fe notes 1 - Newcastle University Staff Publishing
advertisement

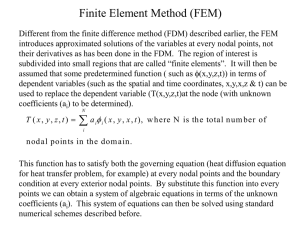
Newcastle University School of Mechanical & Systems Engineering An Introduction to THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD The Finite Element method for 2D continuum problems (c) John C. Appleby, 2008, School of Mechanical & Systems Engineering, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 7RU, U.K. Tel (+44) (0) 191-222 6286 E-mail: John.Appleby@ncl.ac.uk Fax (+44) (0) 191-222 8600 Web: http://www.staff.ncl.ac.uk/john.appleby Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Some examples of 2D problems and their chosen solution form 4 3. Solving the problems 8 4. Elements and shape functions 12 5. Mesh design and boundary conditions 17 6. Derivation of the finite element equations - the Galerkin method 24 7. Two-dimensional problems 28 8. Numerical integration and stress sampling 32 9. Frameworks - rod and beam elements 35 10. Bibliography 40 Appendix Results from stress analysis 41 ii 1. Introduction The Finite Element Method is a computational method for the analysis of stress, vibration, heat conduction, fluid flow, electrostatics and acoustics; it is suitable for a wide range of 2D and 3D continuum problems, which may be steady or unsteady, linear or non-linear. The method has been developed over about thirty years, starting with traditional matrix methods of structural analysis for frameworks consisting of rod and beam elements. In fact, problems with rods and beams are now also handled in finite element terms, since so many aspects are the same, but some features are necessarily distinct. The distinguishing feature of the finite element method for continuum problems is that we choose to represent the solution of the problem in a particular way at the outset. We in effect replace the original problem domain and material, which behaves in a smooth, continuous but probably complex way, with a domain, geometry and 'material' which have simpler behaviour, although not as smooth. We then apply the normal equations for the problem (eg equations of plane stress, Laplace's equation etc) to this simplified form of solution. Because our anticipated solution is not smooth, we need the equations in integral form, and these must be derived from the more familiar differential equations for many problems. The equations may themselves involve approximation, such as plane stress or plate bending formulations, or be exact, as for heat conduction. An example If we wished to solve the problem of a freely-hanging cable (the catenary), with true solution smooth and continuous, we might choose to represent it as a chain of finite links. For the catenary problem, this is not in fact a practical method of solution, but it is a useful illustration of some of the characteristic features of the finite element method. True form of solution Chosen approximation Since each link is defined completely by its end points, what was a continuum problem of infinitely many degrees of freedom has been represented by a system (mesh) of 8 elements joined at 9 nodes, each of which has an x-displacement and a y-displacement, giving 18 degrees of freedom. If we went on to formulate the whole problem in this way, we would obtain a system of 18 simultaneous linear equations in these 18 variables. Now, 4 variables are known, namely zero displacements at the end points, but there are 4 corresponding unknown reactions, so we do indeed have 18 unknowns and a well-defined problem. After solving the equations for the unknown displacements and forces, we may also solve for derived quantities, such as stresses. Moreover, we can calculate the displacements etc at any point in the structure, since each link is defined entirely in terms of its end-points. For framework problems, such as pylons, bridges, conveyors etc made from girders, the structure is already in discrete form, and the only approximation is in the choice of equations such as beams with or without shear effects. This example, though artificial, illustrates the principal stages of a static, linear finite element analysis for a 2D continuum problem: Discretise the structure (design a mesh of nodes and elements), and choose a form of solution in each element. Apply the equations to obtain a system of simultaneous linear equations. Apply boundary conditions and forces (gravity in this example). Solve the equations for the primary variables at the nodes. Solve for reactions and any derived quantities. Calculate values within each element in terms of the nodal values if desired. A 3D problem follows exactly the same steps. A framework problem is different only in the first step. A non-linear problem requires iteration to solve the main system of equations. An unsteady problem solves the equations at each time step. Thus a vast range of problems are susceptible to essentially the same approach if suitable equations can be derived, and it is possible to construct general purpose finite element packages which use common modules for many different problem types. In these notes we concentrate on continuum problems, in contrast to treatments designed primarily for structural engineers; rod and beam elements are considered in section 7. Principal advantages of the finite element method The finite element method was developed initially for structural engineering problems. Because the mesh is designed by the user (though sometimes with computer assistance), it is possible to conform to features of the structure such as: fitting the mesh to the geometry, which can involve the use of curved-sided elements, having different materials and eg thicknesses within different elements (since the integral equations do not fail at discontinuities), elements of varying sizes in different regions to reflect the complexity of the solution in each part. Disadvantages of finite element analysis are that it is more difficult to understand and to program than eg the finite difference method, and can be more difficult to apply for some kinds of domain and boundary conditions, such as free-surface fluid flows. 2 Comparison with other methods The finite element method applies the exact equations (or the normal approximation) to a chosen approximated form of the solution. In contrast, the finite difference method approximates the differential equations for the problem, applied to the solution at points on a grid. For example, ( x h ) ( x h ) 2 ( x h ) 2 ( x ) ( x h ) . , and x 2h x 2 h2 A third method, the boundary element method, also uses an integral formulation, but discretises the solution only on the boundary, which is more economical, particularly when it is the boundary that is actually of greatest interest. The first two methods produce large matrices of coefficients that are usually banded, producing economies of storage and solution time; the third method produces a smaller matrix, but more densely populated. 3 2. Some examples of 2D problems and their chosen solution form (i) A plane stress problem A simple triangular bracket, attached to a wall, is loaded at its tip. The bracket is made from thin sheet mild steel, and the load is in-plane, so the equations of plane stress apply. The simplest model (or representation) of this structure is a single element which deforms in a linear way, ie the displacements are linear functions of x and y, and the deformed plate remains a straight-sided triangle. With this assumption about the way the structure behaves, we know at the outset that the deformed shape must be something like that shown: thickness 0.01m 0.2m y x F=1000N 0.2m Note that we have not so far done any calculation, but simply imposed on the problem a chosen form of solution. Normally, we would choose a form that we expect to be capable of representing the true solution to reasonable accuracy. In this case, the bracket should really bend much more near the tip than we have allowed, and it is not surprising if our model is much stiffer than it should be. Exercise To obtain an order of magnitude estimate of the solution, model the domain as a rectangle of comparable dimensions and apply the force as a one-dimensional analogue. (E Young's modulus for mild steel is 2. 09 1011 Nm2 ) We can improve things by using four elements, each of which behaves linearly, but which together permit more complex behaviour: 4 In practice, we often use more than one mesh, of progressively increasing refinement, to help us assess the likely accuracy of the solution. If the increased resolution makes little difference, it suggests that we may have reached convergence to the true solution. It is important to realise that convergence may be very slow, so that we are much further from the true values than it appears, and convergence to the wrong solution is also possible! We must have independent verification, if only from experience or an approximate estimate, before we can rely on any results. Overall, these meshes produce 6 and 12 variables respectively (3 or 6 nodes x 2 displacements). 3 variables are known (fixed, zero displacements) and also 3 or 9 forces (one imposed, the remainder zero). Therefore we solve for 3 displacements and 3 reactions or 9 displacements and 3 reactions in the two cases. If the boundary conditions are changed, the matrix of coefficients remains unchanged, and it is economical to re-use this with new boundary conditions, especially as the matrix may be processed independently of the altered information, and it is this stage that takes most computer time. All finite element packages should offer such a re-solution facility. (ii) A heat conduction problem A square region (1m along each edge) has the temperature fixed along the edges, and we wish to find the temperature within the region, as well as the heat flow. The thickness and material affect the size of the fluxes, but not the temperature distribution, provided the material is homogeneous. If we model the solution as four elements, joined at five nodes, and we assume the temperature varies linearly within each triangular element, we are in effect assuming that the temperature contours are straight lines. Exercise Sketch the expected form of the contours, and give a rough estimate of the central value of temperature. Since it is obvious that the central value will be below 50 , we can sketch the expected solution as shown: T=100x T=0 T=100y y x T=0 Once again, the form of solution is clearly not satisfactory, and we can design a better mesh which will permit a smoother solution, but even such a simple mesh as this, or the first one for the bracket example, may be useful to: check the operation of the program, data input, boundary conditions etc check that we have a well-defined problem 5 give an order of magnitude estimate of the solution identify areas where the mesh should be refined This problem has one degree of freedom at any point, namely the temperature, and so there are 5 variables (the nodal temperatures) overall. We obtain a system of 5 equations. With the boundary conditions indicated, we know 4 of these temperatures, and our 5 unknowns are the central nodal temperature, together with 4 values of heat flux, with the results given at the nodes. These must be interpreted as integrated fluxes into or out of the boundary surrounding each node. For this mesh, that is the region extending from mid-way between the nodes on each side. Here the total flux will be zero, with flow into the domain around one node, and out of it around three. If we change the boundary conditions, eg imposing fluxes rather than temperatures at the boundary, we can use the same set of equations, as described above. Also note that Laplace's equation, or Poisson's equation if source terms are included, applies to a range of other problems, including electrostatics, torsion and groundwater and other potential flows. (iii) Curved-sided elements One of the principal advantages of the finite element method is the ability to match closely the true geometry of the problem. Simple linear elements, like the 3 node triangle, always have straight sides, but elements whose behaviour is described by quadratic or higher functions can also have a geometry described by curves. parabolic curve water Dam modelled as a single 8-noded quadrilateral Here a single element is able to model a curved side, though in practice many more elements would be used. In general, one quadratic or higher order element of this type has superior performance to the eight linear triangles that could replace it with about the same number of degrees of freedom. (iv) Mesh grading As well as modelling the geometry of the problem, element sizes and shapes may be chosen to give uniform accuracy to the solution, by using more nodes and elements in areas of greatest 'activity'; where changes are most rapid and complex, smaller elements should be used. 6 Here, quadrilateral elements (which might be 4-node, 8-node or more) are graded in size to suit a problem of a point load on a block. Note that 'quadrilateral' does not imply 'rectangular'. In practice, the natural symmetry of this problem would be used to reduce the domain and corresponding calculation by half. 7 3. Solving the problems The above examples have indicated how we can model the geometry and the anticipated solution behaviour. Next we shall look at two of them to see what the computer program does to reach a solution, but deferring until later the derivation of the finite element equations. (i) The simple bracket The bracket problem above, when modelled with a single triangular element, requires the following data (if the package FINEL is to be used) or very similar data. Some packages offer mouse-driven interactive mesh design, so that the geometry is 'drawn' on to the screen, but the data created will be of the same type. 3 thickness 0.01m 0.2m y (1) x 1 2 F=1000N 0.2m Mesh with node and element numbers title bracket in plane stress coordinates 1 0.0 0.0 2 0.2 0.0 3 0.0 0.2 elements 1 1 2 3 dimensions 1 0.01 constraints 1 1 0.0 3 1 0.0 3 2 0.0 forces 2 2 -1.0e3 *end optional title node number, x coordinate, y coordinate element number, nodes numbered anticlockwise size code 1 will have thickness 0.01m node 1, d.o.f. 1, constrained to value 0.0 node 3, both d.o.f. constrained to 0.0 node 2, d.o.f. 2, force in -ve direction a control line, the last line of data To enter and run this example with FINEL, just type finel bracket where 'bracket' will be the name of the input and output files, then enter the data (without the explanatory comments) as given above. Note that these files will be created in the current directory; to place them elsewhere you must enter a 'pathname', eg finel a:\data\bracket. 8 The program has now been given all the information it needs to create the matrices of coefficients in the equations, and to apply boundary conditions and forces before solving the whole system. In this case, there is only one element, with six variables: u1 , v1 , u2 , v2 , u3 , v3 , where u,v are the displacements in the x and y directions. The topology of the element is described by the list of node numbers for the element (going anticlockwise, and starting at any corner for FINEL). For this linear element, the assumed form of solution is u a bx cy, v d ex fy, and this implies that the strain and stress, eg x u / x , x ( E / 1 2 )( x y ) , will be constant throughout each element (these are also known as constant strain elements). The equilibrium equations for plane stress produce the equations: 1 p p 1 p p u1 ? p 1 p p p 1 v 0 1 1 0 0 u2 0 25EtA 1 2 p 0 p p 0 v2 F 1 p p p 0 p p 0 u3 ? 1 0 0 1 v3 ? E is the Young's modulus, is Poisson's ratio, t , A are the element thickness and area, p (1 ) / 2 and ? is an unknown reaction. The matrix of coefficients on the left-hand side is generally called the stiffness matrix, since it corresponds to the stiffness of a simple spring in the equation stiffnessdisplacement = force. The term, coming from structural engineering, is in fact applied to finite element analyses of all kinds. Now, we know that u1 u3 v3 0 , since two nodes are constrained, so we may solve the three equations whose right-hand sides are known for the remaining unknown displacements. Then we can solve for the three unknown reaction forces, represented by ? in the equations. Exercise Solve for the unknowns in terms of E, p, t, A, , and check that the reaction forces agree with equilibrium of forces and moments for the original structure. You will find that the reactions are exact, even though the displacements are much smaller than the true values. When more elements are used, a 6x6 matrix is obtained for each element, and these are then assembled to produce the global matrix of coefficients. Exercise (i) Run the above example data with FINEL and check your calculations for the displacements and reactions. (ii) Plan and enter the data for the four element mesh for the same problem. You will need to modify the sections coordinates, elements, constraints, forces. 9 (ii) The simple heat conduction problem 4 5 (4) (2) y 3 (3) (1) 1 2 x Mesh with node and element numbers The heat conduction problem described in the previous section can be solved by a finite element package if the mesh is numbered as shown. The equation describing heat flow for this problem is Laplace's equation, viz 2 T 0 . The data is entered as follows (for the package FINEL, though similar data will be entered for any package, or created by an interactive interface): title Simple heat conduction problem *laplace coordinates 1 0.0 0.0 2 1.0 0.0 3 0.5 0.5 4 0.0 1.0 5 1.0 1.0 elements 1 1 2 3 2 1 3 4 3 2 5 3 4 3 5 4 constraints 1 0.0 2 0.0 4 0.0 5 100.0 *end optional title gives problem type (not plane stress the default) node number, x, y element number, nodes - anticlockwise fixed nodal temperatures a control line - end of data To run this example, using 'heatflow' as the name of both input and output files, enter: finel heatflow The program has now been given enough information to apply the finite element method and produce solutions for T3 and the four unknown values of (integrated) heat flux. There will be five variables (nodal temperatures) and hence a 5x5 global matrix will be generated. This is assembled from four 3x3 local matrices, one for each element, derived from Laplace's equation as it applies to linear elements. Within each element, the temperature has been assumed to follow 10 the pattern: T a bx cy. As an example (without explaining at this point how it is done), the matrix for element 3 is: 0 0.5 T2 ? 0.5 kt 0 0.5 0.5 T5 ? 0.5 0.5 10 . T3 ? where k is the thermal conductivity, and t is the thickness of the material. Each row actually represents part of an equation, namely of equations 2, 5, 3 respectively, and where the right-hand sides relate to known and unknown heat fluxes. These part-equations are combined, by adding together appropriate entries in the global, 5x5, matrix, to obtain: 1 0 0 1 kt 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 4 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 T1 ? T ? 2 T3 0 T4 ? T5 ? Note that the program has assumed that the thickness is 1m, and the material is mild steel. These will affect the heat fluxes, but not the temperature distribution. Exercise (i) Solve for the unknown temperature T3 in terms of kt, and then for the four unknown heat fluxes. Check that the net heat flux into the domain is zero. (ii) Confirm that the formula T 100 xy gives an exact solution to Laplace's equation that corresponds to the specified boundary conditions, and compare the central value of temperature. (iii) We chose to use linear functions to represent the temperature, so, knowing this, and the values of T at nodes 1,3,5, sketch the graph of the temperature along the line x=y, and, on the same diagram, sketch the exact solution (a curve). The heat fluxes are actually exact, even though the temperature is not exact everywhere. Exercise Run the above example data with FINEL and check your calculations for the temperatures and fluxes. Notes on the examples 1. The solution for the second problem above is much better at the nodes than in between. Although the exact values will be obtained anywhere only by chance or for a very simple problem, it is generally true that the finite element method produces better results at and near the nodes. We shall see why later on. 2. When we use more sophisticated element types, such as the 8-node quadrilateral, the solution between the nodes is represented by pieces of curve, not straight line. 3. Problems like the two considered here can be solved entirely by hand, but clearly more complex meshes need the speed and accuracy of the computer. 11 4. Elements and shape functions Several of the examples above, and many of those supplied with FINEL, use three-node triangular elements with linear variation in the primary variables - displacement, temperature, streamfunction etc. We next look more carefully at how these elements behave, and continue to other element types. We shall then be able to design a mesh representing both the geometry and the behaviour of our problem domain. We shall mostly consider the variable T, which may be interpreted as temperature, because it is easy to visualise, but the identical analysis applies to any variable. Example 1 The variation of T within the triangular element shown is given by T a bx cy. (0,1) 3 1 2 (0,0) (1,0) For this triangle , with nodes at (0, 0), (1, 0), (0,1), we obtain the coefficients T T1 ( T2 T1 ) x ( T3 T1 ) y so that at node 1, T T1 , at node 2, T T2 , and so on . If we rewrite this expression as T (1 x y ) T1 ( x ) T2 ( y ) T3 we see that the temperature T is interpolated between the values at the nodes. We have thus described the form of the solution in terms of the nodal values. The functions that, in this form, are the coefficients of T1 , T2 and T3 are called interpolation functions, or shape functions, and are denoted by Ni , so we write T N1T1 N2 T2 N3 T3 . Note that, by their nature of interpolating T, all three functions have the property: value at 'own' node = 1, value at other nodes = 0. Another property is that the shape functions sum to 1 identically. If we visualise this linear interpolation of T between the three nodal values, we get something like this: Surface representing value of T T3 T1 3 T2 1 Physical domain 2 For a mesh with more elements, we get a 'picture' of the true, curved, surface being represented by a linked surface of flat, triangular pieces (a piecewise linear function), rather like a 'geodesic dome'. 12 Example 2 For the triangle (0,4) 3 2 (3,1) 1 (-3,0) we find that T must be represented as T 1 21 (12 3 x 3 y )T1 211 (12 4 x 3 y )T2 211 ( 3 x 6 y )T3 . Exercise Check that the three functions N1 , N2 and N3 are 1 or 0 at the appropriate node. To derive functions like these for any triangle is straightforward. If we set T a bx cy and then simply require that T T1 at node 1 (with the appropriate coordinates), T T2 at node 2, etc, we get three equations that must be satisfied by a, b, c, and we solve them in terms of T1 , T2 and T3 . Exercise (i) For the first example above, follow this procedure and hence derive the functions as given. That is, at node 1 set T1 a b. 0 c. 0 , etc, and show that a,b,c must be as before. (ii) Derive the shape functions for the second example by the same method. (iii) Derive the shape functions for the triangular element with nodes at (2,0), (2,3), (3,0) and check that they have the required properties. Example 3 We shall consider next the 8-node quadrilateral element, which is probably the most useful element type for common problems of plane stress etc. To match the number of nodes, we need interpolation functions with 8 coefficients. To ensure isotropic behaviour, we must have symmetry in x and y, and the appropriate form of function turns out to be T a bx cy dx 2 exy fy 2 gx 2 y hxy2 . The first six terms give what we call a complete quadratic function. The two cubic terms are needed to give eight coefficients, but have some curious implications when we look in detail at the performance of this element type. For most stress problems the best results are obtained by using a scheme of numerical integration that actually gives an inexact value for these terms; some cancellation of errors occurs. It would be time-consuming to derive the actual function or functions for every element, of any shape and size, in a mesh. Moreover, when we come to calculate integrals of functions of these functions, the algebra is frightful, and actually impossible for elements with curved sides. 13 Therefore, we derive the shape functions for a standard element as shown, and use coordinate mapping to modify them for an arbitrary element geometry, with numerical integration to deal with the algebraic difficulties. Because we often need these features, it is simpler to use them in all cases, even where the geometry is actually simple. A finite element package will automatically use mapping and numerical integration for this and many other element types. (1,1) 7 5 6 y 8 1 x 2 4 3 (-1,-1) A function that has the value 1 at one node, and 0 at seven other nodes, is not so simple as before. Written in a form that makes its properties clear, we get, for example: N1 14 (1 x )(1 y )( 1 x y ), N 2 12 (1 y )(1 x 2 ), with the other functions corresponding to one of these, with changes only in signs and exchanges of x for y in N2 . Exercise Write down possible forms for the remaining shape functions and check that they have the required properties. It is possible to visualise these functions; here is one of N1 , N3 , N5 or N 7 , and one of N 2 , N 4 , N 6 , N8 . Element mapping The idea of mapping an element in real space to a standard element has been mentioned above, and is particularly useful for complex elements that may have curved edges, such as the 8-node quadrilateral. To see how it works, we'll consider mapping a 3-node triangle, although this is not really necessary as it is so easy to derive shape functions for such an element. We'll assume that we wish to map any triangle to the standard triangle shown: 14 (0,1) 3 y 1 (0,0) 2 x (1,0) which has shape functions: N1 1 x y, N2 x , N3 y , and where x,y are local coordinates. We have already discussed the idea of representing the variables using these, viz T N1T1 N2 T2 N3 T3 . We now extend the idea to represent the geometry of an element using the same shape functions (you will appreciate by now the importance of understanding the properties of these functions!). We write x' N1 x1 N2 x 2 N3 x3 y' N1 y1 N2 y2 N3 y3 , where x1 , y1 etc are the coordinates of the nodes of the real triangle, and x', y' are the global coordinates of an arbitrary point within the triangle. Suppose we consider the triangular element with nodes 1,2,3 at (1,-1), (0,1), (-1,0) respectively. Our expressions become: x' 1. N1 0. N2 1. N3 N1 N3 1 x 2 y y' 1. N1 1. N2 0. N3 N1 N2 2 x y 1 Now we consider several points in the standard element, and see to which points in the actual element they correspond. x y 0 gives x' 1, y' 1, so that node 1 corresponds as expected . x 1, y 0 gives x' 0, y' 1, so node 2 also corresponds . x 0. 5, y 0 gives x' 0. 5, y' 0, so mid - points of edges correspond . Exercise (i) Find which points in the real element correspond to the points (0,0.5) and (1/3,1/3) in the standard element. (ii) Investigate the mapping for the element with nodes at (1,0), (0,-2), (1,-2) respectively. The same procedure applies to mapping for more complex elements. However, it does not follow that any shape of element is acceptable. Extreme elongation leads to decreased accuracy, and extreme distortion can lead to a non-unique mapping. Shapes that would be unacceptable include: 15 where the last is no good because the position of the 'mid-side' nodes is too close to the corners and leads to a singular mapping. It is usually best to put such nodes near or at the middle of the side (but in crack propagation problems it is actually possible to exploit the singularity to model crack tip behaviour). Exercise For the 8-node element, if you have found all the shape functions, you can investigate the mapping for an element with nodes at (0,0), (1,-0.5), (2,0), (1.5,1), (2,2), (1,2), (0,2), (0,1), which has two curved sides. Other examples In 2D, other element types include a straight-sided 4-node quadrilateral, a (curved-sided) 6-node triangle (types 3,2 respectively in FINEL), and higher-order elements with cubic and higher shape functions. Although the formulation becomes progressively more difficult, more complex elements generally out-perform simpler ones, since far fewer are needed for the same level of accuracy. On the other hand, conforming to geometry, and applying boundary conditions, sometimes make lower order elements more convenient. Axisymmetric problems can be treated in a way very similar to 2D problems, and the element types are essentially the same. Boundary conditions, and the underlying numerical integration, need special consideration. 3D problems need a comparable range of element types. The equivalent to the 3-node triangle is a 4-node tetrahedron; the 8-node quadrilateral translates to a 20-node 'brick' element. Combination type elements include a 6-node 'wedge' etc. The theory of these is just the same as for 2D, but naturally the algebra is more complex, and the computation is vastly greater! 16 5. Mesh design and boundary conditions The design of an effective mesh for a given problem depends on an anticipation of features of the solution, so that effort can be directed where it is most needed. A systematic strategy can be followed, but experience is invaluable in the initial design and in appropriate refinement or modification. There are sophisticated programs which automate some aspects of the process; generating a mesh of a given resolution is standard for larger packages, and automatic refinement is becoming better established with time. Naturally the geometry and materials are relevant to the design; the accuracy required should also be considered in advance as part of the job specification. Here we will give only some general guidelines and an outline strategy. Before applying finite element analysis, estimate orders of magnitude of the solution, and identify areas needing more attention. Ensure that all boundary conditions are known (except where these are some of the unknowns) so that the problem is well-defined. Concentrate nodes and elements in areas where behaviour is likely to be most complex. Avoid elongated and distorted elements Aspect ratios (ratio of length to width) are best near 1, and certainly less than 5. Corner angles should be between 30 and 150 . Mid-side nodes (for eg 8-node quadrilaterals) should be within the central third of the side. Use a single element type throughout, or a mixture of elements of comparable accuracy, since otherwise convergence as resolution is increased will be uneven. Choose appropriate element types (eg plate-bending problems offer a choice of formulations). A sensible strategy, unless you are solving a problem very similar to one you have solved before, would be: Estimate the solution first (as above). Reduce the problem size by symmetry whenever possible, to reduce effort/cost and increase accuracy. Design a very simple mesh to confirm your estimates and to check operation of the program etc. Design a mesh of varying resolution, but still simple, as a reference point for establishing convergence. Increase resolution, perhaps doubling in all directions and increasing resolution locally in critical areas, and compare values. Smoothness of contours may also be a useful indication. (Many packages always smooth contours, so that this information is unavailable, but FINEL displays the actual contours for every element for stress problems.) Increase again, and compare. With three sets of results, you can now form some estimate of whether you are near a correct solution. If important conclusions or commitments are to be based on your results, check independently unless prior experience is sufficient. Another aspect of a problem might be that the domain is actually unbounded, and some finite extent must be imposed. The technique of so-called infinite elements (which effectively impose an exponential or algebraic form of decay beyond a chosen boundary) is often the best approach, but otherwise you can proceed as follows: 17 Make an initial choice of domain size, based on problem features and experience, and using a simple mesh. If the form of decay at large distances is known for similar idealised problems, this will be very helpful. Extend the domain significantly, but by using additional elements, not stretching elements (since that would introduce two changes in the solution, size and resolution, simultaneously) and compare. Extend again and compare as necessary. Even though the actual values obtained may be very poor, this should indicate whether the additional regions are likely to influence significantly the results in the area of interest. A few examples are useful to show how meshes may be 'graded' in resolution. The example data files provided with FINEL provide more illustrations (though not all of them are well-designed, since they may simply be demonstrating a feature of the program). Example 1 In using trianglular elements, it is better, on the whole, to maintain a uniform resolution as far as possible; the first design is to be preferred to the second: Example 2 To change from larger to smaller triangular elements, this pattern can be used: Example 3 For grading quadrilateral elements, there is a standard 'trick': The same idea can be used to adapt from 1 larger to 3 or 4 smaller. 18 Example 4 Symmetry requires appropriate boundary conditions. For example, for heat conduction: Cold Hot no heat flux across boundary Cold Zero heat flux is imposed by the condition T 0 , where n is the normal. n Stress problems require instead constraints of zero displacement across the line of symmetry, with movement only along it. Bandwidth Many finite element programs, including FINEL, solve the global equations in the order of the numbered degrees of freedom, which essentially means node-by-node. If the node numbering is chosen sensibly, the matrix entries are grouped principally about the main diagonal in a band. If the typical width of this band is w, and the total number of degrees of freedom is N, then the overall storage requirement is proportional to Nw, and the computation is proportional to Nw 2 . If no attention is paid to node numbering, the computation is then proportional to N 3 , which can be beyond the capacity of the computer if N is of the order of 1000 or more. 3D problems require large N and can not avoid fairly large w, so that high computing requirements ensue. More sophisticated packages may offer a node-renumbering routine, but this can itself be slow if the initial numbering is very poor, and is most worthwhile for meshes that will be used repeatedly. The largest problems are usually tackled using a different algorithm, in which only part of the system of equations is held in core at one time. This frontal method requires sensible numbering of elements instead of nodes. Example If we assume a problem with one degree of freedom, such as potential flow, the first of the following will give a matrix with a half-bandwidth of 7, while the second gives a half-bandwidth of 3. This means that the distance from the main-diagonal to the most extreme entry on any row is at most 7 and 3 respectively. This occurs because the range of node numbers surrounding any element is again 7 and 3, and the part-equations described by the local matrix for each element relate the variables at the nodes for that element only. 7 8 9 10 11 12 2 4 6 8 10 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 3 5 7 9 11 19 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 In fact, FINEL and other packages do not store and compute entries only within a fixed band, but allow for a varying profile, so that minor details of numbering make little difference to costs. This is useful because if a mesh is changed after design and entry, eg by refining the mesh in one area, the rest of the mesh need not be renumbered even though locally the bandwidth may be significantly increased. Boundary conditions Static linear problems like heat conduction and plane stress are, in mathematical terms, elliptic problems; their solution is determined entirely by their boundary conditions and not by past history (which would be the case for eg wave propagation problems). Source terms and body forces are also, of course, relevant. At every point of the problem domain, not just at the boundary, one condition is imposed, explicitly or implicitly, and another, corresponding one, is unknown and will form part of the solution. For example, for heat conduction, either the temperature or the heat flux is known everywhere. Within the domain, if there is no source term, the net flux into any small region is zero. On the boundary, either the temperature or the flux is fixed (often zero flux if the boundary is insulated), but we can't physically fix both. For a plane stress problem, either the displacement or the force is known everywhere. The force is usually zero throughout the body, or equal to a body force such as gravity or centripetal effects. Where the displacement is fixed, an unknown reaction force may be found. The two commonest forms of boundary condition are: primary variable fixed (temperature, pressure/streamfunction, displacement), or derivative fixed (flux, velocity, stress/force). Mathematically, these are known as Dirichlet and Neumann conditions. The first is imposed by specifying the values in the input data (section constraints in FINEL); these variables are then ignored in the solution process and their values substituted. A normal derivative can be imposed easily in the finite element method. The derivation of the equations produces a term Ni ds , namely, the integral of the normal derivative times a n shape function along the boundary. For a zero derivative (insulated boundary etc), this term is 20 identically zero, and nothing need be specified (ie the program assumes it is zero). Boundary conditions imposed via this term are known as natural boundary conditions. A non-zero derivative (flux, stress etc) must be applied as an integrated quantity, and the form depends on whether linear or quadratic shape functions are used for each element. The procedure is as follows: The total heat flux into or out of a boundary, or the total force to be applied to a boundary, is divided between relevant elements in proportion to their boundary lengths (ie integral of flux along boundary). For each element, this fraction is then attributed equally to the two nodes. F/6 d F/3 F/6+F/3 F 2d 2F/3 F/3 A force may be applied at any angle, by resolving into components, then distributing them between the nodes in the same way. If a succession of boundary elements have the same length, then the contributions at nodes will be in the ratios 1:2:2:.....:2:1, reminiscent of the trapezium rule for integration (because we are indeed dealing with integrals of linear functions). For quadratic shape functions, the force or flux is distributed between elements as before, but the attribution to nodes is then in the ratio 1:4:1. For a succession of equal length elements, this produces the ratios 1:4:2:4:....:2:4:1 (reminiscent of Simpson's rule). F/12 d F/2 F/3 F/12+F/12 F d F/2 F/3 F/12 Other forms of boundary condition can be specified, but must be added into the original equation before the Galerkin method is applied, as in the technique of 'Lagrange multipliers'. Exercises 21 (i) Number the nodes to give a small bandwidth, treating the mesh as (a) 3-node triangles, and (b) 8-node quadrilaterals. (ii) Complete the central part of these meshes using the same element type, and making the transition from smaller to larger elements. (a) (b) ? ? (iii) Design meshes for the following problem, with no more than 20 3-node or 8-node elements, using smaller elements and more nodes in the area of interest. point load metal block (iv) Use symmetry to reduce the domain of each problem, and indicate all the boundary conditions. Sketch suitable mesh designs for 3-node and 8-node elements. p=0.02 (a) p=-0.02 (b) water q -q (c) (d) hole plate hot (e) - as (iii) above 22 cold (v) Write down the constraint data for typical nodes of: (a) (b) (c) - (g) as (iv) (a) - (e) above (vi) Apply the flux or velocity or field to the nodes: F (a) d d d 2d 3d F (c) F (d) d (vii) d F (b) 2d d 3d 2d Apply the force to the nodes and resolve into x and y components: 45 30 (a) (b) F F 3d 2d d d 23