ESE Terminology
The ABC's of ESE
My Notes | Previous Next Search
General Disability
ESE Terminology:
Deciphering the Alphabet Soup of Acronyms
(Compiled by Professor Eadens)
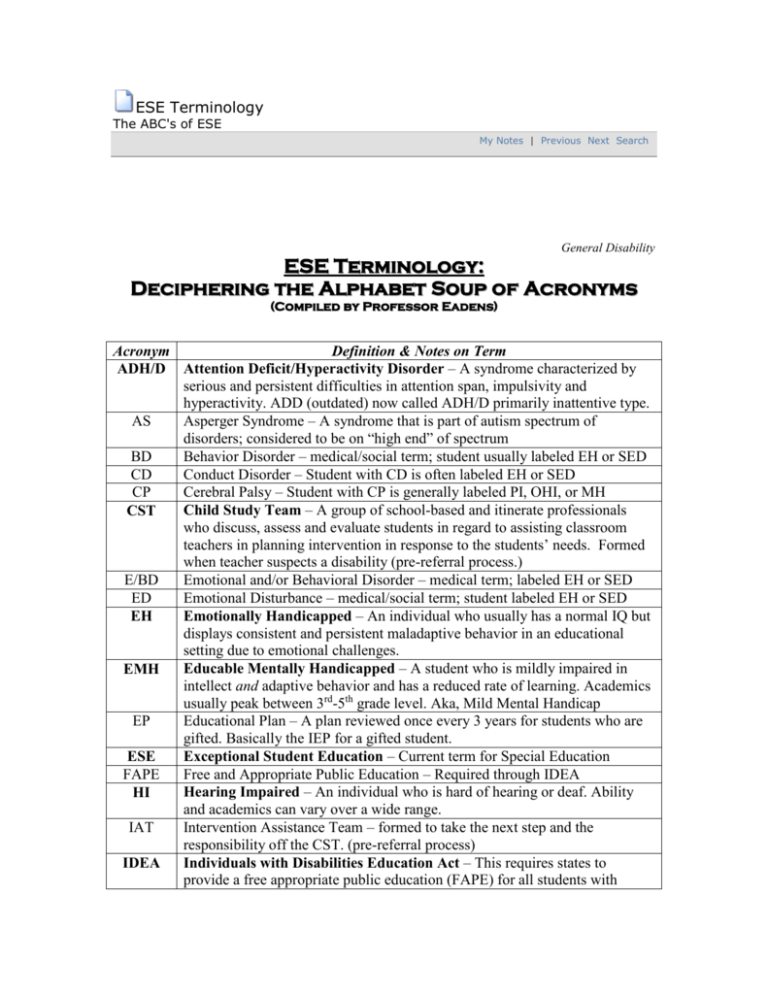
Acronym
Definition & Notes on Term
ADH/D Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder – A syndrome characterized by
serious and persistent difficulties in attention span, impulsivity and
hyperactivity. ADD (outdated) now called ADH/D primarily inattentive type.
AS
Asperger Syndrome – A syndrome that is part of autism spectrum of
disorders; considered to be on “high end” of spectrum
BD
Behavior Disorder – medical/social term; student usually labeled EH or SED
CD
Conduct Disorder – Student with CD is often labeled EH or SED
CP
Cerebral Palsy – Student with CP is generally labeled PI, OHI, or MH
Child Study Team – A group of school-based and itinerate professionals
CST
who discuss, assess and evaluate students in regard to assisting classroom
teachers in planning intervention in response to the students’ needs. Formed
when teacher suspects a disability (pre-referral process.)
E/BD
Emotional and/or Behavioral Disorder – medical term; labeled EH or SED
ED
Emotional Disturbance – medical/social term; student labeled EH or SED
Emotionally Handicapped – An individual who usually has a normal IQ but
EH
displays consistent and persistent maladaptive behavior in an educational
setting due to emotional challenges.
Educable Mentally Handicapped – A student who is mildly impaired in
EMH
intellect and adaptive behavior and has a reduced rate of learning. Academics
usually peak between 3rd-5th grade level. Aka, Mild Mental Handicap
EP
Educational Plan – A plan reviewed once every 3 years for students who are
gifted. Basically the IEP for a gifted student.
Exceptional Student Education – Current term for Special Education
ESE
FAPE
Free and Appropriate Public Education – Required through IDEA
Hearing Impaired – An individual who is hard of hearing or deaf. Ability
HI
and academics can vary over a wide range.
IAT
Intervention Assistance Team – formed to take the next step and the
responsibility off the CST. (pre-referral process)
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act – This requires states to
IDEA
provide a free appropriate public education (FAPE) for all students with
IEP
LI
LLD
LRE
MH
MR
ODD
OHI
OT
PI
identified handicaps. Defines handicaps covered by schools. Schools receive
funding and services are provided to student with identified disability. Aka,
PL 101-476, formerly Public Law 94-142
Individual Education Plan – A written plan of action that lists the student’s
current performance/functioning level, placement in an ESE program, goals
for students, accommodations, diploma decisions, etc. Plans are written
and/or reviewed at least once a year by IEP team (ESE teacher, Gen. Ed.
teacher, parent, student, and any other appropriate personnel.) Mandated by
IDEA.
Language Impaired – A child of average ability whose communication
ability does not coincide with his/her expected level of functioning.
Language Learning Disabilities – A student who has a normal or near normal
IQ but does not perform at that level due to the way they process information
and whose ability to communicate does not coincide with his/her expected
level of functioning. Students generally labeled LI or SLD.
Least Restrictive Environment – IDEA mandates that students are placed in
their LRE. Basically, it means that the child should be placed in the setting on
the highest level of the continuum they can function in which ranges from full
inclusion to self-contained classrooms to center or even residential placement.
Mentally Handicapped - A student who is impaired in intellect and adaptive
behavior and has a reduced rate of learning. Diagnosed through an IQ score
significantly more than a standard deviation from the mean (100) and an
adaptive behavior rating scale. In schools, students are labeled into one of
three levels (from highest IQ score to lowest): EMH, TMH, S/PMH
Mental Retardation – outdated term for MH, still frequently used in social
settings and research.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder – “pattern of negativistic, hostile, and defiant
behavior lasting at least 6 months”; student must not be diagnosed with a CD.
High co-occurrence with ADH/D; diagnosed by a physician.
Other Health Impaired – One of the disabilities classified by IDEA. A
‘catch-all’ label for a variety of disorders. It is often used for students who
have mental illnesses (e.g. bipolar disorder) or severe ADH/D. It may also
include: chronic or acute health problems which could “include: heart
conditions, chronic lung disease, tuberculosis, rheumatic fever, nephritis,
asthma, sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, epilepsy, leukemia, diabetes, cancer,
or some other genetic impairment or illness.” The point is made that it “Must
adversely affect the educational performance or developmental progress of
the student” for the student to be labeled OHI. These referrals are often
parent-initiated.
Occupational Therapy – if a student is labeled ‘OT,’ it means they are
receiving direct therapy or an occupational therapist is consulting regularly to
monitor progress. OT is used to improve fine motor skills, such as cutting
and handwriting. Students often have other disabilities as well.
Physically Impaired – An individual who displays a physical impairment
that may or may not be neurological in nature. Academics and ability can
vary over a wide range. Spina Bifida, CP & Muscular Dystrophy are often
PT
REI
SED
SLD
S/PMH
ST
SWD
SVE
TBI
TMH
categorized as physical impairments. Academic performance must be
adversely affected for student to qualify for services in the school setting.
Physical Therapy – Students labeled PT receive direct therapy or have a
physical therapist consult regularly in order to improve gross motor skills,
such as walking up stairs, carrying items, throwing a ball, etc. For student to
be labeled PT in school setting, gross motor skill difficulty must impact
educational performance and PT must be ‘educationally relevant.’ Generally
students who qualify are younger and/or have additional disabilities.
Regular Education Initiative – A movement undertaken in the mid-80s that
called for education of students with mild disabilities in the general education
classroom. Also called for services to support general educators
implementing REI. Present-day term: Inclusion movement
Severely Emotionally Disturbed – A student who has an emotional
handicap due to severe emotional challenges. This individual requires
extensive support services during the school day because of his/her
handicapping condition. Student generally has a normal IQ. These students
are most often served in a center setting due to their extreme behaviors. Many
students whose behavior worsens are restaffed from a label of EH to SED.
Specific Learning Disability – Students have normal or near normal IQ but
to not perform at that level due to the way they process information. The
student may possess an auditory, verbal, visual, kinesthetic, etc. disability.
Most frequent kinds of LDs are SLD in memory (short-term/long-term) or
reading/visual processing.
Severe and/or Profoundly Mentally Handicapped – The most severe of the
MH labels. Student is profoundly impaired in intellect and adaptive behavior.
Measured intelligence of these students is generally around 5 standard
deviations from the mean. Adaptive behavior generally peaks around
preschool age expectations. High co-occurrence with other disabilities. Many
of these students are non-verbal and/or in specialized wheelchairs and almost
all are served in a center setting.
Speech Therapy – Students labeled ST have a speech impairment & receive
direct or consulting therapy from school’s speech and language pathologist.
Students with Disabilities – a term used socially by many educators/preservice teachers to quickly write in people-first language
Supported Varying Exceptionalities – Self-contained setting serving
primarily TMH students; curriculum covers the SSS for Special Diploma at
the Supported Level
Traumatic Brain Injury – Students who possess injury to the brain caused
by accidental or medical reasons. Resulting impairment may continually
affect learning, behavior, memory, movement, language, and/or social
interactions (depending on which portion of the brain was damaged.)
Trainable Mentally Handicapped – aka, Moderate Mental Handicap;
Individuals are moderately impaired in intellect and adaptive behavior.
Intellect is usually measured to be between 3-5 standard deviations from the
means. Academics usually peak between Kindergarten and 3rd grade.
Adaptive behavior is significantly below age and sociocultural expectations.
Students are generally instructed in a self-contained setting, often SVE. The
media’s stereotypical portrayal of a person with Down Syndrome is a good
representation of a person with TMH.
Varying Exceptionalities – A term used to represent placements serving
students with multiple disabilities. As an example, a “VE Classroom” would
be a self-contained classroom serving students with SLD, EH, and EMH. A
“VE teaching position” could mean that the teacher will teach inclusion,
resource, or self-contained.
Visually Impaired – Individuals who are blind or have impaired vision.
These individuals may or may not possess other handicaps; academics and
ability will vary over a large range.
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 – Federal law that requires that
no student, regardless of their disability, should be denied participation,
benefits of, or be discriminated against based on their disability. It also
mandates that a record be kept of any student who has any type of impairment
that limits a major life activity. A “504 plan” gives a student accommodations
for instruction and testing. They are commonly used for students with
medically-diagnosed disorders, such as ADH/D. In contrast with IDEA &
IEPs, there is no funding attached to students who have 504 plans in place.
504 plans are often parent-initiated.
VE
VI
504
External Resources used:
Florida Uniting Students in Education. ESE Terminology. (Handout)
For ODD: http://www.mentalhealth.com
For OHI: http://www.fpext.appstate.edu/gstudies/dss/ohi.htm
Stay up to date, Add your own:
Acronym
Definition & Notes on the Term
SPC Privacy Policy
© 2004-2005, All Rights Reserved, St. Petersburg College
St. Petersburg College Equal Opportunity Statement - Students and Employees
Site Disclaimer
powered by ANGEL Learning's MindClick™Process Technology