Lecture
advertisement

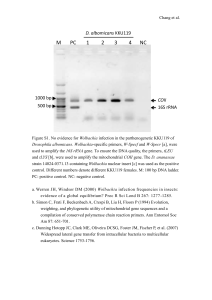
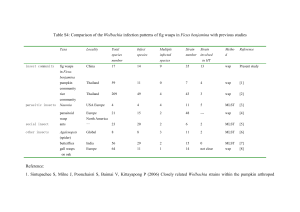
What exactly are Wolbachia and how do we know if an insect is infected with them? Feminization, Parthenogenesis and C.I., oh my! Wolbachia are Important!! Wolbachia are intracellular parasites inherited via infected eggs. Feminization – Somehow, maybe by influencing hormone levels, Wolbachia cause developing male woodlice to be born as female. Wolbachia-infected wasp embryo Parthenogenesis-inducing – In wasps and some other arthropods, females are diploid (result of fertilization) and males are haploid (develop from unfertilized eggs). Wolbachia prevent chromosome division so eggs remain diploid, resulting in all female births. Cytoplasmic Incompatibility (CI) – Infected females can reproduce with any mate whereas uninfected females are restricted to breeding with fewer uninfected males. Q. How might Wolbachia affect gene flow in a population? How might this lead to sympatric speciation? Bacteria “fishing” DNA sequence DNA Replicatiton What do we use to “hook” Wolbachia DNA? Primers – a strand of RNA that serves as the starting point for DNA replication. WSPEC-F (5’-CATACCTATTCGAAGGGATAG-3’) WSPEC-R (5’-AGCTTCGAGTGAAACCAATTC-3’) DNA copies What gene (DNA) is being copied using PCR? PCR + primer animation : http://nitro.biosci.arizona.edu/c ourses/EEB105/lectures/DNA_ replication/DNA_rep.html Use primers in PCR to help copy DNA (animation) http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/pcr/pcr.htm http://www.mcb.harvard.edu/Losick/images/TromboneFINALd.swf Objective: Use primers to copy the 16S rDNA gene in Wolbachia bacteria Bacterium Ribosome with ribosomes synthesizing a protein 16S rDNA gene – codes for making SSU rRNA Forward primer 5’ Conserved region Reverse primer Variable regions 3’ F R Copied DNA (using PCR) Campbell & Reece, 6th Ed. Loops (sites that are more free to mutate & evolve faster) http://en.wikipedia. org/wiki/Image:10_ small_subunit.gif Atomic structure of the small subunit a ribosome. The rRNA, shown in orange, helps match the mRNA (codon) to the tRNA (anticodon). Stems (sites that rarely mutate & are conserved) Small subunit ribosomal RNA http://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/Ribosomal_RNA