CNS Tumors
advertisement

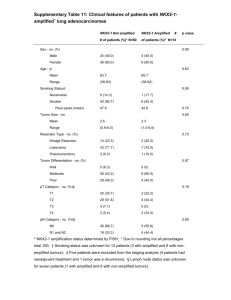
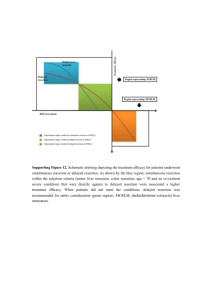
CNS Tumors Gliomas tumor % age location & clinical pres. histology prognosis tx Astrocytomas: morphology & grade determine prognosis diffuse (fibrillary) 20% any usu. cerebral white matter unclear margins grade dependent! surgical resection astrocytoma of seizures infiltrates good: low grade (+ radiation?) glioma headaches GFAP+ cell processes poor: anaplastic type (rarely complete focal signs progress in grade up to (usu. in elderly) resection) GBM brainstem glioma 10CN palsies pons poor radiation (subtype of 20 long tract signs progresses thru grades up median survival <2y no surgery diffuse) gait abnormalities to GBM (50%) cerebellar signs GBM 65% adult usu. cerebral white matter supratentorial very poor, always surgery, glioblastoma peak seizures densely hypercellular recurs surgery + multiforme 50 headaches high anaplasia: often untreated: 3mo radiation/chemo (3 etiologic focal signs astrocytes, oliogos, surgery: 6 mo or none types) 5 ependymoma tissue3 surgery + rad: 10-12 m necrosis, hemorrhage pseudopalisading cells4 pilocytic kids dep. on location circumscribed, low grade cystic cerebellar 90% surgical w/o astrocytoma cerebellar1 mixed loose and dense 5ys even w/ normal tissue hypothalamus microcystic areas incomplete resection margin optic/nerve chiasm (esp. Rosenthal fibers in NF-1 pts2) subependymal rare vascular, intrventricular mixed astrocytic, neural not progressive ? giant cell mass bizarre morphology may cause focal sx usu. part of systemic often hemorrhage tuberous sclerosis 1. older children – the most common childhood astrocytoma, 60% cystic, good prognosis 2. NF-1 = von Recklinghausen’s Disease 3. must take deep, multiple biopsies for accurate dx 4. malignant cells tightly clustered around necrotic center 5. 30% progressed from diffuse (p53, Rb, others; younger pts), 30% spontaneous (EGFR amp, older pts), 30% other CNS Tumors Gliomas, cont. tumor % oligodendroglioma 5% ependymoma infratentorial supratentorial spinal 5% ? 65 myxopapillary subependymoma choroid plexus papilloma rare age location & clinical pres. histology prognosis oligodendrocyte tumors: molecular genetics determine prognosis 30cerebral white matter focal calcification LOH 1&19: 95% 5ys 50 yrs of neurologic sx “fried egg” (perinuc. halo) (most) seizures highly vascularized CDKN2A del <2ys or mixed astro/oligo ependymal tumors: location, stage, tx 10 determine prognosis th 0-10 4 ventricle mass well-differentiated spinal> cerebral> inc. ICP/hydrocephalous prominent vessels infratentorial rosettes & perivascular medial survival 4y all cerebral/lateral ventricles pseudorosettes all spinal intramedullary rarely malig. or infiltrative better w/more resection high incid. in NF-2 pts. & no CSF dissem. inc. ICP/hydrocephalus adult cauda equina/ filum cuboidal cells around usu. benign w/ tx terminale papillary cores mucinous stromal may recur or degeneration metastisize adult 4th & lateral ventricles benign, non-infiltrative curable usu. symptomatic usu. very small may cause hydrocephalus neuroglial origin?? kids most lateral ventricles well-differentiated ? (4th in rare adult form) papillary growth rarely malignant hydrocephalus tx surgery, radiation & chemo total resection crucial, but impossible in brainstem (hence poorer prog. there) total resection necessary surgical excision ? CNS Tumors Parenchymal & Meningeal tumor % age medulloblastoma 30% kids of post. fossa meningioma 15 of >30 head 25 of spine schwannoma 30% of spinal neurofibroma ganglioma craniopharyngeoma 1-5 0-20 location & clinical pres. cerebellum only vermis – kids lateral – adults hydrocephalus attached to dura: 50% convexity, 40% basal, 10% post fossa/spine mass effects histology well-circumscribed friable hyerchromic nuclei mets thru CSF to cauda eq poorly defined cell sheets cellular whorls psammoma bodies infiltrate bone w/ hyperostotic response Nerve and nerve root tumors usu. along CN8 benign, slow-growing (acoustic neuroma) or well-circumscribed CN5 encapsulated bilateral CN8 in NF-2 displaces nerve also spinal, peripheral Antoni A (dense spindle)& Antoni B (loose stellate) Verocay bodies on nerves & nerve trunks Schwann cells mixed w/ usually multiple & part of collagen, reticulin , NF-1 (plexiform nf is fibroblasts pathognomonic) hyperplasia 3rd vent, hypothalamus, or well-circumscribed temporal lobe focal calcification small cysts Developmental tumors bitemporal hemianopsia from Rathke’s pouch (pit. hypothalamus dysfnc. epithelium) hydrocephalus varied but usu. cystic whorls of keratin cells calcification prognosis highly malignant BUT very radiosensitive up to 75% 5ys dpds. on grade, stage, and form aggressive forms: clear cell, rhabdoid, choroid, papillary?* tx excision (total if possible) + radiation of brain and cord ? benign except compression sx resection if necessary chronic resection if necessary most slow-growing anaplastic quickly deteriorate ? ok if small poor if >5cm diam. resection as complete as possible CNS Tumors Miscellaneous tumor % age germinoma1 2 <20 location & clinical pres. histology Developmental tumors pineal or post. 3rd ventricle identical to seminoma prognosis tx dps on grade radiation/chemo worse w/CSF exten. dermoid/ epi: pons, cerebellopontine cyts w/ strat. squamous epi may cause severe epidermoid cysts angle keratinous debris meningitis, derm: midline post fossa dermoid: sebaceous glands ependymitis Non-neural tumors capillary 1-3 20usu. cerebellum endothelial-lined vascular benign: may secrete hemangioblastoma 50 assoc. w/ systemic Lindau channels epoietin-like substance 2 syndrome lipid/foamy cytoplasm primary sarcoma 1 usu. in meninges, choroid fibroblast-derived ? ? plexus primary 1 in immunocompromised B-cell type: DLCL, DLC- poor poor response to lymphoma immunoblastic, or SLL chemo angiocentric growth prod. reticulin lots of necrosis pituitary adenoma mass effects, focal sx uniform cells ? ? 25-30% PRL secretion stippled,delicate chromatin 20-25% GH secretion locally invasive 10-15% ACTH secretion metastatic tumors 50% of all CNS tumors, esp. adults, usu. from lung, breast, melanoma, kidney, GI usu. well-demarcated near white/gray border 1. germinomas are the most common CNS germ cell neoplasm (others: embryonal carcinoma, sinus tumor, choriocarcinoma, teratoma) also most common tumor affecting pineal 2. incl. retinal involvement = von Hippel-Lindau