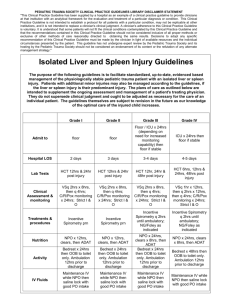
Example 3 - Pediatric Trauma Society

PEDIATRIC TRAUMA SOCIETY CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER STATEMENT
"This Clinical Practice Guideline has been supplied by a hospital as an example of a clinical practice guideline to provide clinicians at that institution with an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of a particular diagnosis or condition. This Clinical Practice Guideline is not intended to establish a protocol for all patients with a particular condition, may not be replicable at other institutions, and it is not intended to replace a clinician's clinical judgment. A clinician's adherence to this Clinical Practice Guideline is voluntary. It is understood that some patients will not fit the clinical conditions contemplated by this Clinical Practice Guideline and that the recommendations contained in this
Clinical Practice Guideline should not be considered inclusive of all proper methods or exclusive of other methods of care reasonably directed to
obtaining the same results. Decisions to adopt any specific recommendation of this Clinical Practice Guideline must be made by the clinician in light of available resources and the individual circumstances presented by the patient. This guideline has not undergone expert review by the
Pediatric Trauma Society and its hosting by the Pediatric Trauma Society should not be considered an endorsement of its content or the refutation of any alternate management strategy."
Title: Trauma Alert Activation Criteria
Purpose: Activation of a trauma alert for utilization of trauma team resources for patients from scene run, interfacility transfers, or upgrade after arrival
LEVEL 1 TRAUMA ALERT CRITERIA
TRAUMA ARREST
Approved 12/16/09
AIRWAY AND BREATHING
Airway or respiratory compromise
Airway maintained by maneuvers, adjuncts or ETT
Pneumothorax and/or breathing supported by thoracostomy tube
Facial or neck injury with potential for airway or cervical spine injury
CIRCULATION
Tachycardia with poor perfusion
Hypotension
Need for more than 2 fluid boluses or 40 ml/kg fluid resuscitation (from time of injury)
Patients who have received and/or are receiving blood products
DISABILITY
Neurologic compromise with GCS < 9, or ‘P’ or ‘U’ on the AVPU scale
Paralysis, motor weakness, or signs of spinal cord injury
SMOKE INHALATION WITH ANY OF THE ABOVE CRITERIA
2° & 3° BURNS (THERMAL, CHEMICAL, OR ELECTRICAL) > 30% BSA
PENETRATING WOUNDS TO THE HEAD, NECK, TORSO, ABDOMEN, THIGH OR
BUTTOCKS
LIMB-THREATENING INJURIES, AS EVIDENCED BY:
Amputation , near amputation or de-gloving injury (any of these to more than fingers or toes)
Extremity with pulselessness, duskiness or cyanosis, paralysis
Consider high-risk mechanisms of injury, including:
Ejection from vehicle and/or
Death of another occupant in the same vehicle
ANY OTHER REASON THE SURGICAL TRAUMA ATTENDING , ED ATTENDING,
TNL, ED CHARGE NURSE OR EMS PROVIDERS BELIEVE THE PATIENT REQUIRES
RESOURCES OF A LEVEL 1 TRAUMA ALERT
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA SOCIETY CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER STATEMENT
"This Clinical Practice Guideline has been supplied by a hospital as an example of a clinical practice guideline to provide clinicians at that institution with an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of a particular diagnosis or condition. This Clinical Practice Guideline is not intended to establish a protocol for all patients with a particular condition, may not be replicable at other institutions, and it is not intended to replace a clinician's clinical judgment. A clinician's adherence to this Clinical Practice Guideline is voluntary. It is understood that some patients will not fit the clinical conditions contemplated by this Clinical Practice Guideline and that the recommendations contained in this
Clinical Practice Guideline should not be considered inclusive of all proper methods or exclusive of other methods of care reasonably directed to
obtaining the same results. Decisions to adopt any specific recommendation of this Clinical Practice Guideline must be made by the clinician in light of available resources and the individual circumstances presented by the patient. This guideline has not undergone expert review by the
Pediatric Trauma Society and its hosting by the Pediatric Trauma Society should not be considered an endorsement of its content or the refutation of any alternate management strategy."
LEVEL 2 TRAUMA ALERT CRITERIA
HEAD
Neurologic injury, as evidenced by:
GCS 9-14, and/or combativeness, disorientation, or confusion
ABDOMEN
Blunt abdominal trauma suspect for intra-abdominal injury:
abdominal pain and/or tenderness, or
abdominal bruising or seat-belt marks
PENETRATING WOUNDS through two or more extremities
BURNS
2° & 3° burns (thermal, chemical, or electrical) 15-30% BSA
EXTREMITY
Suspected or confirmed femur fracture with high risk mechanism of injury (see below)
TRANSFER PATIENTS
Transfer patients with high-risk injuries, including but not limited to :
Head injury:
Open or depressed skull fracture
Intracranial bleed
Thoracic Injury:
Pulmonary contusion
Abdominal Injury:
Known or suspected intra-abdominal injury
Orthopedic
Complex pelvic fractures
HIGH RISK
Consider trauma alert for high-risk mechanisms of injury, such as:
Struck, dragged, or run over by a vehicle
Motor vehicle collision (MVC) with high speed impact or rollover of vehicle
Falls > 20 feet in height
Motocross/dirt bike
ATV (all terrain vehicle)
ANY OTHER REASON THE ED ATTENDING, TNL, ED CHARGE NURSE, OR EMS
PROVIDERS BELIEVE THE PATIENT REQUIRES RESOURCES OF A
LEVEL 2 TRAUMA ALERT
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA SOCIETY CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER STATEMENT
"This Clinical Practice Guideline has been supplied by a hospital as an example of a clinical practice guideline to provide clinicians at that institution with an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of a particular diagnosis or condition. This Clinical Practice Guideline is not intended to establish a protocol for all patients with a particular condition, may not be replicable at other institutions, and it is not intended to replace a clinician's clinical judgment. A clinician's adherence to this Clinical Practice Guideline is voluntary. It is understood that some patients will not fit the clinical conditions contemplated by this Clinical Practice Guideline and that the recommendations contained in this
Clinical Practice Guideline should not be considered inclusive of all proper methods or exclusive of other methods of care reasonably directed to
obtaining the same results. Decisions to adopt any specific recommendation of this Clinical Practice Guideline must be made by the clinician in light of available resources and the individual circumstances presented by the patient. This guideline has not undergone expert review by the
Pediatric Trauma Society and its hosting by the Pediatric Trauma Society should not be considered an endorsement of its content or the refutation of any alternate management strategy."