Gel electrophoresis
advertisement

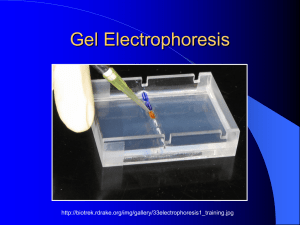
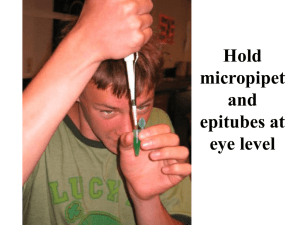
4.4 Using Gel Electrophoresis to Study Gene Molecules Components of Gel Electrophoresis • Powdered agarose • Boiling buffer solution Agarose Gel Concentrates Most commonly used when separating pieces of DNA no smaller than 50 bp and no larger than 25,000 bp Gel Stains The gel is “run” until molecules of different sizes are thought to have completely separated. Agarose Gel Tray. Gel trays differ depending on the manufacturer. Each has some method of sealing the ends so that liquid agarose can mold into a gel. Some gel trays, such as those made by Owl Separation Systems, make a seal with the box, so casting a gel is simple. Other trays require masking tape on the ends to make a mold. Still others, like the one shown here, have gates that screw into position: up for pouring the gel and down for running the gel. Molecules in a Gel Box. If negatively charged molecules are loaded into the wells and run on the gel, the smaller ones run faster and farther than the larger ones toward the positive electrode. This is because smaller molecules pass more easily through the tiny spaces of the gel network. Vocabulary • • • • • • Gel electrophoresis – a process that uses electricity to separate charged molecules, such as DNA fragments, RNA, and proteins, on a gel slab Agarose – a carbohydrate from seaweed that is widely used as a medium for horizontal gel electrophoresis Polyacrylamide – a polymer used as a gel material in vertical electrophoresis; used to separate smaller molecules, like proteins and very small pieces of DNA and RNA Ethidium bromide – a DNA stain (indicator); glows orange when it is mixed with DNA and exposed to UV light; abbreviated EtBr Methylene blue – a staining dye/indicator that interacts with nucleic acid molecules and proteins, turning them to a very dark blue color High through-put screening – the process of examining hundreds or thousands of samples for a particular activity 4.4 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Agarose gels can be used to study what size of DNA fragments? If agarose gel material is labeled 1%, what does the 1% refer to? What causes molecules to be separated on an agarose gel? Name two common DNA stains that are used to visualize DNA on agarose gels. Hold micropipet and epitubes at eye level Micropipet Use 1 2 3 4 Twist dial to desired volume Add disposable pipet tip Press plunger to first stop Insert pipet tip into solution to be transferred 5 Slowly release plunger to retrieve liquid 6 Move pipet tip into desired tube 7 Press plunger past first stop to second stop to transfer liquid, keep the plunger down as you remove it from the tube. 8. Eject tip Micropipetting technique A technique B Close the tips! Technique C Billiard style Micropipet tip should be ABOVE the well NOT IN IT!!!! Micropipet tip punched right through the gel See dye under the wells NICE!