12 ( p 3)( p 3) 4 p 10 ( p 3)( p 3) 2(2 p 5) ( p 3)( p 3) 2 t2 2 t2 2 1 t 1 t c. t 1 t 2 t 2 t 2 t 1 t 2 (t 1)(t 2) (factor denominators) t 1 t2 2 1 t2 t t 1 t 2 t 2 t 1 (t 1)(t 2) t 2 t (t 1) t 2 2 (t 1)(t 2) t 2 t2 t t2 2 (t 1)(t 2) 0 (t 1)(t 2) 0, for t 1, t 2 (add / subtract numerators) 3 d. For this example it is helpful to recognize the following fact: –(a – b) = b – a 3y2 12 12 y 3y2 1 12 12 y y2 2 y y 2 1 2 y 3y2 1 (12 12 y ) y2 y2 3 y 2 (1)(12 12 y ) y2 3 y 2 12 12 y y2 3( y 2 4 y 4) y2 3 ( y 2) ( y 2) y2 3( y 2), for y 2 Try these yourself and check your answers. Perform the indicated operations; simplify your result completely. a. 1 x 2x 3 x 4 b. b2 4 2 b 3 b 2b 3 SOLUTIONS: a. x4 2x 3 1 x 1 x 2x 3 x 4 2x 3 x 4 x 4 2x 3 x 4 x(2 x 3) (2 x 3)( x 4) x 4 2 x 2 3x (2 x 3)( x 4) 2 x2 2 x 4 (2 x 3)( x 4) 2( x 2 x 2) (2 x 3)( x 4) 2( x 1)( x 2) (2 x 3)( x 4) (create common denominators) 4 b. b2 b2 4 4 2 b 3 b 2b 3 b 3 (b 3)(b 1) (factor denominators) b 1 b2 4 b 3 b 1 (b 3)(b 1) 4(b 1) (b 2) (b 3)(b 1) 4b 4 b 2 (b 3)(b 1) 3b 2 (b 3)(b 1) (create common denominators) EXAMPLE: If f ( x) 3x 5 , find and simplify the expression f ( x h) f ( x ) . h SOLUTION: f ( x h) f ( x) 3( x h) 5 (3 x 5) h h 3x 3h 5 3x 5) h 3 h h 3, for h 0 Try this one yourself and check your answer. If g ( x) 7 x 10 , find and simplify the expression g ( x + h) - g ( x ) . h SOLUTION: g ( x h) g ( x) 7( x h) 10 (7 x 10) h h 7 x 7h 10 7 x 10 h 7h h 7, for h 0 5 EXAMPLE If g ( x) 4 , find and simplify the expression g (a 2) g (a ) . 3x SOLUTION: g (a 2) g (a) 4 4 3(a 2) 3a 4 a 4 a2 3(a 2) a 3a a 2 (create common denominators) 4(a 2) 4a 3a(a 2) 3a(a 2) 4a 4(a 2) 3a(a 2) 8 3a(a 2) 8 3a(a 2) Try this one yourself and check your answer. If f ( x) 1 , find and simplify the expression f ( w 1) f ( w 1) . 2x SOLUTION: f ( w 1) f ( w 1) 1 1 2( w 1) 2( w 1) w 1 w 1 1 1 2( w 1) w 1 2( w 1) w 1 w 1 ( w 1) 2( w 1)( w 1) w 1 w1 2( w 1)( w 1) 2 2( w 1)( w 1) 1 ( w 1)( w 1) (obtain a common denominator)