Chapter 17: The Autonomic Nervous System
advertisement

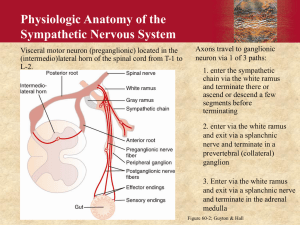
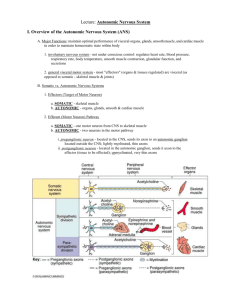
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2. Distinguish between the pre- and postganglionic neurons, in terms of location. 3. Specify the different origins and destination ganglia for the sympathetic (thoracolumbar) and parasympathetic (craniosacral) preganglionic neurons. 4. Describe the differing locations of the ganglia of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF THE ANS 5. Discuss the primary purpose of the sympathetic division and the general body functions it directs. 6. Describe specific responses of effectors due to increased sympathetic stimulation. 7. Discuss the primary purpose of the parasympathetic division and the general body functions it directs. 8. Describe specific responses of effectors due to increased parasympathetic stimulation. ANS NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND RECEPTORS 9. Identify the cholinergic neurons, receptors, and neurotransmitters. 10. Identify the adrenergic neurons, receptors, and neurotransmitters. Chapter Lecture Notes Characteristics of the autonomic nervous system (Table 15.1) Involuntary control Sensory input mostly from interoceptors Motor pathways divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions Two-neuron pathway (Fig 15.1) Preganglionic Postganglionic Neurotransmitters Preganglionic – acetylcholine Postganglionic – acetylcholine (parasympathetic and sympathetic to sweat glands (except on palms and soles), blood vessels in skeletal muscle and arrector pili muscles) or norepinephrine (remainder of sympathetic) Effects smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands Physiological effects of the autonomic nervous system (Table 15.4) Sympathetic – “E” situations (exercise, emergency, excitement and embarrassment) - fight or flight response Pupils dilate Heart rate, force of contraction and blood pressure increase Airways dilate Blood vessels to kidneys and gastrointestinal tract constrict Blood vessels to skeletal muscles, cardiac muscle, liver and adipose tissue dilate Liver cells perform glycogenolysis and lipid cell perform lipolysis Release of glucose by the liver Parasympathetic – rest and digest response Increased salivation, lacrimation, urination, digestion and defecation Decreased heart rate, diameter of airways and diameter of pupils (constriction) Anatomical Differences between the Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Divisions (Table 15.3) Characteristics Parasympathetic Sympathetic Origin (Fig 15.2 & 15.3) Craniosacral outflow: Thoracolumnar outflow: brainstem nuclei of cranial lateral horn of gray matter of nerves III, VII, IX and X; spinal cord segments T1-L2 spinal cord segments S2-S4 Location of ganglia Ganglia in (intramural= Ganglia within a few cm of terminal) or close to visceral CNS: alongside vertebral organ served column (paravertebral ganglia=chain) and anterior to vertebral column (prevertebral ganglia) Relative length of pre- and Long preganglionic; short Short preganglionic; long postganglionic fibers postganglionic postganglionic Sympathetic ganglia (Fig 15.5) Paravertebral ganglia = chain ganglia Innervate organs above the diaphragm like the heart and lungs Prevertebral ganglia = collateral ganglia Prevertebral ganglia surround the following arteries that branch from the aorta Celiac artery (celiac ganglia forms the solar plexus) Superior mesenteric artery Inferior mesenteric artery Neurotransmitters and receptors (Table 15.2 & Fig 15.7) Cholinergic neurons – release acetylcholine (all preganglionic neurons, select sympathetic postganglionic neurons and all parasympathetic postganglionic neurons) Cholinergic receptors – receptors on the postsynaptic membrane that bind acetylcholine Nicotinic receptor Found in the dendrites and cell bodies of sympathetic and parasympathetic postganglionic neurons, the motor end plate in the neuromuscular junction and adrenal medullary cells (excitatory) Is mimicked by nicotine Muscarinic receptor Found in all parasympathetic target organs (excitatory in all but cardiac muscle where it is inhibitory), sweat glands (activation) and some blood vessels in skeletal muscle (inhibition; vasodilation) and arrector pili muscle (excitatory) Is mimicked by muscarine (a mushroom poison) Adrenergic neurons – release norepinephrine (most sympathetic postganglionic neurons) Adrenergic receptors – bind norepinephrine and epinephrine α1 Smooth muscle of blood vessels (excitation; vasoconstriction) radial muscles of eye (dilation of pupil) sphincter muscles of stomach and urinary bladder (closing) salivary gland cells (decreased salivation) sweat glands on palms and soles (increased sweating) α2 Smooth muscle in some blood vessels (inhibition; vasodilation) beta cells in pancreatic islets (decrease insulin secretion) pancreatic acinar cells (inhibition of digestive enzyme secretion) blood platelets (aggregation) β1 Cardiac muscle (excitation; increased force and rate of contraction) posterior pituitary (secretion of antidiuretic hormones) adipose cells (breakdown of triglycerides) β2 Smooth muscle in airways (relaxation; bronchodilation) blood vessels (relaxation; vasodilation) walls of internal organs (relaxation) cillary muscles (inhibition; relaxation) hepatocytes (glycogenolysis) β3 – Brown adipose tissue (thermogenesis) Sympathetic Responses Target Organ Ganglia Effect Location Blood vessels of skeletal and Paravertebral Dilation cardiac muscle Blood vessels of skin, gut Paravertebral Constriction and kidneys Arrector pili muscle Sweat Glands Eyes Paravertebral Contraction Paravertebral Sweat production Paravertebral Dilates pupils and relaxes ciliary muscles for far vision Lungs Heart Paravertebral Dilates bronchi Paravertebral Increased rate and force of contraction Liver Prevertebral Small and Large Intestines Paravertebral Slows digestion, stops secretions and contracts sphincters Paravertebral Contracts sphincter Stimulates release of norepinephrine and epinephrine Urinary Bladder Adrenal Medulla Breakdown of glycogen to glucose and triglycerides to fatty acids Parasympathetic Responses Target Organ Origin Effect Eyes Cranial Nerve III Constricts pupils and ciliary muscles for near vision and stimulates tears Salivary Glands Cranial Nerve VII&IX Stimulate salivation Lungs Cranial Nerve X Constricts bronchi and stimulates secretion Heart Cranial Nerve X Decreased rate and force of contraction Gall Bladder Cranial Nerve X Constriction Pancreas Cranial Nerve X Small and Large Intestines Urinary Bladder Cranial Nerve X and Sacral Nerves Sacral Nerves Genitals Sacral Nerves Stimulation of exocrine secretions and release of insulin Increases motility and secretions and relaxes sphincters for increase defecation Contracts bladder (micturition) and relaxes sphincter Erection Drugs that Effect the Autonomic Nervous System Drug Mechanism Action Uses Drugs that Stimulate the Sympathetic Nervous System (Sympathomimetic) Phenylephrine Stimulates α1 receptors Clonidine Stimulates α2 receptors Stimulates β receptors Elevates blood pressure; stimulates smooth muscle Lowers blood pressure Stimulates heart rate; dilates respiratory passages Albuteral, terbutaline Stimulates β2 receptors Dilates respiratory passages Ephedrine, psuedoephedrine Stimulates NE release at synapses Similar to epinephrine Isoproterenol MAO Inhibitors Nasal decongestant and to elevate blood pressure Treatment of high blood pressure Treatment of respiratory disorders and as a cardiac stimulant during cardiac resuscitation Treatment of asthma, severe allergies and other respiratory disorders Nasal decongestant and to elevate blood pressure or dilate respiratory passages Antidepressant Increases NE levels in Boosts mood in the the synapse by brain inhibiting the enzyme that breaks it down Tricyclic Increases NE levels in Boosts mood in the Antidepressant antidepressants the synapse by brain (Moxadil, Endep) blocking reuptake Drugs that Stimulate the Parasympathetic Nervous System (Parasympathomimetic) Muscarine, Stimulates muscarinic Similar to effects of Applied topically to pilocarpine, receptors Ach cornea of eye to cause methacholine pupil contraction Physostigmine, Block action of Increase Ach Stimulate digestive neostigmine, acetylcholinesterase concentrations at tract and smooth malathion, nerve synapses muscles of urinary gases bladder Drugs that Block the Sympathetic Nervous System Prazosin (Minipress) Lowers blood Treatment of high Blocks 1 receptors pressure blood pressure Tamsulosin (Flomax) Blocks 1a receptors Relaxes smooth Treatment of benign muscle surrounding prostrate hyperplasia the urethra Yohimbine (herbal Dilates blood vessels Aphrodisiac Blocks 2 receptors supplement) and relaxes smooth muscles Propranolol (Inderal) Reduces metabolic Treatment of high Blocks 1 and 2 activity in cardiac blood pressure: used receptors muscle but may to reduce heart rate constrict respiratory and force of passageways: slows contraction in heart heart rate disease Metoprolol (Lopressor), atenolol Blocks 1 receptors Reduces metabolic activity in cardiac muscle Drugs that Block the Parasympathetic Nervous System Atropine, related Block muscarinic Inhibit drugs receptors parasympathetic activity Similar to those of Inderal but has less of an effect on respiratory muscles Treating diarrhea; dilating pupils; raising heart rate; blocking secretions of digestive and respiratory tracts prior to surgery; used to treat accidental exposure to anticholinesterase drugs, such as pesticides or military nerve gases