New Powerpoint template
advertisement

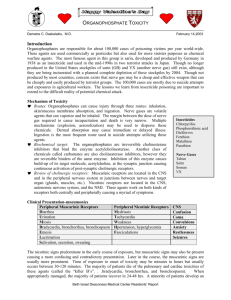
Oximes, atropine and diazepam in organophosphate and carbamate poisoning Dr Martin Wilks, Syngenta Crop Protection AG, Basel, Switzerland Modes of action of the top-selling insecticides/acaricides and their world market share (Nauen, 2002) Mode of action 2 1987 (%) 1999 (%) Change (%) Acetylcholinesterase 71 51 -20 Voltage-gated Na channel 17 18 +1.4 Nicotinic receptor 1.5 12 +10 GABA-gated Cl channel 5.0 8.3 +3.3 Chitin biosynthesis 2.1 3.0 +0.9 Other 0.5 2.9 +2.4 The scale of the problem ● Asia: est. 300,000 deaths /year from pesticide poisoning ● Est. 200,000 involve ingestion of OPs (and carbamates) (Eddleston and Phillips, 2004, BMJ 328: 32 – 44) ● Sri Lanka - 17000 admissions - 35% ICU - 10% Die (20% of symptomatic) 3 Outline ● Review the Mechanism ● Does the type of compound matter? ● Aspects of treatment - Do they need Atropine? - Do they need Decontamination? - Do they need Oximes? ● Magnesium, Diazepam, Bicarbonate ● Lessons learned 4 Organophosphate Carbamate O(S) II P-O-X O II R1 - NH - C - O - R2 R1 R2 R1,2 = alkyl or aryl groups X = wide range of branched or substituted groups 5 R1 = methyl, aromatic or benzimidazol group R2 = aromatic or aliphatic group Acetylcholinesterase and OP Organophosphate 6 Nicotinic, muscarinic and central syndrome 7 Clinical Syndromes ● Acute Cholinergic: - Central - Peripheral Muscarinic - Peripheral Nicotinic ● Intermediate Syndrome ● Delayed peripheral neuropathy ● Neurocognitive dysfunction 8 Respiratory failure Acute Cholinergic Syndrome 9 Severity AChE (RBC) Muscarinic Nicotinic CNS Mild > 40% nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, salivation, bronchorrhoea and -constriction, bradycardia Moderate 20 - 40% as above, + miosis, incontinence fasciculations (fine muscles) Severe < 20% as above, + as above, + fasciculations coma, (diaphragm, resp. convulsions muscles) headache, dizziness as above, + dysarthria, ataxia Moat common OP pesticides used in self-poisoning in Sri Lanka Eddleston M et al Differences between organophosphorus insecticides in human self-poisoning: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2005 Oct 22-28;366(9495):1452-9 10 Chlorpyrifos Dimethoate Fenthion Number of cases WHO Toxicity 440 266 100 II II II Formulation 40% EC 40% EC 50% EC Chemistry Diethyl Dimethyl Dimethyl Rat oral LD50 (mg/kg) WHO OSHA 135 150 Not Given 97 250 215-245 Eddleston M et al Differences between organophosphorus insecticides in human self-poisoning: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2005 Oct 22-28;366(9495):1452-9 11 Relative human toxicity of pesticides in self-poisoning X symptomatic X X X Eddleston M et al Differences between organophosphorus insecticides in human self-poisoning: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2005 Oct 22-28;366(9495):1452-9 12 Time to Death ● Early & late respiratory failure ● Hypotensive Shock (Dimethoate) ● Iatrogenic 13 Chlorpyrifos poisoning 3000 AChE in vivo 600 mU/ml Plasma mU/µmol Hb 700 AChE in vitro 500 400 300 200 0 24 48 Time [h] 14 2000 BChE 1500 1000 500 100 ti -5,0 2500 72 96 ti -5,0# 0 24 48 Time [h] 72 96 Fenthion poisoning 500 3000 AChE in vitro 2500 AChE in vivo mU/ml Plasma mU/µmol Hb 400 300 200 100 ti -3,7 BChE 1500 1000 500 0 24 48 Time [h] 15 2000 72 96 ti -3,7 0 24 48 Time [h] 72 96 Dimethoate poisoning 3000 500 400 mU/ml Plasma mU/µmol Hb AChE in vivo AChE in vitro 300 200 100 ti -2,2 2000 BChE 1500 1000 500 0 24 48 Time [h] 16 2500 72 96 ti -2,2 0 24 48 Time [h] 72 96 OPs are different ● Differing Toxicity ● Different Kinetics ● Different Clinical Syndromes ● Different Response to Antidotes ● ? Need Different Treatment Responses Complicates Assessment of the Evidence 17 Sequence of Medical Management 18 1. Basic Supportive Care 2. Does the patient need Atropine ? - Poor air entry into the lungs due to bronchorrhoea and bronchospasm - Bradycardia - Excessive sweating - Small pupils - Hypotension. 3. Decontamination ? 4. Oximes? 5. Adjunctive Treatment ? Atropine – mechanism and endpoints ● Mechanism - Blocks the muscarinic effects due to excess acetylcholine ● Endpoint - Which cholinergic effect should be the endpoint? - Pupil size? - Competitive inhibitor - Control of symptoms determines the dose by titration - Secretions? - Heart rate? - Blood Pressure? - Measurement of peripheral vascular resistance? 19 Atropine Dose in Organophosphates ● Sri Lankan ventilated OP patients who survived require - Mean initial dose of 23.4 mgs. - Maximum initial dose of 75 mg ● 38 texts with 31 different recommendations Eddleston M et al .Speed of initial atropinisation in significant organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. J Tox Clin Tox 2004;42(6):865-75 20 Range of times it would take to give adequate doses of atropine (23mg and 75 mg) following the expert advice from each text 21 Scheme of atropinization (endpoints to be reached) 2 4 8 16 40 Atropine requirement Atropinization Poor air entry into lungs caused by bronchospasm and bronchorrhoea Clear lungs Excessive sweating Dry axillae (Hypotension) Systol. BP > 80 mm Hg Heart rate > 80/min No miosis 30 20 (Bradycardia) 10 (Miosis) 0 0 5 10 min after first atropine dose 22 15 Atropine ● Loading - Doubling dose regime e.g. 2 4 8 16 mgs every 5 minutes ● Maintenance - Continuous infusion < 3mg/hr - 10-20% of loading dose/hour ● Endpoints - Clear chest on auscultation with no wheeze - Heart rate >80 beats/min ● Withdrawal - Atropine toxicity - Clinical Improvement 23 Decontamination ● Don’t confuse creating mess with efficacy ● Decisions based on risk/benefit analysis 24 Gastric emptying – what happens if you stop? Case fatality Anuradhapura Hospital 1998-2002 Case fatality 30 20 10 25 20 02 20 01 20 00 19 99 19 98 0 The results of observational data on gastric emptying (GE) in pesticide self-poisoning Case fatality Anuradhapura Hospital in and not in RCT 75 Case fatality No GE (in trial) GE (NIT) 50 25 0 GCS <14 26 GCS <10 Eddleston M, et al (2008) Multiple-dose activated charcoal in acute self-poisoning: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 371: 579 - 587 ● 4632 patients recruited ● Overall death rate around 7%, pesticide death rate around 13% - No significant difference between no AC, SDAC and MDAC ● Mortality did not differ between groups. Odds ratios: - SDAC vs no AC 1.05 (95% CI: 0.79, 1.40) - MDAC vs no AC 0.93 (95% CI: 0.69, 1.25) - MDAC vs SDAC 0.89 (95% CI 0.66, 1.19) ● No difference in rates of ventilation for OP and Carb poisoned patients 27 Therapy with Oximes: Basics H 3C RO H 3C P O + EOH RO X H 3C P O RO H2O R P O O EOH + H 3C + X- Inhibition H2O HO RO EOH + H 3C + H+ X HON O E O E P O O E H 3C P O P O + R+ + H + O RO N R Reactivatio n Spontaneous reactivation Aging Worek et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 28 AChE-Status in a Patient with Parathion Poisoning 800 200 reactivatability 600 inhibitory activity 150 poison activity (mU/µmol Hb) obidoxime 400 100 200 RBC-AChE in vivo 0 50 0 0 25 50 75 hours 100 0 25 50 75 100 hours Patient: A 45-year old, male Emergency situation: Unconscious, severe signs and symptoms of cholinergic crisis. 1.5 mg of atropine, intubation and initiation of artificial ventilation. Clinical course: 2 bolus doses of obidoxime together with an atropine infusion at the local hospital. Transfer to the ICU of Technical University, Munich. The patient recovered uneventfully. Eyer et al. Toxicol Rev. 2003 29 Oximes ● Effective protocols not established - Variation in use - Zero – 24 grams a day - Intermittent bolus vs continuous infusion ● Ineffective against some OPs ● Issues of availability/affordability - Pralidoxime - USA $600 / gram - India $9 / gram - Sri Lanka 30 55 cents / gram ... but do they work? ● Buckley et al (2005) Cochrane Database Syst Rev, CD005085 - Two published RCTs, one abstract RCT - Insufficient evidence whether oximes are harmful or beneficial ● Peter et al (2006) Crit Care Med 34: 502 – 510 - Two published RCTs, 5 controlled trials - Oximes either ineffective or harmful ● Rahimi et al (2006) Human Exp Toxicol 25: 157 – 162 - Six clinical trials - Oximes are not effective and can be dangerous 31 New antidotes, new therapies? • Protect AChE • Cholinesterase inhibitors • Supply AChE Sacrifice • Synthetic and Natural (FFP) • Reduce ACh Release • Magnesium, Clonidine • Protect Receptor • Neuromuscular Blockers • Reduce OP Load • Increase Hydrolase capacity • Multiple Mechanisms • Altering Ph 32 Magnesium ● Reduces acetylcholine release - Blocks pre-synaptic calcium channels - Central and Peripheral Nervous System ● Decrease toxicity in animal models Pajoumand A et al (2004) Hum Exp Toxicol 23(12):565-9 ● 16 gram continuous infusion MgSO4 for 24 hours ● Normal care (oximes and atropine) in both groups - 0/11 patients died with magnesium - 5/34 control patients - Methodological issues - pseudorandomisation 33 Diazepam ● Routinely used in OP poisoning for treatment of agitated delirium and seizures ● Diazepam reduces respiratory failure (rats) and cognitive deficit (primates) ● Postulate “uncoordinated stimulation of the respiratory centres decreases phrenic nerve output” ● Role for peripheral benzodiazepine receptor? 34 Diazepam ● Synergistic response with anticholinergics - Dickson EW et al Diazepam inhibits organophosphate-induced central respiratory depression. Acad.Emerg.Med. 2003;10(12):1303- 35 Organophosphates and pH ● Organophosphate Hydrolase is pH sensitive. ● Binding of pralidoxime is pH sensitive. ● Acetylcholinesterase ● Aging of OP-AChe complex and reactivation. 36 Comparative efficacy of i.v. pralidoxime vs. NaHCO3 in rats lethally poisoned with OP insecticide (A Wong, Brazil) ● 5 Groups of 10 rats 37 a) DDVP only (no treatment) 0/10 b) Atropine (17 mg/kg) alone 3/10 c) Atropine + pralidoxime (1 g/kg) 4/10 d) Atropine + NaHCO3 (3 meq/kg) 9/10 e) Atropine + NaCl 0.9% (1.9 ml/kg) 5/10 Comparative efficacy of i.v. pralidoxime vs. NaHCO3 in rats lethally poisoned with OP insecticide (A Wong, Brazil) 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 7012.12 2611.17 0 D.D.V.P. p<0.001 D~B and D~C p<0.01 D~E 309.43 462.17 Atropine Atrop. + Oxime N = 10 rats in each group 38 Atrop. + Bicarb. Atrop. + NaCl BalaliMood M. Effect of High Doses of Sodium Bicarbonate in Acute Organophosphorous Pesticide Poisoning. Clinical Toxicology, 43:571574, 2005 ● RCT N=30 ● NaHCO3 pH 7.45-7.55 - 5 mEq/Kg over 60 minutes - 5-6 mEq/Kg over 24 hours ● Length of hospital stay - Controls 5.59 ± 1.97 - Treatment 4.33 ± 1.99 39 Some lessons from clinical research ● Influence of Initial Care on Mortality - Risk of decontamination ● Predictors of Mortality - Pesticide type & Clinical Status ● Use Atropine Aggressively but Titrate - The doubling protocol ● Reasons for Oxime Failure - Chemical and Kinetic - Implications for where, how and what treatment is delivered ● More Large-Scale Randomised Controlled Trials Are Needed, and They Will Be Coming from Sri Lanka 40 Special thanks to Andrew Dawson Michael Eddleston Horst Thiermann for helpful discussion, permission to use their slides, and many shared drinks 41