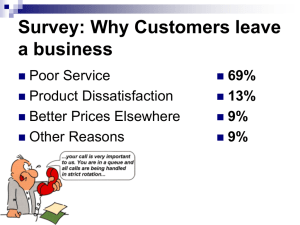
“Quality” means
advertisement
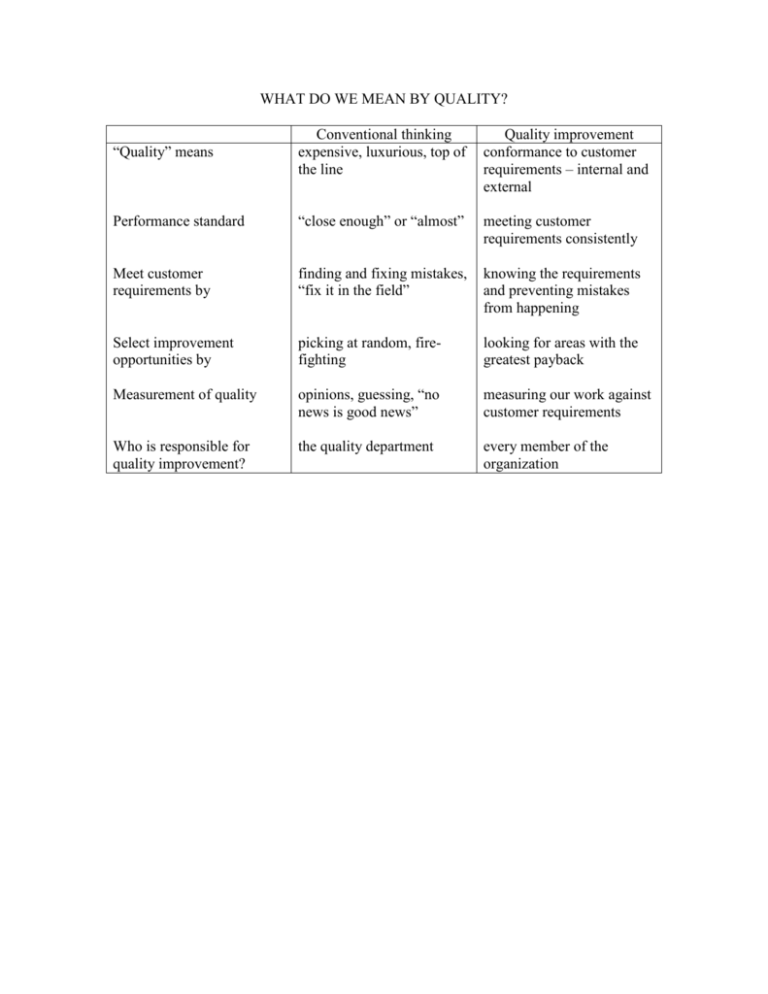
WHAT DO WE MEAN BY QUALITY? “Quality” means Conventional thinking expensive, luxurious, top of the line Quality improvement conformance to customer requirements – internal and external Performance standard “close enough” or “almost” meeting customer requirements consistently Meet customer requirements by finding and fixing mistakes, “fix it in the field” knowing the requirements and preventing mistakes from happening Select improvement opportunities by picking at random, firefighting looking for areas with the greatest payback Measurement of quality opinions, guessing, “no news is good news” measuring our work against customer requirements Who is responsible for quality improvement? the quality department every member of the organization Examples of Cultural Changes Required CATEGORY Mission PREVIOUS STATE Maximum return on investment/management by objectives (ROI/MBO) NEW CULTURE Ethical behavior and customer satisfaction. Climate for continuous improvement. ROI a performance measure Customer Requirements Incomplete or ambiguous understanding of customer requirements Use of a systematic approach to seek out, understand, and satisfy both internal and external customer requirements. Suppliers Unidirectional relationship Partnership Objectives Orientation to short-term objectives and actions with limited long-term perspective Deliberate balance of long-term goals with successive short term objectives Improvement Acceptance of process variability and subsequent corrective action as the norm Understanding and continually improving the process. Problem-Solving Unstructured individualistic problem-solving and decisionmaking Predominantly participative and interdisciplinary problem-solving and decision-making based on substantive data. Jobs and People Functional, narrow scope management-controlled Management and employee involvement; work teams; integrated functions. Management Style Management style with uncertain objectives that instills fear of failure Open style with clear and consistent objectives, which encourages groupderived continuous improvement Role of manager Plan, organize assign, control, can enforce Communicate, consult, delegate, coach, mentor, remove barriers, and establish trust Rewards and recognition Pay by job. Few team incentives Individual and group recognition and rewards, negotiated criteria. Measurement Orientation toward data gathering for problem identification Data used to understand and continuously improve processes. Stages of People Involvement TRADITIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE TYPICAL IMPROVEMENT EFFORTS DECISION POWER PARTICIPATION HIERARCHICAL HIERARCHICAL AND AD HOC TEAMS SUGGESTION PROGRAM AD HOC TEAMS WORK ON PROBLEMS WORK MEASUREMENT QUALITY CIRCLES TOP DOWN RECOMMEND CHANGES LIMITED TEAMBASED DECISIONMAKING GAINSHARING MANAGEMENT FOCUS APPROVED SUGGESTIONS INDIVIDUAL WORK PERFORMANCE SUPERVISING SOME TEAM/UNIT PARTICIPATION AND RECOGNITION COACHING INVOLVEMENT CUSTOMERFOCUSED, AUTONOMOUS WORK TEAMS TEAMS CONSISTENTLY ANALYZE AND IMPROVE PROCESSES MAKE PROCESSRELATED DECISIONS INPUT INTO STRATEGIC DECISIONS TEAM RECOGNITION e.g. GAINSHARING CREATING ENVIRONMENT FOR TEAMWORK W. Edward Deming: A Universally Applicable Philosophy? Deming’s theories about quality management were accepted earlier and more wholeheartedly in Japan than in the United States. Why? Does Deming’s philosophy reflect some values and beliefs that are more acceptable to some cultures than others? The chart below lists Deming’s fourteen points and suggests values and beliefs that these points may reflect in the middle column. The column on the right suggest opposing values and beliefs that may be held by some cultures. Deming’s Points Cultural Value or Belief Cultural Counterpoint 1. Create constancy of purpose for improvement of product and service. One should constantly be thinking about the future. Our goal is constant progress. One should work to make the present moment as pleasant as possible. The future will take care of itself. (Or: Allah will take care for he future.) (Or: We should seek harmony with our past traditions.) 2. Adopt the new philosophy. Change is a good thing. Change is threatening. We should honor our traditions. 3. Cease dependence on mass inspection. Hierarchy is bad. Too much structure stifles good work. If given freedom, people will do the right thing. Hierarchy is good. Rules make things work. Too much freedom leads to chaos. 4. End the practice of awarding business on price tag alone. Cooperation is the best way to do business. One should be close to one’s suppliers. Competition destroys trust. Competition is the best way to do business. One should keep one’s suppliers at arm’s length. Competition brings out the best in people. 5. Improve constantly and forever the system of production and service. One should constantly be thinking about the future. Our goal is constant progress. One should work to make the present moment as pleasant as possible. The future will take care of itself. (Or: Allah will take care for he future.) (Or: We should seek harmony with our past traditions.) 6. Institute training. Anyone can learn to be strong contributor. Everyone should have the opportunity for education. Everyone has his place in the universe. It is wrong to educate people beyond that which is appropriate for their station in life. 7. Institute leadership. Workers want to work hard and achieve. Management needs to get out of their way so that workers can perform. If given freedom, people will do the right thing. Workers are lazy and shiftless. management needs to impose strict controls to ensure that the job gets done. Too much freedom leads to chaos. Deming’s Points 8. Drive out fear. Cultural Value or Belief Cultural Counterpoint People should have freedom to suggest new ideas and challenge the status quo. Competition among different ideas will ultimately leads to a better way of doing things. People must respect the existing order. Challenges to authority ultimately destroy the organization. 9. Break down barriers Teamwork is the best way to get between staff areas. things done. cooperation is the best way to get things done. Competition destroys trust. Individuals should be encouraged to excel. Competition is the best way to do business. Competition brings out the best in people. 10. Eliminate slogans, exhortations, and targets for the workforce. People naturally do the best they can in the situations they find themselves in. Slogans won’t make any difference. Workers are lazy and shiftless. They need to be constantly reminded of their responsibilities. 11. Eliminate numerical quotas. Employees who have goals without a means to achieve them loose motivation. Employees who have challenging goals may be inspired to new heights. 12. Remove barriers to pride of workmanship. Workers want to work hard and achieve. Management needs to get out of their way so that workers can perform. If given freedom, people will do the right thing. Workers are lazy and shiftless. Management needs to impose strict controls to ensure that the job gets done. Too much freedom leads to chaos. 13. Institute a vigorous program of education and retraining. Anyone can learn to be a strong contributor. Everyone should have the opportunity for education. Everyone has his place in the universe. It is wrong to educate people beyond that which is appropriate for their station in life. 14. Take action to accomplish the transformation Action is good. Don’t just stand there; do something! What we do is not nearly as important as who we are. Reflection is more important than action. Deming’s philosophy has a strong future time orientation. It suggests that we should think in terms of constant progress, that we should strive to make tomorrow better than today. Deming’s philosophy is egalitarian. Anyone can learn how to improve quality. Everyone can and should make contributions to quality. Deming’s philosophy is optimistic. Workers will do the right thing if given a chance. People want to work hard and achieve, if only management will let them. Deming’s philosophy emphasizes collaboration over competition. People must work together, not against each other. Questions for discussion: 1. Do you think that the chart above accurately reflects Deming’s values and beliefs? Why or why not? 2. Think of a culture that you are familiar with. In what ways is Deming’s philosophy compatible with this culture? What aspects of Deming’s philosophy of management might people from this culture have a hard time with? Ability to Do Job Old employee leaves with knowledge Time New employee begins Ability to Do Job EYELASH LEARNING CURVE New employee comes on; picks up almost where previous employee left off. Time RAPID LEARNING CURVE