P10-2A In recent years, Juresic Transportation
advertisement
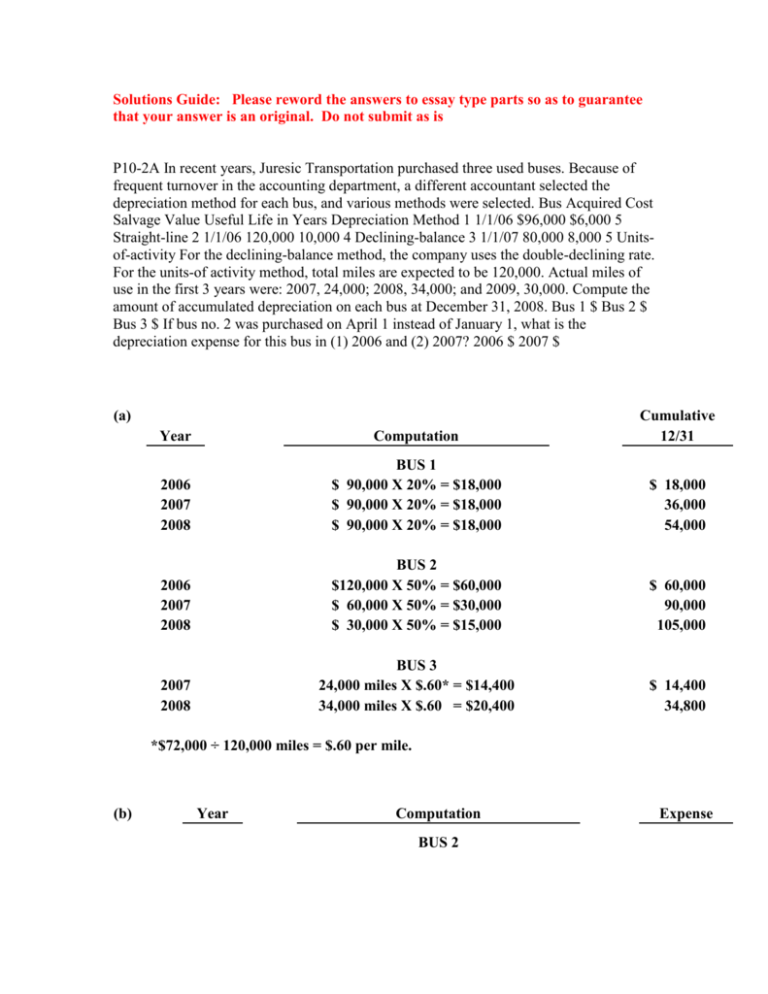
Solutions Guide: Please reword the answers to essay type parts so as to guarantee that your answer is an original. Do not submit as is P10-2A In recent years, Juresic Transportation purchased three used buses. Because of frequent turnover in the accounting department, a different accountant selected the depreciation method for each bus, and various methods were selected. Bus Acquired Cost Salvage Value Useful Life in Years Depreciation Method 1 1/1/06 $96,000 $6,000 5 Straight-line 2 1/1/06 120,000 10,000 4 Declining-balance 3 1/1/07 80,000 8,000 5 Unitsof-activity For the declining-balance method, the company uses the double-declining rate. For the units-of activity method, total miles are expected to be 120,000. Actual miles of use in the first 3 years were: 2007, 24,000; 2008, 34,000; and 2009, 30,000. Compute the amount of accumulated depreciation on each bus at December 31, 2008. Bus 1 $ Bus 2 $ Bus 3 $ If bus no. 2 was purchased on April 1 instead of January 1, what is the depreciation expense for this bus in (1) 2006 and (2) 2007? 2006 $ 2007 $ (a) Year Computation Cumulative 12/31 2006 2007 2008 BUS 1 $ 90,000 X 20% = $18,000 $ 90,000 X 20% = $18,000 $ 90,000 X 20% = $18,000 $ 18,000 36,000 54,000 2006 2007 2008 BUS 2 $120,000 X 50% = $60,000 $ 60,000 X 50% = $30,000 $ 30,000 X 50% = $15,000 $ 60,000 90,000 105,000 2007 2008 BUS 3 24,000 miles X $.60* = $14,400 34,000 miles X $.60* = $20,400 $ 14,400 34,800 *$72,000 ÷ 120,000 miles = $.60 per mile. (b) Year Computation BUS 2 Expense (1) 2006 $120,000 X 50% X 9/12 = $45,000 $45,000 (2) 2007 $75,000 X 50% = $37,500 $37,500 P10-3A On January 1, 2008, Pele Company purchased the following two machines for use in its production process. Machine A The cash price of this machine was $38,000. Related expenditures included: sales tax $1,700, shipping costs $150, insurance during shipping $80, installation and testing costs $70, and $100 of oil and lubricants to be used with the machinery during its first year of operations. Pele estimates that the useful life of the machine is 5 years with a $5,000 salvage value remaining at the end of that time period. Assume that the straight-line method of depreciation is used. Machine B The recorded cost of this machine was $160,000. Pele estimates that the useful life of the machine is 4 years with a $10,000 salvage value remaining at the end of that time period. Prepare the following for Machine A. The journal entry to record its purchase on January 1, 2008. The journal entry to record annual depreciation at December 31, 2008. Account / Description Debit Credit 1. Depreciation expenseShippingAccumulated depreciationSalesSales tax expenseAccounts receivableInsurance expenseMachineryRepairs expenseCashAccounts payable $ Insurance expenseMachinerySales tax expenseRepairs expenseSalesShippingAccounts payableAccumulated depreciationCashDepreciation expenseAccounts receivable $ 2. CashSales tax expenseShippingInsurance expenseRepairs expenseAccounts receivableAccounts payableDepreciation expenseMachinerySalesAccumulated depreciation $ Depreciation expenseAccounts payableAccumulated depreciationInsurance expenseMachineryShippingSalesCashAccounts receivableSales tax expenseRepairs expense $ Calculate the amount of depreciation expense that should record for machine B each year of its useful life under the following assumptions. (Round depreciation cost per unit to 2 decimal places. Round final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125.) Pele uses the straight-line method of depreciation. Pele uses the decliningbalance method. The rate used is twice the straight-line rate. Pele uses the units-ofactivity method and estimates that the useful life of the machine is 125,000 units. Actual usage is as follows: 2008, 45,000 units; 2009, 35,000 units; 2010, 25,000 units; 2011, 20,000 units. Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 1. Straight-line $ $ $ $ 2. Declining-balance $ $ $ $ 3. Units-of-activity $ $ $ $ Which method used to calculate depreciation on machine B reports the highest amount of depreciation expense in year 1 (2008)? all methods are the samedeclining-balance methodunits-of-activity methodstraight-line method The highest amount in year 4 (2011)? all methods are the samestraight-line methoddeclining-balance methodunits-of-activity method The highest total amount over the 4-year period? (a) (1) Purchase price ............................................................................................... Sales tax.......................................................................................................... Shipping costs ................................................................................................ Insurance during shipping ........................................................................... Installation and testing ................................................................................. $ 38,000 1,700 150 80 70 Total cost of machine .......................................................................... Machine ....................................................................................... Cash ................................................................................... (2) (1) (2) 40,000 $ 40,000 5,000 $ 35,000 ÷ 5 $ 7,000 7,000 7,000 Recorded cost ................................................................................................ Less: Salvage value ...................................................................................... Depreciable cost ............................................................................................ Years of useful life......................................................................................... Annual depreciation............................................................................ Book Value at Beginning of Year $160,000 80,000 40,000 20,000 (3) 40,000 Recorded cost ................................................................................................ Less: Salvage value ...................................................................................... Depreciable cost ............................................................................................ Years of useful life......................................................................................... Annual depreciation............................................................................ Depreciation Expense ................................................................ Accumulated Depreciation .............................................. (b) $ 40,000 160,000 10,000 $150,000 ÷ 4 $ 37,500 DDB Rate Annual Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation *50%* *50%* *50%* *50%* $80,000 40,000 20,000 ** 10,000 $ 80,000 120,000 140,000 150,000 **100% ÷ 4-year useful life = 25% X 2 = 50%. Depreciation cost per unit = ($160,000 – $10,000)/125,000 units = $1.20 per unit. Annual Depreciation Expense 2010: $1.20 X 45,000 = $54,000 2011: 1.20 X 35,000 = 42,000 2012: 1.20 X 25,000 = 30,000 2013: 1.20 X 20,000 = 24,000 (c) The declining-balance method reports the highest amount of depreciation expense the first year while the straight-line method reports the lowest. In the fourth year, the straight-line method reports the highest amount of depreciation expense while the declining-balance method reports the lowest. These facts occur because the declining-balance method is an accelerated depreciation method in which the largest amount of depreciation is recognized in the early years of the asset’s life. If the straight-line method is used, the same amount of depreciation expense is recognized each year. Therefore, in the early years less depreciation expense will be recognized under this method than under the declining-balance method while more will be recognized in the later years. The amount of depreciation expense recognized using the units-of-activity method is dependent on production, so this method could recognize more or less depreciation expense than the other two methods in any year depending on output. No matter which of the three methods is used, the same total amount of depreciation expense will be recognized over the four-year period.







