Pharmacokinetic study of nerve agent antidotes in blood and target
advertisement
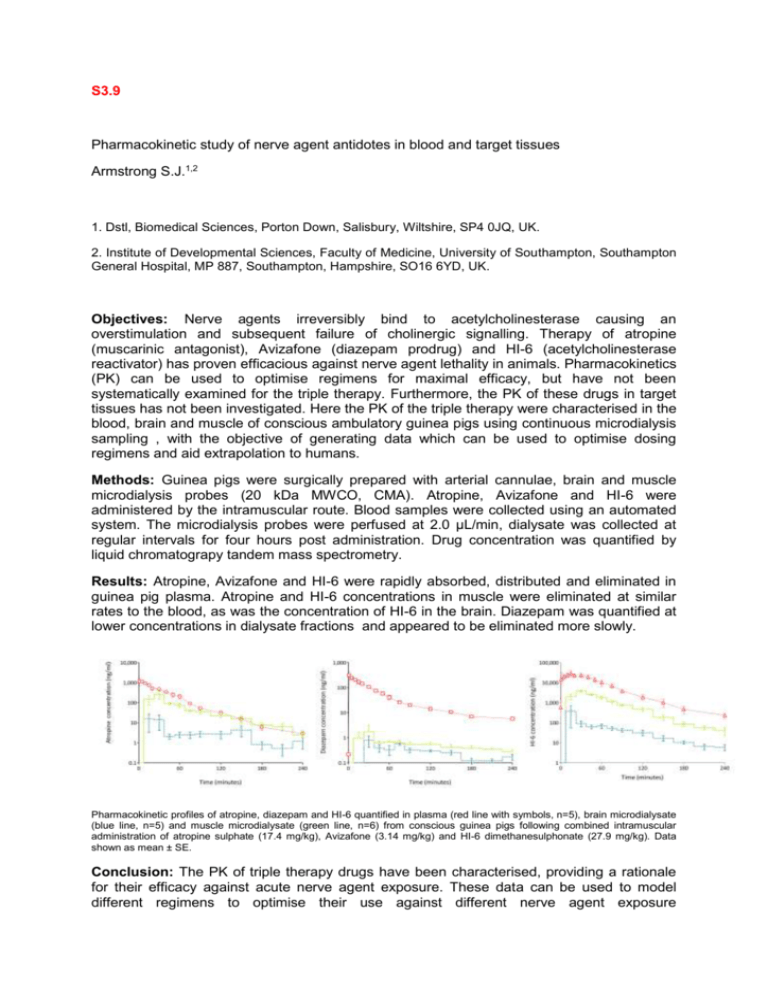
S3.9 Pharmacokinetic study of nerve agent antidotes in blood and target tissues Armstrong S.J.1,2 1. Dstl, Biomedical Sciences, Porton Down, Salisbury, Wiltshire, SP4 0JQ, UK. 2. Institute of Developmental Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, MP 887, Southampton, Hampshire, SO16 6YD, UK. Objectives: Nerve agents irreversibly bind to acetylcholinesterase causing an overstimulation and subsequent failure of cholinergic signalling. Therapy of atropine (muscarinic antagonist), Avizafone (diazepam prodrug) and HI-6 (acetylcholinesterase reactivator) has proven efficacious against nerve agent lethality in animals. Pharmacokinetics (PK) can be used to optimise regimens for maximal efficacy, but have not been systematically examined for the triple therapy. Furthermore, the PK of these drugs in target tissues has not been investigated. Here the PK of the triple therapy were characterised in the blood, brain and muscle of conscious ambulatory guinea pigs using continuous microdialysis sampling , with the objective of generating data which can be used to optimise dosing regimens and aid extrapolation to humans. Methods: Guinea pigs were surgically prepared with arterial cannulae, brain and muscle microdialysis probes (20 kDa MWCO, CMA). Atropine, Avizafone and HI-6 were administered by the intramuscular route. Blood samples were collected using an automated system. The microdialysis probes were perfused at 2.0 µL/min, dialysate was collected at regular intervals for four hours post administration. Drug concentration was quantified by liquid chromatograpy tandem mass spectrometry. Results: Atropine, Avizafone and HI-6 were rapidly absorbed, distributed and eliminated in guinea pig plasma. Atropine and HI-6 concentrations in muscle were eliminated at similar rates to the blood, as was the concentration of HI-6 in the brain. Diazepam was quantified at lower concentrations in dialysate fractions and appeared to be eliminated more slowly. Pharmacokinetic profiles of atropine, diazepam and HI-6 quantified in plasma (red line with symbols, n=5), brain microdialysate (blue line, n=5) and muscle microdialysate (green line, n=6) from conscious guinea pigs following combined intramuscular administration of atropine sulphate (17.4 mg/kg), Avizafone (3.14 mg/kg) and HI-6 dimethanesulphonate (27.9 mg/kg). Data shown as mean ± SE. Conclusion: The PK of triple therapy drugs have been characterised, providing a rationale for their efficacy against acute nerve agent exposure. These data can be used to model different regimens to optimise their use against different nerve agent exposure