Common Pediatric Diseases and Disorders
advertisement
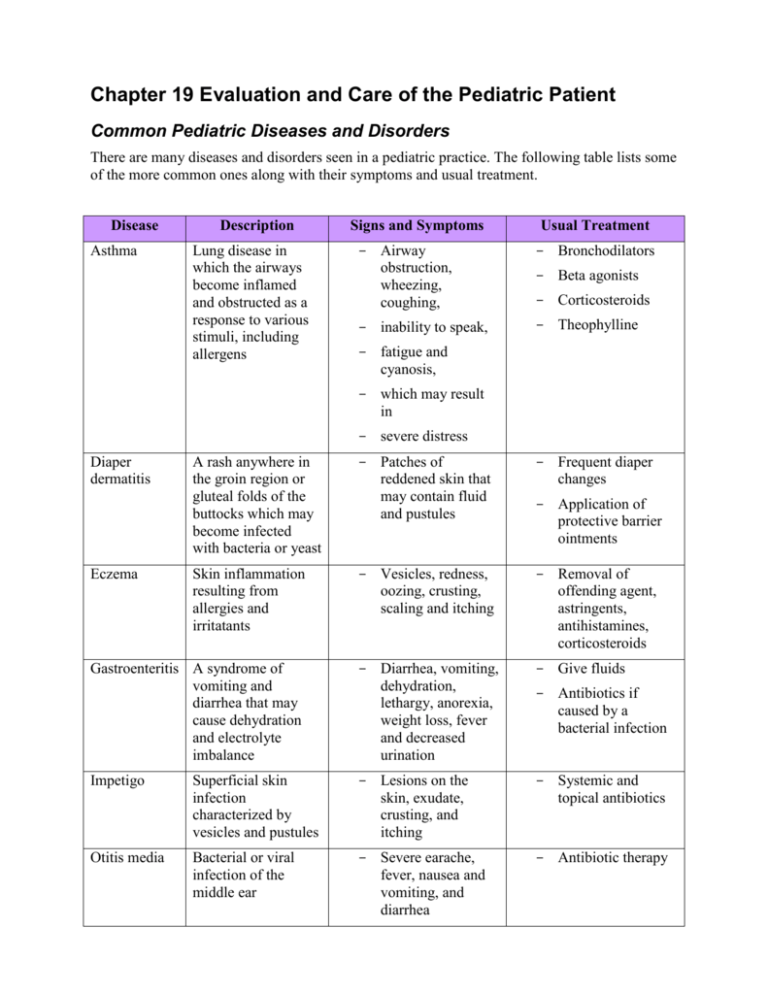
Chapter 19 Evaluation and Care of the Pediatric Patient Common Pediatric Diseases and Disorders There are many diseases and disorders seen in a pediatric practice. The following table lists some of the more common ones along with their symptoms and usual treatment. Disease Asthma Description Lung disease in which the airways become inflamed and obstructed as a response to various stimuli, including allergens Signs and Symptoms Usual Treatment - Airway obstruction, wheezing, coughing, - Bronchodilators - inability to speak, - Theophylline - Beta agonists - Corticosteroids - fatigue and cyanosis, - which may result in - severe distress A rash anywhere in the groin region or gluteal folds of the buttocks which may become infected with bacteria or yeast - Patches of reddened skin that may contain fluid and pustules - Frequent diaper changes Skin inflammation resulting from allergies and irritatants - Vesicles, redness, oozing, crusting, scaling and itching - Removal of offending agent, astringents, antihistamines, corticosteroids Gastroenteritis A syndrome of vomiting and diarrhea that may cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalance - Diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, lethargy, anorexia, weight loss, fever and decreased urination - Give fluids Impetigo Superficial skin infection characterized by vesicles and pustules - Lesions on the skin, exudate, crusting, and itching - Systemic and topical antibiotics Otitis media Bacterial or viral infection of the middle ear - Severe earache, fever, nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea - Antibiotic therapy Diaper dermatitis Eczema - Application of protective barrier ointments - Antibiotics if caused by a bacterial infection Pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis) Scabies Small worms that infest the large intestine - Irritation of the anal region, allergic skin reaction, intense itching, and secondary infection - Oral medication for the entire family, thorough cleansing of the house, bedding, and sleepware, topical medication for irritation Contagious skin infestation caused by the itch mite - Severe itchy rash characterized by fine wavy dark lines. - 5% permethrin cream - Lesions may occur between the fingers, at the wrist or elbow, in the axilla, and on the trunk or extremities Strep throat Severe throat infection caused by the Streptococcus genus of bacteria - Red, sore throat, pustules, and high fever - Antibiotics Urinary tract infection An infection of the kidneys, ureters, or bladder caused by microorganisms - Painful and frequent urination, foul-smelling urine, and hematuria - Antibiotics Other Pediatric Conditions In today’s society, we hear a lot about issues that can have a profound effect on the pediatric patient’s learning abilities and social interactions. Conditions such as ADHD, autism, Down’s syndrome, cerebral palsy and childhood obesity are more prevalent now and need to be dealt with in a professional but helpful manner. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Although first described in 1845, this condition appears to be on the increase in current years. It may first be apparent in preschool, while others cases are diagnosed in late adolescence and even adulthood. The most classic symptoms of ADHD are: Being overly impulsive Unable to maintain attention during important tasks Hyperactivity Usually the child is viewed as one who is disruptive and highly active. Another child with ADHD might be a day dreamer. Poor concentration is a term often used to describe the patient. This condition is difficult to diagnose as these symptoms may also be an indication of other physical or emotional problems. If diagnosed, the patient can be treated with medication and support by the health care team. Autism Autism is a brain disorder that hinders a person’s ability to communicate or relate to others. It is thought to be a genetic disorder, as it often runs in families. This disorder can also affect how a child understands and processes information that is sensory in nature. Autism is usually diagnosed by the time a child reaches the age of three; however, some cases are not diagnosed until later. Typically parents are the first to notice the signs and seek the advice of their pediatrician. There are diagnostic guidelines that have been established by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) which the clinician will use to determine if the child has the core symptoms of autism. Signs and symptoms may include: Toddlers who do not begin to talk or do not interact like other children do Little or no eye contact with others Plays alone Delayed language development Repetitive patterns of behavior such as, rocking, keeping to a certain routine or ritual, and resistance to any change There is no “mold” that all persons with autism fit into. Some need help with the simplest aspects of daily living, while others are able to function at a level high enough that permits them to attend school in a regular class and participate in sports and other activities. Treatment methods include: behavioral, speech, and occupational therapy, parent education, and sometimes medications. Since each child with autism is different, treatment methods are usually individualized. Collectively, most children with autism need to be in a structured and specialized educational program in order to achieve their highest potential. Down Syndrome Down syndrome is a common birth defect that occurs in approximately one in every 800 to 1,000 newborns. This syndrome includes mild to moderate mental retardation and other health problems such as cardiac valvular disease, along with specific physical characteristics which include a sloping forehead, low-set ears, and short, broad hands. The most common form of Down syndrome, trisomy 21, is caused by the presence of an extra 21st chromosome. The cause of the occurrence of this extra chromosome is unknown but appears to be related to the age of the mother and usually occurs in women over the age of 40. Cerebral Palsy Cerebral palsy is a term that is used to describe a range of disorders that impairs control of movement due to damage to the brain during its developmental stage. It is one of the most common causes of disability in children. While CP is not a progressive disease, symptoms may get better for a time only to worsen later on. The exact cause of CP is unknown but is thought to be related to the oxygen levels in the brain before, during, and after birth, infections, and injuries occurring during the birth process. Children with CP not only have physical disabilities, but may also have some level of retardation, learning disabilities, and vision, speech, hearing, and language problems. Patient Tutor Parents, especially first-time parents, and caregivers may need to be provided with educational information on infant and child safety issues, including car seats, cribs, animals/pets, etc. Brochures and pamphlets are useful tools along with information about community resources available to assist the parent with these issues. Pediatric Disorders Related to Abnormal Vital Signs and Measurements The following table identifies some possible medical conditions related to abnormal measurements. The medical assistant should be familiar with pathology related to pediatric patients. Familiarity with common diseases and disorders helps to increase communication opportunities with patients and family members, thus enabling better patient education and patient compliance. Abnormal Vital Sign Possible Pediatric Pathology Low Weight (less than 5th percentile) GI disease, neurological disorder, environmental influences, failure to thrive Low Height, Short Stature Endocrine disorder, growth hormone deficiency, Inflammatory bowel disease, renal disease, celiac disease (disorder of the immune system that damages lining of the small intestine if foods are consumed that contain gluten) Small Head Circumference Premature suture closure, chromosomal abnormalities, infection, maternal metabolic disorder Large Head Circumference Hydrocephalus, subdural hematoma, brain tumor, benign brain growth Elevated Blood Pressure Renal artery disease, coarctation (stricture) of the aorta, primary hypertension, drugs High Pulse Rate (Tachycardia) Supraventricular tachycardia Low Pulse Rate (Bradycardia) Hypoxia, intracranial disorders, heart block, drug ingestion, anorexia Rapid, Shallow Respirations Cardiac disease, metabolic acidosis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia Fever Infections, anxiety, dressing the infant too warmly