Evaluate 5y + x2
advertisement
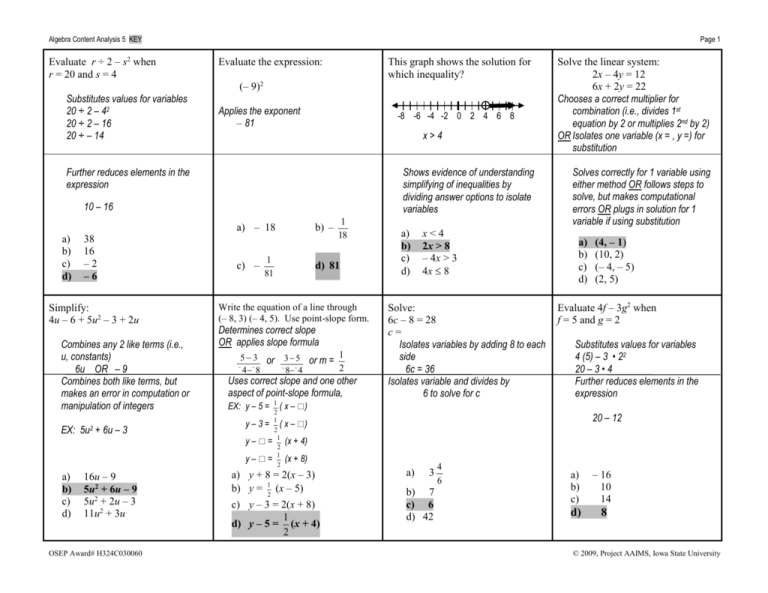
Algebra Content Analysis 5 KEY Evaluate r ÷ 2 – s2 when r = 20 and s = 4 Page 1 Evaluate the expression: This graph shows the solution for which inequality? (– 9)2 Substitutes values for variables 20 ÷ 2 – 42 20 ÷ 2 – 16 20 ÷ – 14 Applies the exponent – 81 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 x>4 Further reduces elements in the expression Shows evidence of understanding simplifying of inequalities by dividing answer options to isolate variables 10 – 16 a) b) c) d) a) – 18 38 16 –2 –6 Simplify: 4u – 6 + 5u2 – 3 + 2u Combines any 2 like terms (i.e., u, constants) 6u OR – 9 Combines both like terms, but makes an error in computation or manipulation of integers c) – d) 81 Determines correct slope OR applies slope formula 5 3 or 3 5 or m = 1 2 4 8 8 4 Uses correct slope and one other aspect of point-slope formula, EX: y – 5 = 1 ( x – ) 2 16u – 9 5u2 + 6u – 9 5u2 + 2u – 3 11u2 + 3u 1 81 1 18 Write the equation of a line through (– 8, 3) (– 4, 5). Use point-slope form. EX: 5u2 + 6u – 3 a) b) c) d) b) – 1 ( 2 1 = 2 = 1 2 y–3= x – ) y– (x + 4) y– a) b) c) d) x<4 2x > 8 – 4x > 3 4x 8 Solve: 6c – 8 = 28 c= Isolates variables by adding 8 to each side 6c = 36 Isolates variable and divides by 6 to solve for c (x + 8) a) b) 7 c) 6 d) 42 (x – 5) c) y – 3 = 2(x + 8) 1 d) y – 5 = (x + 4) 2 1 2 Solves correctly for 1 variable using either method OR follows steps to solve, but makes computational errors OR plugs in solution for 1 variable if using substitution a) b) c) d) (4, – 1) (10, 2) (– 4, – 5) (2, 5) Evaluate 4f – 3g2 when f = 5 and g = 2 Substitutes values for variables 4 (5) – 3 • 22 20 – 3 • 4 Further reduces elements in the expression 20 – 12 a) y + 8 = 2(x – 3) b) y = Solve the linear system: 2x – 4y = 12 6x + 2y = 22 Chooses a correct multiplier for combination (i.e., divides 1st equation by 2 or multiplies 2nd by 2) OR Isolates one variable (x = , y =) for substitution 3 4 6 a) b) c) – 16 10 14 d) 8 © 2009, Project AAIMS, Iowa State University OSEP Award# H324C030060 Algebra Content Analysis 5 KEY Page 2 Write the equation in slope-intercept Simplify: 9(2p – 1) – 6(p – 2) 2 form if m = and b = – 5 3 Distributes either term so that response includes 18p – 9 OR – 6p + 12 OR 12p Distributes both terms correctly 18p – 9 – 6p + 12 OR Distributes either term correctly and includes 12p or + 3 in response a) b) c) d) 3p – 3 24p – 21 12p – 3 12p + 3 Finds slope, but makes an error in computation c) 1 2 2 x – 5 (but no ‘y = ‘) 3 2 a) y = x – 5 3 2 b) y = x + 5 3 2 c) y = – 5x + 3 Simplify the expression: 3 b) 2 d) – Multiplies across to combine terms OR simplifies by reducing either the f or g terms 3 3 3 EX: f g or f g OSEP Award# H324C030060 g f Simplifies both the f and g terms, but expression is not fully reduced. a) 1 2 2 f g g 2 g fg g3 f a) – 2 2 x 3 d) y = – 5x + 2 Find the slope of a line through (2, 3), (8, – 9) Draws a graph to determine slope OR uses slope formula 93 3 9 or 82 28 y = mx + b OR an expression that includes f 3g 2 fg 3 2 2 EX: f g2 g f b) g c) f 2 d) f3 fg Solve: 7x – 3 = – 2x + 6 x= Isolates variables on 1 side (+ 2x or – 7x to both sides) OR Isolates constants on 1 side (– 6 or + 3 to both sides) Which line on the graph is y + 2x = – 3? y = – 2x – 3 B A C D Isolates constants and variables OR Isolates variables or constants and divides to solve for x a) 3 5 c) 1 b) – 1 d) 9 2 Simplify: 4(3 – f) + 2(3f + 4) Distributes either term so that response includes 12 – 4f OR 6f + 8 OR 2f Distributes both terms correctly 12 – 4f + 6f + 8 OR Distributes either term correctly and includes 2f or + 20 in response a) 10f + 20 b) 2f +7 c) 8f + 16 d) 2f + 20 a) b) c) d) Line A Line B Line C Line D Solve the linear system: 2x + y = 11 x–y= 4 Combines equations or chooses a correct multiplier for combination (i.e., multiplies 2nd equation by – 2) OR Isolates one variable (x = , y =) for substitution Solves correctly for 1 variable using either method OR follows steps to solve, but makes computational errors OR plugs in solution for 1 variable if using substitution a) b) c) d) (7, – 3) (5, 1) (7, 3) (3, 5) © 2009, Project AAIMS, Iowa State University