T-ALL - SAHH - Sociedad Asturiana de Hematología y Hemoterapia
advertisement

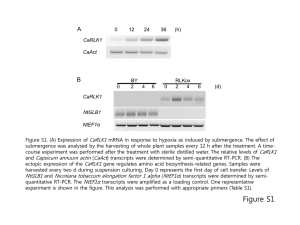
V Reunión de la Sociedad Asturiana de Hematología y Hemoterapia Gijon, 9 de marzo de 2012 Diagnóstico y monitorización de hemopatías malignas JM Ribera Servicio de Hematologia Clínica ICO-Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol Badalona Universidad Autónoma de Barcelona Diagnosis in Malignant Hematology From clinical symptoms to DNA • Anamnesis and physical examination • Diagnostic techniques – CBC, biochemistry – Studies in PB, BM, other fluids, lymph node, tumor mass • Morphology, cytochemistry, cytofluorometry, cytogenetics, molecular genetics – – – – Imaging studies: X-ray, CT, MRI, PET scan Isotopic studies “Omic” studies: genomic, proteomic, metabolomic Nanotechnology Importance of diagnostic methods • • • • • Accuracy of diagnosis Staging Prognostic assessment Analysis of response to therapy Follow-up Diagnostic work-up in ALL • • • • • • • • • • • • • Anamnesis, physical examination Complete blood count, coagulation status, serum biochemical study Serology for hepatitis and HIV EKG, LVEF (advanced age or history of cardiac disease) Chest X-ray Bone marrow aspirate (morphology, cytochemistry) Bone marrow biopsy (only if dry tap) Immunophenotypic study (BM, PB) Cytogenetics (BM, PB) FISH (BM, PB) Study of molecular rearrangements (PCR) CSF study (morphology, FCM?) HLA typing as soon as possible • Storage: cells, DNA, RNA. ALL. WHO Classification, 2008 • B precursor ALL – B precursor ALL/B-LL, non specified – B precursor ALL/B-LL, with recurrent genetic abnormalities • • • • • • • t(9;22); BCR/ABL 11q23; MLL t(1;19); E2A/PBX1 (TCF3/PBX1) t(12;21); ETV6/RUNX1 (TEL-AML1) t(5;14); (IL3/IgH) Hyperdiploid ALL Hypodiploid ALL • Precursor T-ALL/T-LL • Burkitt-like ALL (mature B-ALL) – t(8;14), t(2;8), t(8;22); C-MYC ALL Morphology Sensitivity: 10-2 Immunologic classification of ALL B-lineage ALL: CD19+ and CD79a+ and/or CyCD22+ CD10CD10+, cyIgCig+, sIgsIg+ Pro-B ALL (B-I) Common ALL (B-II) Pre-B ALL (B-III) Mature B ALL (B-IV) T-lineage ALL: cyCD3+ and CD7+ cyCD3+ Cd7 only CD2+ and/or CD5+ CD1a+ sCD3+, CD1asCD3+, anti TCR α/β+ sCD3+, anti TCR γ/δ+ Pro-T ALL (T-I) Pre-T ALL (T-II) Cortical T-ALL (T-III Mature T-ALL (T-IV) α/β+ T-ALL γ/δ+ T-ALL Recommendations of the EWALL Group, 2012 Phenotypic study Sensitivity: 10-4 (4 colors), ≥10-5 (>4 colors) Cytogenetics Hyperdiploidy 52,XY,+X,+6,+14,+17,+21,+mar Hypodiploidy 41,XX,-4,-9,add(9)(p21),-15,-20,-22 Sensitivity: 10-2 Pseudodiploidy 46,XX,t(4;11)(q21;q23) 46,XX,+8,-12,der(19)t(1;19)(q23;p13.3), +der(19)t(1;19)(q23;p13.3),-20 Sensitivity: 10-2 Pseudodiploidy Burkitt ALL 46, XY, t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2) ALL FISH BCR-ABL IgH/c-MYC nuc ish(ABL1x3),(BCRx3),(ABL1con BCRx2)[90/100] Sensitivity: 5x10-2 IgH & TCR rearrangements IgH clonal TCR clonal FR1 (310-360pb) 310pb Sensitivity: 10-4 – 10-5 (RQ-PCR) Quantification of the amount of mRNA transcripts BCR/ABL - t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 & 2: Patient 1 (positive p190) 3 & 4: Patient 2 (negative p190) 5: Positive control p190 6: Negative control 7: Marker of molecular weight RQ-PCR Standard curve Linear dynamic range (5 Logs) Sensitivity: 10-5- 10-6 Recommendations for genetic diagnosis and follow-up of hematologic neoplasias. ALL (AEHH, FEHH, GCECGH, Grupo BMH)(2007) Subtype Phase Sample Conventional cytogenetics FISH Molecular biology Diagnosis BM Always BCR/ABL, MLL BCR/ABL, AML/AF4 Relapse BM Optional Optional No Burkitt’s lymphoma/ leukemia Diagnosis BM/Tumor tissue Always C-MYC No Relapse BM/Tumor tissue Optional Optional No Pediatric ALL Diagnosis BM Always If NK or no metaphases: TEL/AML1, PBX1/E2A, MLL, BCR/ABL TEL/AML1, PBX1/E2A, AF4/MLL BCR/ABL MRD BM No According to diagnosis According to diagnosis Diagnosis BM Always No No Relapse BM Optional No No Precursor BALL T-ALL Main genetic abnormalities in B-ALL Abnormality Genes involved Incidence Molecular detection t(9;22)(q34;q11) BCR-ABL Adults 30% Children 3% RT-PCR t(12;21)(p13;q22) TEL-AML1 Adults <1% Children 20% RT-PCR t(4;11)(q21;q23) MLL-AF4 Adults 5% Infants 60% RT-PCR t(1;19)(q23;p13) E2A-PBX1 5% RT-PCR t(8;14)(q24;q32) C-MYC-IgH 1% FISH t(17;19)(q22;p13) E2A-HLF <1% RT-PCR t(11;19)(q23;p13) MLL-ENL <1% RT-PCR JAK 1/2/3 mutations 10% Sequencing Recommendations of the EWALL Group, 2012 Main genetic abnormalities in T-ALL Abnormality Genes involved Incidence Molecular detection t(10;14)(q24;q11) t(7;10)(q34;q24) HOX11-TCRα/δ HOX11-TCβ Adults 31% Children 7% RT-PCR t(5;14)(q35;q32) HOX11L2-TCRα/δ Adults 13% Children 20% RT-PCR, FISH t(1;14)(q23;p13) TAL1-TCRα/δ 1-3% RT-PCR Normal 1p32 SIL-TAL1 9-30% RT-PCR Inv(7)(p15q34), t(7;7) HOXA-TCRβ 5% FISH, RT-PCR t(10;11)(p13;q14-21) CALM-AF10 10% FISH t(9;9)(q34;q34) NUP214-ABL1 6% FISH t(9;14)(q34;q34) EML1-ABL1 <1% FISH NOTCH1 mutations NOTCH1 50% Sequencing JAK1 mutations JAK1 18% Sequencing Recommendations of the EWALL Group, 2012 Genetic Heterogeneity in Adult ALL Pui C.-H., Jeha S. Nature Rev Drug Discovery 2007; 6:149-165 Minimum diagnostic approach in ALL Morphology/Cytochemistry •Blast percentage in BM above 25% •MPO negative Immunophenotyping (minimum marker panel) •CyMPO, CD117, TdT, cyCD3, CD7, cyCD79a, CD19 Cytogenetics/molecular genetics •Identification of t(9;22)/ BCR-ABL and t(4;11)/MLL-AF4 Recommendations of the EWALL Group, 2012 Comprehensive diagnostic approach Morphology/cytochemistry As above Immunophenotyping (refined panel) •First step: cyMPO, CD117, TdT, cyCD3, CD7, cyCD79a, CD19, CD13, CD33, CD34, HLA-DR •Second step: - B-ALL: CD10, CD20, CD22, cyIgM, sIg, CD52, CD45, CD58, Ng2 or CD133, CD66c - T-ALL: CD1a, CD2, CD3, CD5, CD4, CD8, CD52, CD99 Cytogenetics As above; whenever possible, other approaches such as CGH and aCGH may be performed Molecular genetics •Detection of fusion genes as required for risk stratification •Detection of Ig/TCR rearrangements •Gene expression profilling (research/diagnosis purposes) Recommendations of the EWALL Group, 2012 Usefulness of diagnostic work-up • • • • Diagnosis Prognosis and treatment stratification MRD evaluation and follow-up Early detection of relapses Prognostic impact of genetic and molecular classification of childhood ALL Pui C-H. Lancet 2008;371:1030 Genetics and prognosis in adult ALL. (MRC UKALLXII/ECOG 2993, n= 1522) Moorman, AV. et al. Blood 2007; 109:3189-97 CIR and EFS according to CD20 expression and WBC in adult ALL Maury, S. et al. Haematologica 2010;95:324-328 Outcome by CD20 expression and therapy according to age subgroups Protocol Young Elderly Thomas, D. A. et al. Blood 2009;113:6330-6337 T-ALL: prognostic value of differentiation stage/phenotype GMALL protocols Baak U et al, Leukemia 2008 Prognostic impact of HOX11/TLX1 in adult T-ALL Bergeron, J. et al. Blood 2007;110:2324-2330 Impact of BAALC expression on survival in adult T-ALL Baldus, C. D. et al. J Clin Oncol; 25:3739-3745 2007 Effect of NOTCH1 mutation status on long-term prognosis in childhood T-ALL Breit, S. et al. Blood 2006;108:1151-1157 . OS in adult T-ALLALL according to NOTCH1 and/or FBXW7 mutations and chemotherapeutic protocol Asnafi, V. et al. Blood 2009;113:3918-3924 . EFS impact of NOTCH1-FBXW7 mutations within ERG/BAALC expression groups Low ERG/BAALC High ERG/BAALC Baldus, C. D. et al. Haematologica 2009;94:1383-1390 Genetic Alterations of IKZF1, EBF1, and BTLA/CD200 and the Cumulative Incidence of Relapse in the Original Cohort Mullighan C et al. N Engl J Med 2009;360:470-480 CIR according to IKZF1 deletion in BCR-ABL+ ALL Martinelli, G. et al. J Clin Oncol; 27:5202-5207 2009 Spanish PETHEMA protocols in adult ALL Front line Standard risk ALL-SR08 High risk Very high-risk (Ph+ ALL) ALL-AR-03 Young (<55yr) Ph+ALL08 DASACORD Elderly PhALL LAL Old* Burkitt ALL BURKIMAB** Elderly (>55yr) LAL OLDPh+ * EWALL trial **Joined with GMALL Usefulness of diagnostic work-up • • • • Diagnosis Prognosis MRD evaluation and follow-up Early detection of relapses CIR among 379 children with B-lineage ALL whose MRD levels were less than 0.01% on day 46 Stow, P. et al. Blood 2010;115:4657-4663 Prognostic significance of MRD in adult ALL Bassan R, et al. Blood 2009; 113: 4153-4162 JM Ribera et al, ASH 2009 Usefulness of diagnostic work-up • • • • Diagnosis Prognosis MRD evaluation and follow-up Early detection of relapses MRD as a Predictor of Relapse in Adults with Standard-Risk, Ph-negative ALL Raff, T. et al. Blood 2007;109:910-915 Clinical case Female, 35 years old Clinical picture: weakness, gum bleeding and fever in the last 15 days Phisical exam: pale, petechiae and ecchymoses on arms and legs, gum bleeding, liver enlargement (3 cm below right costal margin) Complete blood count Hb 88 g/L, hematocrit 0,24 L/L, MCV 90fL, WBC count 48x109/L (20% N, 30% L, 50% blasts), platelet count 15x109/L, coagulation status normal Serum biochemical parameters Uric acid 8.8 mg/dL, LDH 2230 U/L. Chest X-ray: normal EKG: normal BM aspirate: 98% blasts, lymphoid appearance Cytochemistry: peroxidase negative Cytogenetics: 46, XX, t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2)[22] Immunophenotypic study: Precursor B-ALL CD10+, with myeloid markers Molecular biology: BCR-ABL, p190 CSF study: normal May-Grünwald-Giemsa Flow Cytometry CD10+ ALL with My: CD33+; CD66C++ 46, XX, t(9;22) (q34.1;q11.2) [22] FISH. BCR-ABL BCR ABL1 p190BCR-ABL 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 & 2: Patient 1 (positive p190) 3 & 4: Pacient 2 (negative p190) 5: Positive control p190 6: Negative control 7: Marker of molecular weight [(BCR-ABL)/ABL]x100: 130.12 Treatment Induction: - Imatinib, VCR, DNR, PDN (clinical trial CSTIBES02) - Result: Complete remission - [(BCR-ABL)/ABL]x100: 0.032 Consolidation-1 - Imatinib, HD-MTX, HD-ARA-C - [(BCR-ABL)/ABL]x100: 0.0079 Allogeneic SCT from a HLA-identical sibling - Conditioning regimen: cyclophosphamide + ICT - Grade 2 cutaneous acute GVHD - Chronic GVHD with limited skin involvement - [(BCR-ABL)/ABL]x100: 0.00001 Imatinib post TPH -Well tolerated - [(BCR-ABL)/ABL]x100: 0.000003 -Sustained complete molecular remission Molecular follow-up (RQ-PCR) EFS. CSTIBES02 vs. ALL Ph08 Ph+ ALL TKI era Imatinib+CHT Allo-SCT Tx post TPH PH+ ALL in the TKI era Unsolved questions • Induction - Intensity of CHT, number of cycles? - Type of TKI. Combination of TKI? •SCT - Always? - Modality? - MRD status at SCT •Maintenance after SCT - Always or in MRD+ status? - Type of TKI - TKI + other cytotoxic/immunomodulatory drugs? - Duration? Thank you! White blood cells from a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Lancet Oncology 2009