chronic myeloproliferative disease1
advertisement

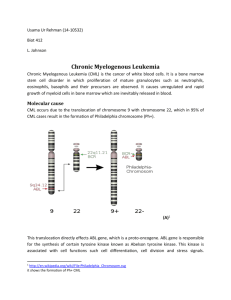
Chronic myeloproliferative disease • سلول مادر خونساز پلوری پتانسیل بدخیمی دارد. • بیماریهای میلوپرولیفراتیو از نظر تظاهرات بالینی ،خونی و مغز استخوان همپوشانی دارند. • اسپلنومگالی عالمت مهمی است. • درنهایت می توانند به لوسمی حاد تبدیل شوند یا به سمت میلو فیبروز روند. • بیماری Old ageهستند. • عالیم عمومی بالینی :خونریزی ،ترومبوز ،عفونت ،رنگ پریدگی ،ضعف • یافته های عمومی آزمایشگاهی :آنمی ویا پلی سیتمی ،لکواریتروبالستوزیس، لکوسیتوزیس ،ترومبوسیتوزیس،پالکتهایbizarr Chronic myeloproliferative disease • • • • • • CML: chronic myeloid leukemia CNL: chronic neutrophilic leukemia PV: Polycythemia vera PMF: primary myelofibrosis ET: Essential Thrombocythemia CEL-NOS:chronic eosinophilic leukemia, not otherwise spesified • Mastocytosis • Myeloproliferative neoplasm, unclassified CML: Chronic myeloid leukemia :PB افزایش ،bimodal peak ،WBCبازوفیلی،ائوزینوفیلی و افزایش مونوسیتها در اکثر بیمارن ،بالست کمتر از %10 آنمی نرموسیتیک به همراه تعدا کمی ،NRBC ترومبوسیتوز در نیمی از بیماران وتروبوسیتوپنی در %15از بیماران :BMهایپر سلوالرگرانولوسیتیک Leukemoid Reaction وCML افتراق Splenomegaly Basophilia & eosinophilia NAP Score Philadelphia chromosome Philadelphia chromosome Philadelphia chromosome is the first cytogentic disorder that cause a neoplasm Philadelphia chromosome is short 22 chromosome derived from reciprocal translocation, t( 9; 22) ( q34; q11) 9 Translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11) 10 Gene & protein structure of BCR-ABL There is three form of BCR-Abl oncogene( P230, P210, P185) There is three breakpoint in BCR gene( M-BCR, m-BCR, µ-BCR) 11 There is some leukemia caused by BCR-ABL P190 BCR- ABL = ALL P210 BCR- ABL = CML P230 BCR- ABL = CML-N Leukemogenic activity P190 > P210 > P230 12 درمان Hydroxy urea INF-a & Allo-SCT Imatinib mesylate: Gleevec: STI-571 Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) Imatinib mesylate is the first tyrosine kinase which used in clinic Imatinib is now recommended as initial therapy in all patients with CML Imatinib is clearly impacting the overall survival of patients with chronic phase CML - Median survival: 3-5 years (prior to imatinib) --> 20-25 years or more? Imatinib mesylate occupies the ATP binding pocket of the Abl kinase domain 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3pyridinyl)-2-]amino]-phenyl]benzamide methane sulphonate 14 Normal Bcr-Abl Signaling The kinase domain activates a substrate protein, eg, PI3 kinase, by phosphorylation This activated substrate initiates a signaling cascade culminating in cell proliferation and survival Substrate Effector Bcr-Abl ADP P P P P ATP P P P ADP = adenosine diphosphate; ATP = adenosine triphosphate; P = phosphate. Savage and Antman. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:683 Scheijen and Griffin. Oncogene. 2002;21:3314. SIGNALING 15 Imatinib Mesylate: Mechanism of Action Imatinib mesylate occupies the ATP binding pocket of the Abl kinase domain This prevents substrate phosphorylation and signaling A lack of signaling inhibits proliferation and survival Savage and Antman. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:683. Bcr-Abl P ATP P P P Imatinib mesylate SIGNALING 16 What is CML? • Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) is defined as, “a malignant cancer of the bone marrow. It causes rapid growth of the blood-forming cells (known as myeloid precursors) in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and body tissues.” • CML represents about 15% of all occurrences of leukemias. • Patients who have CML are said to be in one of the following three phases (in order of occurrence): 1. 2. 3. the chronic phase (between 1 and 10% blasts) the accelerated phase (between 10% - 19% blasts) the blast phase (more than 20% blasts). 17 Accelerated phase of CML Most patients eventually became resistant to therapy and the disease enters a more agressive phase Criteria of accelerated phase Blasts in blood or bone marrow-10-19% Basophilia ≥ 20% Thrombocytopenia <100×109/L Thrombocytaemia >1000×109/L Additional chromosomal aberrations Refractory splenomegaly or refractory leucocytosis 18 Blast phase (blast crisis) of CML Criteria of blast phase Blasts ≥20% extramedullary tumors Phenotype of blasts Myeloblasts Lymphoblasts Acute myelofibrosis 19 Epidemiology 1 to 2 case per 100000 %15 of all at leukemia 7-20% of adult leukemia Male/female = 1.3 – 2.2/1 Median age is 45 to 55 At presentation 50% diagnosed by routine laboratory tests 85% diagnosed during chronic phase 22 ABL/BCR در این جابه جایی ها معموال اگزون شماره 2به بعداز ABLبه صورت قطعه جدا می شود()a2 در BCRمعموال سه ناحیه شکست وجود دارد. M-BCR -1اگزون شماره 13یا )b2 ,b3( 14 μ-BCR -2اگزون شماره 19 m-BCR -3اگزون شماره 1 با انتقال ژن ablاز کروموزوم 9به کروموزوم 22بجای اگزون شماره 1ژن ablاگزون های ناحیه 5ژن bcrدر قسمتهای مختلف شکست قرار می گیرند. BMدر CML • • • • هایپر پالزی شدید گرانولوسیتی M/Eبیشتر از10/1 سلول بالست کمتر از %5 افزایش مگاکاریوسیتها Pseudo gaucher cells چند نکته در مورد فاز تسریع شده وبالستیک تغییرات سیتوژنتیک در 80-70درصد بیماران وارد شده به این فازها:ایزوکروم +8،+19، 17qوکسب کروموزوم فیالدلفیای اضافی مرحله بالستیک یا بالست بیشتر از 20درصد یا کشف توده سلول بالست به صورت غده در فضای خارج از BM مرحله بالستیک 70درصدAML-m1تا m7و 30درصد ALLعمدتا پیش سازهی )tdt+,CD34+, CD19+, CD10+,sIg-(Bوبه ندرت سلولهای )CD3+, cCD3+,CD7+, tdt+(T جهشهای نقطه ای در فاکتورهای سرکوب کننده تومور مانند P53,P16,Rbدر مواردی از acceleratedو blasticدیده شده است در فاز بالستیک )t(7,11 ) t(8,21) t(3,21در مواردی دیده شده است. شناسایی کروموزوم فیالدلفیا • روش کاریوتیپ به روش سنتی و قدیمی • روش FISH • روش RT-PCR Fish: fluoresence insitue hybridization MRD: Minimal Residual Disease • مرفولوژی :در حضور 1012سلول سرطانی تشخیص سرطان می دهد. • کاریوتیپ %5: • %1 :FISH • 1 :RT-PCRدر 100000