Fingerprinting and Restriction Enzymes Lecture
advertisement
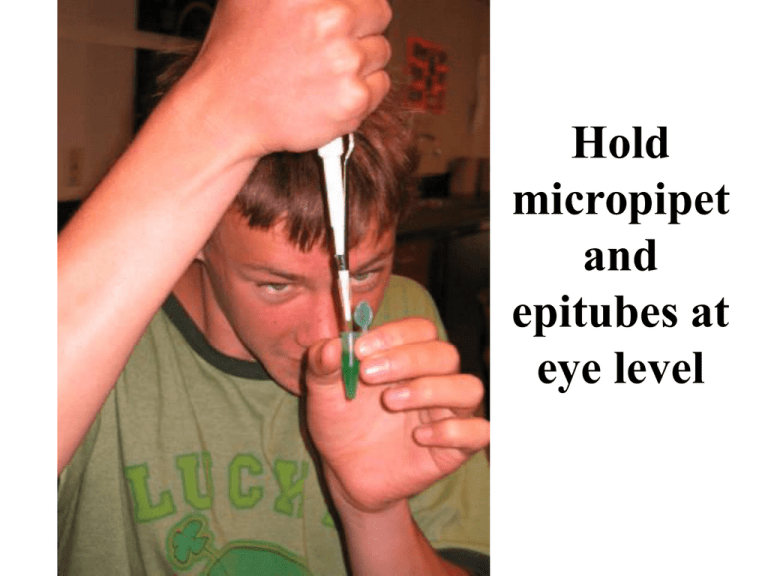
Hold micropipet and epitubes at eye level Micropipet Use 1 Add disposable pipet tip 2 Press plunger to first stop 3 Insert pipet tip into solution to be transferred 4 Slowly release plunger to retrieve liquid 5 Move pipet tip into desired tube 6 Press plunger past first stop to second stop to transfer liquid, keep the plunger down as you remove it from the tube. 7 Eject tip Micropipetting technique A technique B Close the tips! Micropipet tip should be ABOVE the well NOT IN IT!!!! Micropipet tip punched right through the gel See dye under the wells NICE! When you to into the lab today, you Each person in your group will transfer 15 uL of colored will firstmicrotube. practice the you liquid into an empty Once using this is completed, should have 60 uL of brownish colored liquid in your practice micropipette tube. 15 uL 15 uL 15 uL 15 uL After practicing how to use the micropipette, a biotechnology student will demonstrate and load the victim’s DNA into the gel. You will then load your DNA into the gels. Each student in the group can then load 1 well of the gel with the suspect’s DNA. There are four suspects total. You may NOT load the gel without the help of a biotechnology student watching you! To understand electrophoresis, you must understand the structure of DNA Phosphate groups of nucleotides have a - charge 5’ 5’ 2- 1 PO4 1 2 3’ OH O O-P=O O 3 5’ 4 2- PO4 Phosphodiester bond 2 5 6 3’ OH 3’ Charge on a DNA Double Helix 3’ 5’ 1 2 3 4 5 Large groove 6 Small groove 7 8 9 10 1 Twist = 10.5 bp 5’ 3’ Gel Electrophoresis • Gel Electrophoresis: technique uses the difference in electrical charge to separate polymers (DNA, RNA, protein) on the basis of size Let’s see a model of how gel electrophoresis works DNA Electrophoresis analysis after DNA has been cut by enzymes at various points, A and B Restriction enzymes C A B A+B L A B 10 kb A 8 kb 2 kb B 7 kb 3 kb A 5 kb + 3 kb B 2 kb Juang RH (2004) BCbasics Purpose of Gel Electrophoresis? • Get a “DNA Fingerprint” of individuals • Trace a sequence of genetic markers in families • Diagnose disease • Compare genes of different people, different species • Find mutations • Paternity tests Restriction Enzymes • • • • • • • rDNA (recombinant DNA)—the produced piece of DNA from inserted another piece of DNA recognize specific sites to cut the DNA Blunt ends—straight across Sticky ends—one side of DNA is longer than the other, these overhangs allow for complementary matches between two DNA pieces cut by the same enzyme, the sticky ends match and pasting ma occur to produce an rDNA molecule More than 1200 restriction enzymes discovered & isolated from bacteria Read 5 3 Palindromic (example radar or GAATTC CTTAAG Reviewing Homework Based on this DNA Fingerprint created, who should the police arrest as the prime suspect? Suspect 1 or 2? Why?