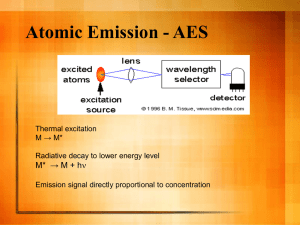
The deposition of films by plasma techniques and the plasma
advertisement

''Intoduction to Complex plasmas (preliminary title)'' Eds. Michael Bonitz, Norman Horing and Jürgen Meichsner X-ray diagnostics of plasma deposited thin layers. H. Wulff Abstract The deposition of films by plasma techniques and the plasma treatment of solid surfaces are well known and widely used methods. In order to understand the complexities involved in film formation it is necessary to take a close look at the deposition region. This is usually the substrate area that is subjected to plasma radiation and, in particular, to fluxes of energetic and reactive charged and neutral particles in various excited states. Therefore, results of detailed plasma diagnostics have to correlate with film properties. Of particular interest is the analysis of film properties in the nanometer range. X-ray methods can give a range of interesting information about how plasma deposition techniques and plasma parameters influence deposited films and surface layers. Grazing incidence x- ray diffractometry (GIXD) and x-ray reflectometry (XR) have been introduced as well suited tools for investigations of plasma deposited thin layers. These x-ray methods have a number of advantages compared to other commonly used techniques They are nondestructive techniques, therefore a sample can be reused an can be measured with other techniques such as x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), or atomic force microscopy (AFM). A usable combination of GIXD and XR requires that the film thickness does not exceed the upper physical absorption limit for the reflectometry measurements. If this condition is fulfilled a combination of GIXD and XR can give a range of interesting information about chemical, physical and crystallographic properties of thin films. Conclusions can be drawn how plasma deposition techniques and plasma parameters influence the film growth. In this chapter - the basic principles of GIXD and XR were introduced, - the efficiency of these x-ray methods will be discussed in comparison with other surface analysis methods - examples will presented in consideration to phase analysis of thin films The most frequently used and the most important problem in the film analysis is to prove the existence of a desired phase after film deposition or to find out which phase or phases were formed the influence of plasma parameters of film properties gas composition, gas pressure, plasma power, substrate voltage can influence chemical as well as physical properties of plasma deposited films. The effect of oxygen flows and negative substrate voltages on film formation process of ITO layers deposited by a dc magnetron will be presented defect structure analysis of deposited films Additional energy flux to growing films due to ion energy caused by different substrate potentials can influence film properties observed in x-ray data. plasma chemical reactions in the surface layers Chemical reactive plasmas can form new compounds in the surface range. By means of a combination of XR and GIXD the whole kinetic process of the aluminium oxidation in a microwave plasma can be investigated and will be presented here. the influence of cluster size on cluster melting point Fundamental physical interest on clusters arises due to their reduced size. Connections between cluster size and melting behaviour investigated by insitu GIXD were discussed. .