Single-Gene Methylation presentation 2014
advertisement

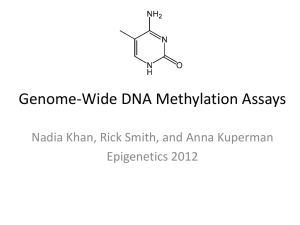
Gene-specific Methylation Analyses Fade Gong & Nam Nguyen Introduction DNA methylation in mammals occurs at CpG sites, where it serves many functions: • Self vs. non-self identification (such as in viral/bacterial infection) • Target for further regulatory events; examples: • Maintenance methyltransferases (functions after replication on hemi-methylated DNA) • Proteins involved in chromatin folding • CpG islands are elements of most promoters, which typically downregulate transcription in the methylated state Principles of DNA Methylation Analyses 1. Single-gene methylation analyses a. b. Sensitivity of restriction enzymes for methylated CpG sites Bisulfite-mediated conversion of DNA 2. Genome-wide methylation analyses a. Anti-methylcytidine Ab b. HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography)/mass spectrometry Overview: Single-gene methylation analyses a) Methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes • Southern-blot hybridization b) Bisulfite conversion of DNA • • • • • • Sequencing Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) Real-time MSP COBRA Pyrosequencing MassARRAY Southern-blot Hybridization Restriction endonucleases: CpG-sensitive • the majority are active on CpG and are inhibited by presence of CMepG (we will focus on such an example: HpaII) (Bird & Tollefsbol) Southern-blot Hybridization (cont’d) Steps for Southern blotting: 1. Run DNA sample on gel a. treated with HpaII, in our example b. run against untreated control (as in lanes 3 and 4, here) 2. Transfer to sticky membrane, such as nitrocellulose 3. Probe with oligonucleotide, conjugated to radioactive label 4. Expose to x-ray film (Bird) Southern-blot Hybridization (cont’d) Advantages 1. Relatively quantitative 2. Low cost Disadvantages 1. Low flexibility in selection of DNA region (i.e. must be isolated via other restriction enzymes that don’t degrade the fragment of interest) 2. Large amount of high-quality DNA required 3. Not all CpG’s presented are subjected to the assay (depends on selectivity of the restriction enzymes) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Review: (McGraw-Hill Companies) Bisulfite-mediated Conversion of DNA Bisulfite Sequencing PCR products are then sequenced and compared to the original sequence. CpG sites that remained CpG represent the presence of a 5-methylcytosine Advantages: 1. Provides detailed information about all CpG sites 2. Requires smaller sample of DNA Disadvantages: 1. Labor-intensive Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis (COBRA) COBRA is based on the appearance or disappearance of a restriction site after bisulfite conversion (Images are from wiki page of combined bisulfite restriction analysis) Characteristics: Advantage: quantification; small amount DNA sample; cheap Disadvantage: CpG site regions are limited (Specific restriction site) Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) • MSP takes advantage of changes in DNA sequence caused by bisulfite treatment • Primers are designed that contain CpG sites and can thus select for expansion of methylated or unmethyled CpG’s (Image was redrawn from the wiki page of Bisulfite sequencing) MSP (cont’d) Advantages: Disadvantages: • Simple technique • Flexibility • Cheap • Optimal number of PCR cycles & annealing temperatures • Appropriate negative control • Not a quantification method Real-time MSP Overview: quantitative PCR (qPCR)/ Real-time PCR • Double-stranded DNA-binding dyes as reporters (SYBR Green) • Fluorescent reporter probe method (MethyLight: a Taqman probe) (Image from Life technology website) Real-time MSP (cont’d) Typical amplification plot for qPCR Comparison between qPCR and PCR (Images are from Qiagen website) Real-time MSP (cont’d) Experiment Procedure: Bisulfite conversion; design methylation- and unmethylation-specific primers Results analysis: Comparing amplification of test samples with standard samples that contain known numbers of DNA molecules. Characteristics: High flexibility; accuracy; quantification; small amount samples; low cost Methylight has higher specificity than SYBR Green based real-time MSP Pyrosequencing Overview: ((PPi = pyrophosphate!)) (Nature methods, 2005) Pyrosequencing for CpG Methylation Characteristics Advantage: • Small amount of DNA • Flexibility • Accuracy • Quantification, etc. Disadvantage: • Suitable primers • Expensive • Specific instruments (Nature methods, 2005) MassARRAY MassARRAY Procedure: Bisulfite conversion PCR In vitro transcription RNase digestion Mass Spectrometry Readout: Mass of products with C or T (16Da) Base Specific RNases RNase A: digest pyrimidine (Uracil) (SEQUENOM, Product Preview Note, 2005) MassARRAY Characteristics: Advantage: • Small amount of DNA • Flexibility • Quantification Disadvantage: • Expensive • Specific instruments References Bird, A. P., Southern, E. M. “Use of Restriction Enzymes to Study Eukaryotic DNA Methylation”. J. Mol. Biol. 118 (1978). 27-37. Critical Factors for Successful Real-Time PCR. Qiagen, Real-Time PCR Brochure, 2010. Ehrich, M. et al., Introduction to DNA Methylation Analysis Using the MassARRAY System. SEQUENOM Preview Note, 2005. Herman, James G. “Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands”. Proc, Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93 (1996). 9821-9826. Pyro Q-CpGTM: quantitative analysis of methylation in multiple CpG sites by Pyrosequencing. Nature Methods 2005, 2. doi:10.1038/nmeth800 TaqMan® Chemistry vs. SYBR® Chemistry for Real-Time PCR. Life Technologies, qPCR Education. Tollefsbol, Trygve. Handbook of Epigenetics: The New Molecular and Medical Genetics. Oxford, UK: Elsevier Inc., 2011. 125-134. Print. Wikipedia: Bisulfite sequencing http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bisulfite_sequencing Wikipedia: Combined bisulfite restriction analysis http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combined_bisulfite_restriction_analysis