Population Predictions
advertisement

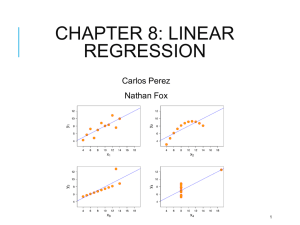
Linear Regression & Population Predictions Steps of lesson: 1. Warm-up Activity: Ask students to estimate the population for the following areas United States - 318,892,103 (July 2014 est.) Atlanta 4,715,000 (2012 est.) Chicago 9,121,000 (2012 est.) Los Angeles 14,900,000 (2012 est.) Miami 5,582,000 (2012 est.) New York City 20,464,000 (2012 est.) 2. After discussing population as a class, students will predict the population for various global cities. The cities are listed on the student handout. Students are to record their predictions before researching population data. 3. Monitor student progress in locating population data. 4. After data is retrieved and organized, students will write a linear regression equation that compares predicted population to actual population. Students should have previous experience in writing linear regression equations as well as understanding the components to the equation. 5. Teacher Notes: Guide students to graph their regression equation and y = x on the same coordinate plane and to compare the equations. If a student consistently guessed the population correctly, the equation would be y = x. If their line is below y = x, then they over predicted population, if it is above, then they under predicted population. Likewise, if the slope of the line is less than 1, then the populations were over predicted and if the slope is greater than 1, then were under predicted. Compare the slopes of student equations to determine whose slope is closest to one. The student that has the slope closest to one is the best predictor. See the answer key for graphical displays. Extension: Student may interview their parent and ask him or her to predict population for the same global cities. Then students can write a regression equation for their parent and compare their predicting abilities to their parent. Students may locate the global cities on a map. The North Carolina Geographic Alliance http://geo.appstate.edu/NCGA Linear Regression & Population Predictions 1. Predict populations for the following cities. Record your results in the chart below. City/Town Predicted Population (x) Actual Population (y) Beijing, China Cairo, Egypt Delhi, India London, United Kingdom Mexico City, Mexico Moscow, Russia Paris, France Seoul, South Korea Tokyo, Japan 2. Find the actual population for the cities listed in the chart. Record your results in the chart above. 3. Write a regression equation comparing the predicted population to the actual population. Round slope and y – intercept 4 decimal places. 4. What would the equation be if you predicted the population for each city correctly? Compare your results to this equation. The North Carolina Geographic Alliance http://geo.appstate.edu/NCGA Linear Regression & Population Predictions ANSWER KEY: Population Predictions Predict populations for the following cities. Record your results in the chart below. City/Town Predicted Population (x) Beijing, China Cairo, Egypt Delhi, India London, United Kingdom Mexico City, Mexico Moscow, Russia Paris, France Seoul, South Korea Tokyo, Japan Actual Population (y) 17,311,000 17,816,000 22,242,000 8,586,000 19,463,000 15,512,000 10,755,000 22,547,000 37,126,000 Examples of Scatter Plots compared to y = x. a) Underestimating: The actual population is greater than the predicted, therefore the student underestimated. Actual Population Predicted Population b) Overestimating: The actual population is less than the predicted, therefore the student overestimated. Actual Population Predicted Population Sources: US Census, World Atlas The North Carolina Geographic Alliance http://geo.appstate.edu/NCGA