MALDI-TOF: Bringing Bacteriology into the 21st Century
advertisement

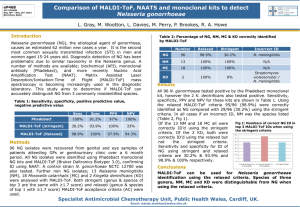
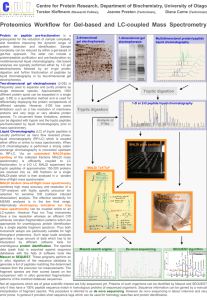
MALDI-TOF Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization – time of flight MALDI-TOF: Bringing Bacteriology into the 21st Century Ross Davidson PhD, FCCM, D(ABMM) Director, Bacteriology Dept. Of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine CDHA Disclosure • I have NO affiliation, financial or otherwise, with any company whose products or devices are discussed within this presentation. MALDI-TOF At the end of this session, participants will be able to: • Understand the principles of MALDI-TOF • Understand the application and integration of MALDI-TOF into the clinical laboratory • Describe the benefits of MALDI-TOF for patient care and potential cost savings for the laboratory • Describe potential future applications of MALDI-TOF Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Advances in Bacterial Identification Biochemical to MALDI-TOF Bacterial Identification • Most significant advance in Clinical Microbiology (Bacteriology) in 30 years! – Rapid and cost effective identification of bacteria directly from isolated colonies and positive culture bottles based on protein biomarkers • Protein biomarkers measured are highly expressed proteins responsible for housekeeping functions, such as ribosomal (16S) and transcription/translation factor proteins 6 FASTER, BETTER, CHEAPER, BUT NOT PERFECT! Conventional ID vs MALDI • • • • Monday, 12pm, Mr. J’s blood culture flags positive Bottle removed, gram stain /culture prepared Gram negative rods seen, floor called at 1:10pm 3pm – Mr. J started on Ceftriaxone • Tuesday, 10:30am P. aeruginosa identified • Floor called 10:45am • Mr J started on Pip/tazo • MALDI ID would have seen Mr J on appropriate antiPseudomonal therapy 20-24 hours earlier MALDI TOF Sample Preparation Step 1 Spot target slide with direct colony (can be up to 5 days old). Step 2 Add matrix solution* Step 3 Step 4 Load target slides NOTE: Other sample types: - sediment from positive blood cultures - sediment from certain specimen (e.g. urines) Air dry for 1-2 min. Bacteria, molds, yeasts, Mycobacteria Target 8Slide 48 wells Matrix Solution: (0.5 µl -cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid) Create Spectra General schematic for MS analysis of ionized microbiological isolates Clark A E et al. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013;26:547-603 MALDI Mechanism Laser matrix & analyte Sample support 1. Sample (A) is mixed with excess matrix (M) and dried on a MALDI target + m m m a + a m a m + a m a m a + m m m+ 2. Laser ionises matrix molecules 3. Sample molecules are ionized by proton transfer from matrix: MH+ + A M + AH+. Principle of MALDI-TOF Time of Flight Molecular masses The Workflow: Measurement automated spectrum acquisition ~ 60 sec ionization of intact proteins and molecular weight measurement < C : \ D o k u m e n t e u n d E in s t e lu n g e n \ m . e r h a r d \ E ig e n e 100 e ie n \ A n a g n o s T e c - d c \ Z w is c h e n a b la g e \ D o k u m e n t B a n n e r . t x t > > S p e c [ B P = 3 5000 7000 11000 11906 11572 10226 10347 9000 Mass (m /z) 10608 10 9654 8450 9330 7863 7367 20 7092 3581 40 6837 50 5931 5015 60 10939 9994 7980 70 % Intensity t 9453 8744 8074 7075 80 0 3000 a 1648.1 90 30 D 3775 < 13000 Low influence of culture conditions Psdm. oleovorans B396_Medium 360 1000 0 Psdm. oleovorans B396_Medium 464 1000 0 Psdm. oleovorans B396_Medium 53 1000 0 Psdm. oleovorans B396_Medium 65 1000 0 Psdm. oleovorans B396_Medium 98 1000 500 0 Psdm. oleovorans B396_MRS10 2000 1000 0 Psdm. oleovorans B396_YPD 2000 1000 0 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 11000 m/z Bacterial Identification by Mass Spectrometry Concordance between Conventional Routine Identification (Vitek) and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Timeof-Flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry 84.1% 95.4% Seng P et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:543-551 Bizzini et al. J Clin Microbiol 2010;48:1549 van Veen et al. J Clin Microbiol 2010:48:900 Retrospective Validation Maldi Correlation Summary Mismatch, 3% Total Tested 838 Correlates 810 97% Mismatch 28 Correlates Mismatch 3% Correlates, 97% 16s rDNA used as gold standard Prospective Validation Total Tested Correlates Mismatch No Growth No Data 356 342 7 --7 96% 1.9% Urinary Tract Isolates (2010 – 2012) Organisms Number Percentage TOTAL Specimens 190,757 -- TOTAL Negatives 146,586 77% TOTAL Positives 44,121 23% E.coli 24,415 *55% KES 5,148 *12% Enterococcus 5,036 *11% Gp B Streptococcus 2,005 *4.5% Proteus 1,890 *4.0% Candida albicans 1,211 *2.7% S.saprophyticus 1,006 *2.3% 380 *0.8% Citrobacter 92.5% of positive cultures Cost Calculations Urine cultures • Cost of Chrom-agar vs Blood agar + MALDI • Crom-agar $0.62 / Blood agar $0.27 • MALDI $0.51 (plate, matrix, toothpicks, pipette tips, etc.) • LAP $1.19 / PYR $1.95 / Ox $0.94 / PH B $2.69 / Strep A,C,G $1.46 Cost Calculations Urine cultures • Total # of specimens / year: 63,585 • Total # of negatives / year: 48,862 • Total # of positives / year: 14,707 • Cost of a negative culture: 48,862 x 0.62 - 48,862 x 0.27 ($30,294 - $13,192 = $17,102 SAV) Cost Calculations Urine cultures # Negatives 48,862 Positives 14,707 ChromAgar Chrom + MALDI $30,294 Yeast Chrom Blood Agar BL + MALDI $13,192 $5047 $17,102 E.coli 8140 KES 1716 $1956 $1356 Enterococcus 1680 $1915 $1325 Bp B Strep 668 $762 $528 Proteus 630 $718 $497 Candida 404 $461 $319 Misc Pos 1462 $1667 $1178 $251 +/- Cost $6430 +$1382 -$600 -$590 -$235 -$221 -$489 Projected cost savings of moving back to Blood agar is approximately $18,000 / year Cost calculations Throat cultures • Gp A Strep $2996 (PYR) vs $1298 (MALDI) = $1698 SAV • Gp C Strep: Costs $534 for a neg PYR $445 extraction $650 Gp C latex = $1629 vs $231 (MALDI) = $1398 SAV • Gp G Strep: Costs $377 for a neg PYR $314 extraction $458 for a neg Gp C latex $458 Gp G latex = $1607 vs $163 (MALDI) = $1444 SAV • Approx $5000 / year Saving!! What Does an Instrument Cost? Instrument Service Contract Disposables ~ cost per test ~$ 220,000 ~$ 20,000 / yr ~ $3-7,000 / yr ~ $ 0.51 / test We currently spend ~$ 65 – 75,000 / yr on Vitek ID panels Impact of MALDI-TOF MS Study from Methodist Hospital, Huston TX • Intervention arm (Gram Negative Bacilli): – Integrated rapid ID with active antimicrobial stewardship – Results called to infectious diseases pharmacist 24/7 – Pharmacist recommends de-escalation or adjustment of therapy based on the rapid ID – Time to adjusted therapy was significantly reduced by 31 hrs. Time to therapy adjustment 60 48 P = 0.04 Hours 40 20 17 26 0 Perez KK, et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012 Pre-intervention Intervention EFFECTS ON HEALTH CARE COST Hospitalization cost reduction of $19,547/patient 27 Perez KK, et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012 MALDI – TOF Laboratory Integration E X P E C T A T I O N S Current Level MALDI – TOF Laboratory Integration Challenges • Technologist buy-in • Spotting plates an “art”, not a science • Updated nomenclature (New names) -Wohlfahrtiimonas chitinclastica (Wool farti WHAT??) -isolated from 3rd stage larvae of Wohlfahrtia magnifica • Workflow No Test is perfect! • E.coli vs Shigella • Acinetobacter baumanii-calcoaceticus complex (A. baumanii, A. calcoaceticus, A. genospecies 3, A. genospecies 13) Pre MALDI - Good Clinical Microbiology Begins With Good specimens – Garbage In = Garbage Out • Control of sample acceptability • • • • • Verification that appropriate sample(s) collected Correct volume submitted Sample placed promptly in correct transport media Optimal and timely transport conditions Sample handled properly in laboratory • • Shared samples Reflexed samples 31 Future Direction • Direct specimen applications (already blood / urine data) • Ability to resolve poly-microbial specimens • Antimicrobial resistance determination (already MRSA, carbapenemase) • Strain typing Direct Detection for Positive Blood Culture Bottles By MALDI Purpose: Separate human and bacterial/yeast ribosomal proteins Methods: Lysis/centrifugation or membrane filtration Journal of Clinical Microbiology 51;805-809, 2013 Issues: • Removal of human proteins • Extraction protocol required • Bacterial concentration • need~107/mL • Polymicrobial specimens • Seen on Gram stain? • Charcoal • Antibiotic resistance genes • Yeasts? • Unique database, different cutoffs? 33 Journal of Clinical Microbiology 48;1584-1591, 2010 Potential Options for Direct detection from clinical specimens Clark A E et al. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013;26:547-603 MALDI-TOF Bacterial ID • Minimal sample preparation • Cost effective - low consumable cost • Powerful bioinformatic approaches • Species to strain resolution • Non-expert identification possible • Dedicated databases continue to expand MALDI-TOF Limitations • Databases : still in their infancy • High initial capital expenditure • New approaches (business models) • Potential instrument downtime - single instrument MALDI-TOF in the Clinical Laboratory • Rapid turn around time, high throughput - impact on appropriate emperic therapy • Single colony requirement - direct from blood culture • Low exposure risk –sample inactivation • Broad applicability (all types bacteria including anaerobes, yeasts, fungi) • COST SAVINGS Questions General schematic for MS analysis of ionized microbiological isolates Clark A E et al. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013;26:547-603