Cellulitis and Soft-Tissue Infections Module
advertisement

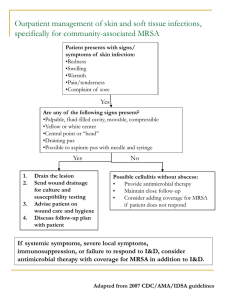
Resident Version Cellulitis and Soft-Tissue Infections Module created by Dr. Dana Fotieo Objectives: 1. Review definition and clinical features of cellulitis and erysipelas. 2. Recognize symptoms/findings that are suggestive of a deeper soft-tissue infection. 3. Discuss treatment of cellulitis (including CA-MRSA) 4. Consider risk factors for development of CA-MRSA skin and soft-tissue infections. References: 1. Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et. al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005; 41:1373-1406. 2. Swartz MN. Cellulitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2004; 350: 904912. Discussion I. Definitions: *Cellulitis- infection of the skin with extension into the subcutaneous tissues, not sharply demarcated. Most commonly caused by B-hemolytic strep. *Erysipelas- superficial cellulitis with distinct margins. *Furuncle (boil) - infection of hair follicle with pus extending into subcutaneous tissues. Usually caused by staph aureus. *Carbuncle- involvement of several hair follicles resulting in an inflammatory mass that expresses pus from multiple openings. II. Local Findings (cellulitis) *Confluent, macular erythema *Swelling of the involved area *Warmth of the skin *Tenderness *Tender regional lymphadenopathy *Lymphangitis *May have abscess formation *May have associated dermatological findings (ex. Tinea pedis, psoriasis) III. Etiology *Usually not necessary to determine etiology if mild infection. Streptococci most common pathogen (particularly if no obvious portal of entry and diffuse). Coverage for staph aureus often done (particularly if associated abscess). Need to consider CA-MRSA (which will be discussed later). *If patient is systemically toxic (fever, hypothermia, tachycardia, hypotension), it is recommended that the following labs be obtained: Blood culture and sensitivity (of note, blood cultures are positive in < 5% of cases) CBC with diff Creatinine Bicarbonate CPK CRP *May need to pursue further diagnostic workup with GS and culture from abscess/wound if present. *If unusual circumstances (such as immunosuppression, immersion injury, animal bite, malignancy), may need biopsy or aspiration to help guide antibiotic therapy. IV. Clues of more serious or deep infection: *Pain out of proportion to exam *Violaceous bullae *Hemorrhage of the skin *Sloughing of the skin *Dermal anesthesia *Rapid spread *Gas in tissue ****EMERGENT surgical evaluation indicated**** V. Treatment of “Typical Infections”: A) MSSA Skin Soft-Tissue Infections *Nafcillin or Oxacillin IV (dicloxacillin oral equivalent) *Cefazolin (Ancef) IV (for PCN allergic patients, unless immediate hypersensitivity rxn). Cephalexin (Keflex) is oral equivalent. *Clindamycin IV or oral can be used (bacteriostatic; potential resistance for erythromycin-resistant strains; potential to induce resistance with MRSA). *Alternatives might be a macrolide. However, need to be aware of potential for macrolide (erythromycin) resistant strep pyogenes. B) Community-associated (CA) MRSA Potential Risk Factors *Close contact with people infected or colonized with MRSA *Prisoners *Members of competitive sports teams *Military personnel *Children in daycare centers *Prior skin infection *Previous antibiotic use *Men who have sex with men *Illicit drug use *Tattoo recipients *Native Americans VI. Treatment *Think about CA-MRSA skin and soft-tissue infections (SSTI) in high risk groups and treatment failures for “typical” SSTI. *Drain fluctuant lesions. Obtain GS and culture. *Possible antibiotic choices: *Doxycycline (avoid in kids <8 and pregnant women) *Clindamycin (may have resistance with certain strains that have inducible resistance to erythromycin) *Bactrim can be used (most treatment failures occur when actually dealing with MSSA). *If quinolones chosen, need to choose one with increased gram positive activity (such as levaquin). *Vancomycin, linezolid, daptomycin are all effective. In the case of CA-MRSA SSTI, they should be reserved for serious infections or after treatment failure with other agents. Review Questions 1) A 21 year old male who plays on the college soccer team presents to the emergency room with a red area on his left lower extremity. He is not aware of any specific trauma to that leg. He reports occasional alcohol use. No IVDA. Past medical history is unremarkable. On physical examination, his vital signs are all stable. The erythematous area on his left distal lower extremity measures 5 x 6 cm and is tender to palpation. No fluctuance is appreciated. The patient is discharged from the emergency room with a prescription for keflex 500 mg po every 6 hours and advised to use warm compresses. The patient returns to the emergency room 3 days later. He has been able to continue with soccer practice; however, the red patch has increased in size and has become increasingly tender. His vital signs remain stable. There is now evidence of a fluctuant area. What is the most appropriate course of action now? (A) Admit to the hospital and start IV Vancomycin. (B) I & D the wound and start IV Vancomycin. (C) I & D the wound and start po bactrim. (D) Initiate po linezolid. 2) 38 year old male with PMH significant for AODM, HTN, venous insufficiency presents to the ER with a 2 day h/o LLE redness and pain. Physical: Temp= 101.2 HR=105 BP=86/50 LLE (distal aspect)- erythematous area 4x 5 cm; some ecchymoses; small stasis ulcer; some anesthesia lateral aspect of calf; sloughing skin; tissue feels “wooden.” The most appropriate initial course of action would be: (A) Obtain MRI LLE; blood cultures; start broad-spectrum antibiotics (B) Culture wound site; blood cultures; start broad-spectrum antibiotics (C) Consult surgery; blood cultures; start broad-spectrum antibiotics (D) Obtain plain film LLE; blood cultures; start broad-spectrum antibiotics Post Module Evaluation Please place completed evaluation in an interdepartmental mail envelope and address to Dr. Wendy Gerstein, Department of Medicine, VAMC (111). 1) Topic of module:__________________________ 2) On a scale of 1-5, how effective was this module for learning this topic? _________ (1= not effective at all, 5 = extremely effective) 3) Were there any obvious errors, confusing data, or omissions? Please list/comment below: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4) Was the attending involved in the teaching of this module? Yes/no (please circle). 5) Please provide any further comments/feedback about this module, or the inpatient curriculum in general: 6) Please circle one: Attending Resident (R2/R3) Intern Medical student