Comparison of Current Diagnostic Criteria with Proposed Criteria
advertisement
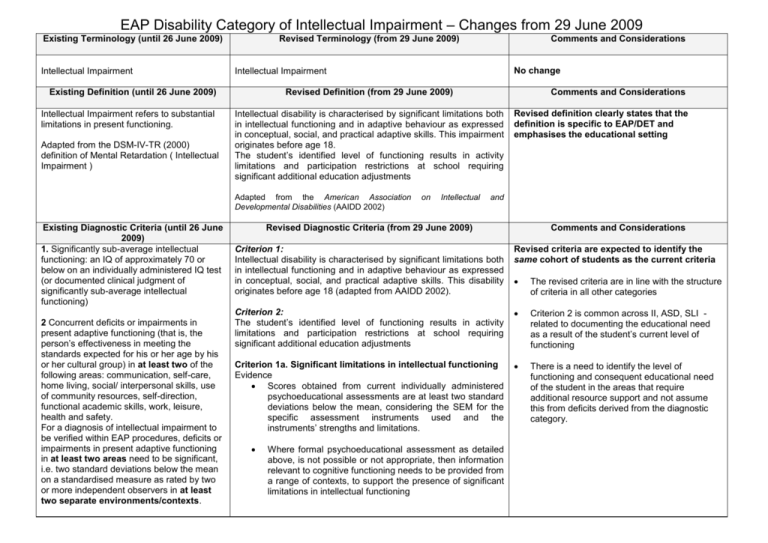
EAP Disability Category of Intellectual Impairment – Changes from 29 June 2009 Existing Terminology (until 26 June 2009) Intellectual Impairment Revised Terminology (from 29 June 2009) Adapted from the DSM-IV-TR (2000) definition of Mental Retardation ( Intellectual Impairment ) Revised Definition (from 29 June 2009) 2 Concurrent deficits or impairments in present adaptive functioning (that is, the person’s effectiveness in meeting the standards expected for his or her age by his or her cultural group) in at least two of the following areas: communication, self-care, home living, social/ interpersonal skills, use of community resources, self-direction, functional academic skills, work, leisure, health and safety. For a diagnosis of intellectual impairment to be verified within EAP procedures, deficits or impairments in present adaptive functioning in at least two areas need to be significant, i.e. two standard deviations below the mean on a standardised measure as rated by two or more independent observers in at least two separate environments/contexts. Comments and Considerations Intellectual disability is characterised by significant limitations both in intellectual functioning and in adaptive behaviour as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical adaptive skills. This impairment originates before age 18. The student’s identified level of functioning results in activity limitations and participation restrictions at school requiring significant additional education adjustments Adapted from the American Association Developmental Disabilities (AAIDD 2002) Existing Diagnostic Criteria (until 26 June 2009) 1. Significantly sub-average intellectual functioning: an IQ of approximately 70 or below on an individually administered IQ test (or documented clinical judgment of significantly sub-average intellectual functioning) No change Intellectual Impairment Existing Definition (until 26 June 2009) Intellectual Impairment refers to substantial limitations in present functioning. Comments and Considerations on Intellectual Revised definition clearly states that the definition is specific to EAP/DET and emphasises the educational setting and Revised Diagnostic Criteria (from 29 June 2009) Comments and Considerations Criterion 1: Intellectual disability is characterised by significant limitations both in intellectual functioning and in adaptive behaviour as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical adaptive skills. This disability originates before age 18 (adapted from AAIDD 2002). Revised criteria are expected to identify the same cohort of students as the current criteria The revised criteria are in line with the structure of criteria in all other categories Criterion 2: The student’s identified level of functioning results in activity limitations and participation restrictions at school requiring significant additional education adjustments Criterion 2 is common across II, ASD, SLI related to documenting the educational need as a result of the student’s current level of functioning Criterion 1a. Significant limitations in intellectual functioning Evidence Scores obtained from current individually administered psychoeducational assessments are at least two standard deviations below the mean, considering the SEM for the specific assessment instruments used and the instruments’ strengths and limitations. There is a need to identify the level of functioning and consequent educational need of the student in the areas that require additional resource support and not assume this from deficits derived from the diagnostic category. Where formal psychoeducational assessment as detailed above, is not possible or not appropriate, then information relevant to cognitive functioning needs to be provided from a range of contexts, to support the presence of significant limitations in intellectual functioning Existing Diagnostic Criteria (until 26 June 2009) 3. The onset is before age 18 years. Existing Form (until 26 June 2009) PART A: Student Details (common for all categories) Revised Diagnostic Criteria (from 29 June 2009) Comments and Considerations Criterion 1b.Significant limitations in adaptive behaviour. Evidence Significant limitations in adaptive behaviour are operationally defined as performance that is at least 2 standard deviations below the mean of either (a) one of the following three types of adaptive behaviour: conceptual, social, or practical, or (b) an overall score on a standardised measure of conceptual, social, and practical skills. Limitations in adaptive behaviour are determined by using a broad range of assessment methods across a range of sources and settings Criterion 1c. The impairment originates before 18 years of age. Criterion 2 The student’s identified level of functioning results in activity limitations and participation restrictions at school requiring significant education adjustments Evidence Student’s level of functioning is significantly below peers. Programs and adjustments in areas of need have been implemented and outcomes achieved. Programs and adjustments that need to be maintained (wholly or partially) to address the educational needs. Revised Form (from 29 June 2009) The following five assumptions are essential to the application of this definition: 1. Limitations in present functioning must be considered within the context of community environments typical of the individuals age peers. 2. Valid assessment considers cultural and linguistic diversity as well as differences in communication, sensory, motor, and behavioural factors. 3. Within an individual, limitations often coexist with strengths. 4. An important purpose of describing limitations is to develop a profile of needed supports. 5. With appropriate personalised supports over a sustained period, the life functioning of the person with intellectual impairment generally will improve. PART A PART B PART B: Evidence Supporting Verification PART C: Principal Request for Verification (common for all categories) PART C Student Details Evidence Supporting Verification of Disability Criterion 1 Criterion 2 Quality Assurance and Decision Making Principal Request for Verification of Disability The format is similar to the current form with the following changes: Section 2: Medical Diagnosis - removed Copies of test scoring pages are for verification paperwork only - they are not to be attached to the originals kept in school files Only ONE adaptive behaviour assessment must be completed, but this needs to be accompanied by supporting evidence Adapted from AAIDD 2002 Comments and Considerations The revised form is more explicit in what evidence is required and will assist school teams to document this evidence more clearly SGO continues to provide Profession Specific Quality Assurance and Decision Making As the diagnosis of intellectual disability is proposed to meet DET criteria, diagnoses by other practitioners can support, but are not sufficient for verification purposes.









