CT neoplasm - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital Medical Center
advertisement

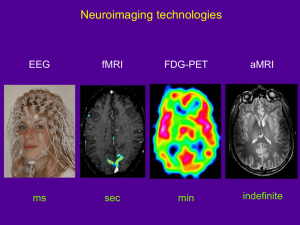
Clinical Neuroradiology Notes Summarized by Kira Armstrong History CT’s developed in 1970’s MRI’s in 1980’s Plain Film Analysis Used to evaluate structures of skull, facial bones, and sinus Usefulness declined with advent of CT and MRI Still used in detection of fractures, abnormal calcifications, developmental abnormalities, osteolytic or osteoblastic disorders. For example Identification of neoplasms Premature closing (craniostynostosis or widening – from increased ICP seen in aqueductal atresia and Dandy-Walker syndrome) Generally not indicated after trauma – CT should be used (although good for dx of facial fractures) Imaging Planes CT and MRI imaging planes are similar to the horizontal (axial) coronal and sagittal planes used to describe basic neuroanatomy (Figure 2.5) But, CT axial slices sometimes adjusted by a few degrees off the true axial plane Lets them get more brain with fewer slices and less radiation exposure to eyes MRI slices are usually true horizontal Scout/localizer images – show the viewer where the image slices are (see figure 4.1). Should be included on all CT and MRI scans so exact angle can be documented and compared Computerized Tomography (CT) Developed directly from X-ray technology….so, similarly it measures the density of tissue 2 differences from conventional x-rays: rather than taking 1 view, x-ray beam is rotated around patient to take many different views X-ray data are reconstructed by a computer to obtain detailed image including soft tissues, liquid, air and bone. Single Slice CT Scanner is shaped like large ring Patient lies on table and moves through ring in small steps Each stop, x-ray is scanned through patient and picked up by detectors on opposite side of ring Amount of energy absorbed depends on the density of tissues traversed Helical CT Acquires data continuously as patient moves through scanner - no stops Instead of single slices, up to 4 rows of detectors provide multiple overlapping slices These advances greatly improved resolution and speed of CT scan (20 minutes vs. 40 minutes) THE FINE PRINT: Caveat emptor! These study materials have helped many people who have successfully completed the ABCN board certification process, but there is no guarantee that they will work for you. The notes’ authors, web site host, and everyone else involved in the creation and distribution of these study notes make no promises as to the complete accuracy of the material, and invite you to suggest changes. Page ~6~ Appearance of CT scans Review figures 4.12 (A-K) for normal CT images (also see below for comparison to MRI) White – dense structures like bone Black – less dense, like air Hyperdense – brighter areas Hypodense – darker areas Grey/Isodense – intermediate density similar to brain tissue Dark Grey – CSF Nearly Black – fat tissue just outside skull White matter is slightly darker than cellular gray matter due to high myelin content Gray matter is slightly lighter than white matter due to high water content Enhancing lesions may be brain neoplasms, abscess, infarct, demyelinating disease, resolving hematoma or vascular malformation HU = Hounsfield Units – density in CT, often expressed in HU HU = 0 for water CT Hemorrhage Appearance (see figure 5.19) Depends on how recently it occurred Fresh intracranial hemorrhage coagulates almost immediately and shows up as hyperdense areas relative to brain As the clot is broken down, after about a week becomes isodense After 2-3 weeks, become hypodense CT cerebral infarct Acute infarcts (in first 6-12 hours) - often cannot be seen with CT >12 hours, cell death and edema lead to an area of hypodensity seen in the distribution of the occluded artery Over weeks to months, brain tissue surrounding infarct may shrink, producing a local are of prominent sulci or enlarged ventricles Persistent areas of hypodensity in the brain tissue may be present as a result of gliosis and brain necrosis by with replacement by CSF CT neoplasm May appear hypodense, hyperdense, or isodense, dependant upon the type or stage Intravenous contrast dye is often helpful in visualizing neoplasm CT mass effect Anything that distorts the brain’s usual anatomy - this can occur with neoplasm, edema, hemorrhage, and other conditions Detected by observation of localized compression of the ventricles, effacement of sulci or distortion in other brain structures (e.g., in herniation) CT intravenous contrast Contrast material contains iodine which is denser than brain and will therefore appear hyperdense (white) in areas of increased vascularity or breakdown of blood-brain barrier Often images are obtained with and without contrast for comparison THE FINE PRINT: Caveat emptor! These study materials have helped many people who have successfully completed the ABCN board certification process, but there is no guarantee that they will work for you. The notes’ authors, web site host, and everyone else involved in the creation and distribution of these study notes make no promises as to the complete accuracy of the material, and invite you to suggest changes. Page ~6~ In suspected intracranial hemorrhage it is very important to obtain noncontrast CT because small hemorrhages often appear on CT as whitish areas at base of brain which could be masked by the normal hyperdense contrast material in blood vessels and meninges at base of brain CT myelography Form of contrast enhancement Iodinated contrast dye is introduced into CSF (usually by lumbar puncture) Allows better visual of nerve roots and of abnormal impingement on the spinal CSF CT vs. MRI in Different Situations Situation CT Better Head trauma xx Lower cost xx Subtle tumor/infarct Brainstem lesion Fresh hemorrhage xx Old hemorrhage Speed needed xx Skull fracture xx Pacemaker xx Anatomical detail needed MRI Better xx xx xx xx MRI provides high-contrast, high-resolution imaging with striking anatomical detail MRI is choice method for detecting low-contrast or small lesions such as MS plaques, low-grade astrocytomas, etc. (CT not as sensitive in detection of white matter or neurodegenerative disorders) The only cranial nerve observable by CT is the optic nerve Provides clear images of basilar structures such as brainstem, cerebellum and pituitary fossa MRI’s cost more and take longer; also inferior performance in imaging fresh hemorrhage and bony structures CT preferred with head trauma or suspected intracranial hemorrhage as a 1st screening – easier to perform on ventilated patients and do not get artifacts from implanted devices In non-urgent situations in which a single more definitive image method is desired, MRI is test of choice Therapeutic Uses – CT scans can be used to study or look for: Acute hemorrhage Edema Mass effect (although cerebellar tonsillar herniation can be missed because of beam hardening artifacts) Ventricular enlargement to detect hydrocephalus Detecting intracranial calcifications (from congenital infections, vascular lesions, metabolic disease, and neurocutaneous disorders) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Review normal MRI scans in Figures 4.13-4.15 Developed from NMR Powerful magnetic field causes protons to align intrinsic spins Protons relevant to conventional MRI are only those forming hydrogen nuclei Unlike CT scans, MRI scans are not described in terms of density. Instead are described in terms of intensity, or brightness of the signal Hyperintense – brighter areas Hypointense – darker areas THE FINE PRINT: Caveat emptor! These study materials have helped many people who have successfully completed the ABCN board certification process, but there is no guarantee that they will work for you. The notes’ authors, web site host, and everyone else involved in the creation and distribution of these study notes make no promises as to the complete accuracy of the material, and invite you to suggest changes. Page ~6~ T1 vs T2 weighted images T-1 weighted images – look like anatomical brain sections T-2 weighted images – look like film negatives So – T1 gray matter is gray, and white matter is white; T2 images are the opposite T1- better for identifying anatomy because resolution is better T2- better for detecting pathological changes; poorer resolution, but better contrast Summary of MRI and CT Appearance of Commonly Scanned Tissues TISSUE T1-WEIGHTED Gray Matter Gray White Matter White (bright) CSF/water Black Fat White Air Black Bone/calcification Black Edema Gray Demyelination/gliosis Gray T2-WEIGHTED Light gray Dark gray White Black Black Black White White CT scan Gray Dark Gray Nearly black Black White Proton density weighted images (first echo images) Contrast between gray and white matter is reduced But better at detecting subtle abnormalities in the parenchyma such as small areas of edema or infarction adjacent to CSF ---- can be easily seen as bright regions Factors that affect intensity of MRI images/signals Protons must be present in order for a signal to be generated, thus, on both T1 and T2 weighted images, air appears black and bony/calcified structures appear dark because of the relatively absence of water protons Images are distorted in patients with metallic implants in the head (e.g., pacemakers, cochlear implants, and old aneurysm clips) Intracranial hemorrhage appearance on MRI (see table 4.4 on page 92) Undergoes characteristic series of changes over time On both T1 and T2, acute hemorrhage may be hard to see because it’s gray and resembles CSF Subacute contains hemosiderin and appears white Chronic contains dark areas resulting from hemosiderin deposits usually bright center with dark rim eventually, the center may reabsorb, forming a fluid filled cavity that is dark on T1 and bright on T2 infarcts become apparent on T2 within 12-24 hours of onset Neuroangiography Figures 4.16 and 4.17 show samples of angiogram imagery Definition – the study of central nervous blood vessels and related cervicocerebral vasculature using radiographs during injection of intravascular contrast medium. It is the gold standard for evaluating vascular diseases in head, neck, and spine. Before availability of CT and MRI – was used to detect slight distortions in the patterns of blood vessels suggestive of intracranial mass lesions THE FINE PRINT: Caveat emptor! These study materials have helped many people who have successfully completed the ABCN board certification process, but there is no guarantee that they will work for you. The notes’ authors, web site host, and everyone else involved in the creation and distribution of these study notes make no promises as to the complete accuracy of the material, and invite you to suggest changes. Page ~6~ Now is used to visualize lesions of blood vessels themselves rather than to provide indirect information about surrounding structures Lesions optimally seen by angiography include: Atherosclerotic plaques and other vessel narrowings Aneurysms AVM’s Can also be used during planning of neurosurgery and to assess the vascular anatomy of tumors Angiography is an invasive process Relies upon continuous x-ray guidance Requires local anesthesia Catheter inserted, usually in femoral artery which is threaded up the aorta Radio-opaque iodinated contrast material is injected into carotid and vertebral arteries on both sides, and sequential images are obtained at different times during the injection and runoff Less invasive means for visualizing blood vessels include: None of these have achieved the specificity or sensitivity of angiography, so risks and benefits must be weighed in each case Doppler ultrasound – used to measure flow and lumen diameter of large blood vessels in head and neck (best for assessing atherosclerotic narrowings which occur proximally, not very good at detecting aneurysms or other vascular abnormalities) Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) – detects direction and speed of blood flow; although the major vessels can be seen, the smaller, more distal branches cannot Used primarily to detect regions of decreased or absent arterial blood flow caused by atherosclerotic narrowing, thrombosis or dissection Also useful for detecting some aneurysms and other vascular abnormalities Venous flow can be visualized using Magnetic resonance venography (MRV) Spiral CT angiograpy (CTA) – rapid injection of IV contrast used with helical CT to obtain images of blood vessels quickly – can be used in patients where MRA may be contraindicated (e.g., pacemaker) Therapeutic Neuroradiography Wada Test – amobarbital is selectively infused into each carotid artery while patient is awake – helpful for localizing language and to aid plans for neurosurgery Treatment of Brain aneurysms and AVM’s – these can sometimes be clotted off and rendered harmless by filling them with glue-like material or tiny metal springs via the angiography catheter Stroke – therapeutic trials are underway in which thrombolytic agents are infused directly at site of clot to try and reestablish perfusion (performed within 6 hours of acute symptoms) With CT or MRI can be used to diagnose venous occlusive disease following stroke Ultrasonography Uses sound waves above audible levels to generate diagnostic medical images Indicated when target area is not blocked by bone or air – very useful in pediatrics especially because of lack of ionizing radiation Direct brain imaging in peds is possible b/c of presence of fontanelles which remain open until 6-9 months of age In young children can be used to detect brain structures and congenital abnormalities; also used to grade hemorrhages Not good at detecting extra-axial hemorrhages or masses or white matter disease In adults can be use to detect vascular lesions of head and neck THE FINE PRINT: Caveat emptor! These study materials have helped many people who have successfully completed the ABCN board certification process, but there is no guarantee that they will work for you. The notes’ authors, web site host, and everyone else involved in the creation and distribution of these study notes make no promises as to the complete accuracy of the material, and invite you to suggest changes. Page ~6~ Functional Neuroimaging EEG Original method for measuring brain activity Sensitivity and spatial resolution in detecting focal brain lesions is poor Useful in evaluating for epileptic (seizure producing) brain activity Useful in detecting widespread abnormality in brain function Evoked potential Similar to EEG in which brain electrical activity is recorded in response to specific stimuli Quantitative EEG analysis and magnetoencephalography (MEG), which uses a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) to detect very weak magnetic signals- for research only Techniques that produce images based on blood flow or dynamic blood flow volume: Xenon regional cerebral blood flow mapping (Xe rCBF) Positron emission tomography (PET) Single photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) Dynamic contrast functional MRI (perfusion MRI) Blood oxygen level dependent functional MRI (BOLD fMRI) In evaluating for Brain tumors – PET studies can be useful High grade neoplasms demonstrate increased metabolism Low grade neoplasms demonstrate decreased activity Radiation necrosis shows decreased activity and tumor recurrence shows increased metabolic activity (SPECT is more limited in evaluating tumors) Functional MRI (fMRI) – (refers to several different MRI techniques): Perfusion MRI - rapid injection of gadolinium and rapid measurements with “echo planar” imaging to produce an image of dynamic blood volume BOLD fMRI - measures relative changes in oxy and deoxyhemoglobin, which occur with changes in regional cerebral blood flow – can be used to localize regions of sensory-motor function and language function (may eventually replace the WADA test) Diffusion MRI - rapid echo planar imaging and strong gradients to measure the diffusion coefficient of water in brain tissue; can detect early areas of ischemia long before conventional MRI Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) detects local concentrations of certain chemicals in the brain including some neurotransmitters Ictal-Interictal SPECT Difference Imaging Can be used to indirectly measure regional brain activity during seizures and to help localize their region of onset Demonstrated decreased regional cerebral blood flow between seizures and increased regional cerebral blood flow ictally THE FINE PRINT: Caveat emptor! These study materials have helped many people who have successfully completed the ABCN board certification process, but there is no guarantee that they will work for you. The notes’ authors, web site host, and everyone else involved in the creation and distribution of these study notes make no promises as to the complete accuracy of the material, and invite you to suggest changes. Page ~6~