Dialysis Facility Practices Aimed at Target Weight Achievement and
advertisement
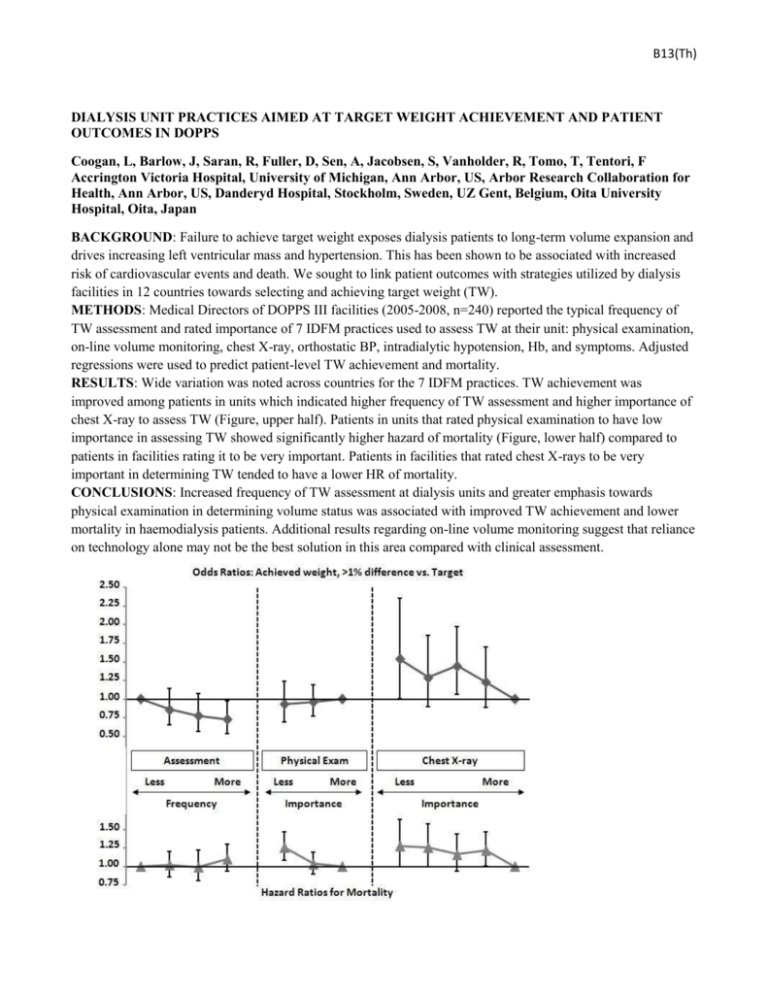
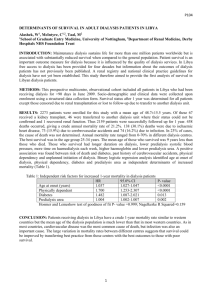
B13(Th) DIALYSIS UNIT PRACTICES AIMED AT TARGET WEIGHT ACHIEVEMENT AND PATIENT OUTCOMES IN DOPPS Coogan, L, Barlow, J, Saran, R, Fuller, D, Sen, A, Jacobsen, S, Vanholder, R, Tomo, T, Tentori, F Accrington Victoria Hospital, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, US, Arbor Research Collaboration for Health, Ann Arbor, US, Danderyd Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden, UZ Gent, Belgium, Oita University Hospital, Oita, Japan BACKGROUND: Failure to achieve target weight exposes dialysis patients to long-term volume expansion and drives increasing left ventricular mass and hypertension. This has been shown to be associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events and death. We sought to link patient outcomes with strategies utilized by dialysis facilities in 12 countries towards selecting and achieving target weight (TW). METHODS: Medical Directors of DOPPS III facilities (2005-2008, n=240) reported the typical frequency of TW assessment and rated importance of 7 IDFM practices used to assess TW at their unit: physical examination, on-line volume monitoring, chest X-ray, orthostatic BP, intradialytic hypotension, Hb, and symptoms. Adjusted regressions were used to predict patient-level TW achievement and mortality. RESULTS: Wide variation was noted across countries for the 7 IDFM practices. TW achievement was improved among patients in units which indicated higher frequency of TW assessment and higher importance of chest X-ray to assess TW (Figure, upper half). Patients in units that rated physical examination to have low importance in assessing TW showed significantly higher hazard of mortality (Figure, lower half) compared to patients in facilities rating it to be very important. Patients in facilities that rated chest X-rays to be very important in determining TW tended to have a lower HR of mortality. CONCLUSIONS: Increased frequency of TW assessment at dialysis units and greater emphasis towards physical examination in determining volume status was associated with improved TW achievement and lower mortality in haemodialysis patients. Additional results regarding on-line volume monitoring suggest that reliance on technology alone may not be the best solution in this area compared with clinical assessment.