Post Operative PVC`s, When to Worry
advertisement

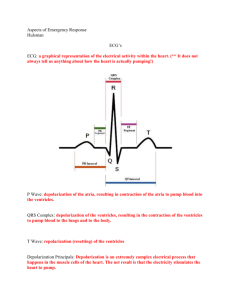
Post Operative PVC’s, When to Worry? Definition PVC’s are premature ventricular contractions, also known as Ventricular premature beats (VPBs) or Ventricular Premature Depolarization (VPDs). PVC’s are ectopic impulses originating from a focus distal to the His Purkinje system. PVC’s are the most common ventricular arrhythmia with variable prognostic importance. Pathophysiology Enhanced Automaticity- new site of depolarization in non-nodal ventricular tissue. Associated with electrolyte abnormalities, ischemia, or increased catecholamines. Triggered Activity- early or late afterdepolarizations that can be associated with electrolyte abnormalities, ischemia, or drug toxicity (digoxin, prolonged QT) Reentry- occurs with unidirectional block (slow conducting myocardium next to normal conducting tissue). Occurs in the setting of damaged myocardium. Causes Cardiac- Acute MI, Valvular disease (MVP), Cardiomyopathy (ischemia, dilated, hypertrophic), Cardiac Contusion, LVH, CHF (EF<40%), and Tachycardia (associated w/ high catecholamine state), Previous Cardiac Surgery, Congenital Heart Disease (h/o tetrology of fallot) NonCardiac- electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia), medications (digoxin, TCA, amitriptyline, pseudophedrine, flouoxetine), drugs (cocaine, amphetamines, caffeine, alcohol), stress response (surgery, infection), anesthestics (sevoflurane, droperidol, ondansetron, etc…) Evaluation Symptomatic- palpitations, skipped beat, dizziness Past Medical/Surgical History/Physical Exam- high risk patient identification as well as possible identification of underlying causes (renal failure, acute MI, etc…) Frequency- greater then 10/hr, bigeminy, trigeminy Character- multifocal vs. unifocal Work-Up- look for underlying/reversible causes EKG- evaluate for ischemia, prolonged QT Electrolyte Panel- chem. 10 as well as Ca and Mg Treatment- only needed for symptomatic pt’s, high risk pt’s (CHF, cardiomyopathy or previous MI and EF<40%), or frequent PVC’s Beta-Blockers- 1st line treatment Amniodarone, Sotalol Bottom Line Worry If: Pt is high risk: previous MI, CHF, Cardiomyopathy w/ EF<40% PVCs are frequent >10/hr, mutifocal, or bigeminy/trigeminy If there is any evidence of Acute Ischemia, hemodynamic instability, or altered mental status References: 1. Curry T., Gaver R., & White R. Acquired Long QT syndrome and Anesthesia. Pediatric Anesthesia. Feb 2006;16,471-478. 2. Clinical Significance and Treatment of VPBs. www.uptodate.com 3. Ventricular Premature Complexes. www.emedicine.com Kim Howard-Quijano M.D. 9/17/2008