Chapter 8 Review
advertisement

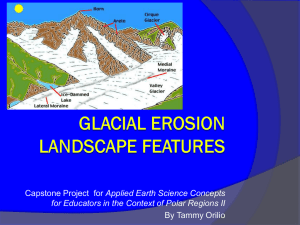
Chapter 8 Review Mass Movements, Wind, and Glaciers Which is NOT a factor that influences mass movements? 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 t 14 0% il ty ei gh w w 1 0% tim e 0% pe 0% so water weight soil type time at er 1. 2. 3. 4. 15 16 17 18 19 20 A once straight fencepost is now tilted slightly. What type of mass movement is this demonstrating? 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% ll 0% fa id e flo cr 1 0% w 0% sl creep flow slide fall ee p 1. 2. 3. 4. 15 16 17 18 19 20 At which location would a catastrophic mass-movement be most common? 1. On a slope of 15° in an area of 120 cm of annual rainfall. 2. On a slope of 35° in an area of 72 cm of annual rainfall. 3. On a slope of 30° in an area of 110 cm of annual rainfall. 4. On a slope of 18° in an area of 88 cm of annual rainfall. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 0% 0% 0% O 15 n a e op l s 1 of 5° O 16 n in a a. .. e op l s 3 of 5° O 17 n in a a. .. e op l s 3 of 0° O 18 n in a a. .. e op l s 19 1 of 8° in a. .. 20 Where is wind erosion least likely to take place? 1. 2. 3. 4. deserts prairies seashores lakeshores 0% d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 e es rts 14 0% ai pr 15 0% s rie se 16 as re ho 0% s la 17 k s re o h es 18 19 20 What is formed when two cirques on opposite sides of a valley meet? 1. 2. 3. 4. hanging valley arete horn U-shaped valley 0% h 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 g an g in y lle a v 0% ar e et 0% ho rn U 15 16 17 0% 18 -s p ha ed 19 lle va y 20 What makes a kame different from an esker? 1. 2. 3. 4. its layering its origins its sediments its shape 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 0% its 13 la g rin e y 14 its 15 0% s in g i or its 16 0% d se 17 im 0% ts en its 18 a sh 19 pe 20 Which of the following actions could prevent mass-movement disasters? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 rie s se di gg i ng a pe at in g uc ed 16 of ab op le s tre e g m ov in re 15 t.. . ... fr om ld in .. bu i tin g tru c ns 14 o. . 0% 0% 0% 0% co 1. constructing buildings and roads in stream drainage paths 2. removing trees from steep slopes 3. educating people about the advantages of building on steep slopes 4. digging a series of trenches to divert water around a slope 17 18 19 20 Which of the following statements is true about wind transport? 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 . c.. .. .. ca n e. ne ra lly , wi nd rt an d po tr a ns in d an d wa te r ha ve . ... an te r, c wa in d , li ke in d 16 Ge 3 W 2 W 1 0% 0% 0% 0% W 1. Wind, like water, can only move materials downhill. 2. Wind and water have the same relative ability to erode materials. 3. Wind transport and erosion primarily occur in areas with little vegetative cover. 4. Generally, wind can carry particles as large as those transported by moving water. 17 18 19 20 Dune formation will take place when 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 av ai ar e s w in d w ith gh ly hi on 16 la b ... sa ar tz qu h ,h ig nd 15 nd n. .. w in ds ,a n. .. ,a sa nd s, 14 sa w in d hi 1 le 0% 0% 0% 0% gh 1. high winds, sand, and no vegetation are present 2. sand, high winds, and vegetation are present 3. only with quartz sand, high winds, and vegetation are present 4. high winds are available 17 18 19 20 Where there is limited sand available and strong prevailing winds, 1. longitudinal dunes are formed 2. parabolic dunes form 3. no dune formation can take place 4. transverse dunes are formed 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 0% 0% 0% 0% lo 14 15 16 ng u it n di d al u n es p ... ar ab ar o lic d un n 17 o es d 18 rm fo u n e fo rm io at n an tr 19 ca ... er sv se du n es 20 e. ar .. Which of the following statements is NOT true about valley glaciers? 1. Flow rates are the same within the various portions of the glacier. 2. The speed of the glacier is affected by the slope of the valley floor. 3. They widen V-shaped stream valleys in U-shaped glacial valleys. 4. Movement is usually less than a few millimeters a day. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 0% 0% 0% 0% F 16 w lo te ra s e ar e th T h 17 e .. sa sp ee d o he ft T h a gl ey 18 .. ci w id en V p ha -s M o ed m ve ... en 19 t is u us ly al ... 20 A ridge consisting of mixed debris deposited by a glacier is a(n) ____. 1. 2. 3. 4. outwash plain kettle moraine esker 0% o 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 w ut h as a pl 14 in 0% t ke 0% tle m 15 16 ne ai r o 17 0% k es 18 er 19 20 Slumps are common after a rainfall because the water ____. 1. reduces friction between soil grains 2. breaks the underlying rock 3. causes snow to melt 4. washes away the vegetation cover 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 0% 0% 0% 0% re 12 du s ce 13 tio rf ic n t.. be ea br 14 . ks e th de un in rly c ... s au es ow sn w 15 16 a to t el m es sh 17 aw ay e th 18 g ve ... 19 20 Which of the following causes deflation? 1. glacial erosion 2. deposition by meltwaters 3. wind deposition 4. wind erosion 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 er os io n tio n po si w in d de w de po si ti gl on in d by ac ia le ro si m el tw ... on 0% 0% 0% 0% 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Glaciers covered 30 percent of the earth during the last ice age that began about 1. 2. 3. 4. 10 000 years ago 1.6 million years ago 2000 years ago 50 million years ago 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 0% 0 00 13 ar ye s 1. ag 6 14 0% o ill m n io ye s ar ag 0% o 20 00 a ye rs o ag 50 15 16 17 0% i ill m on a ye 18 rs o ag 19 20 When two cirques on opposite sides of a valley meet, they form a(n) ____. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 0% 14 0% 0% 15 he an c av al or a in e dr um lin êt e 0% m arête drumlin moraine avalanche ar 1. 2. 3. 4. 16 17 18 19 20 a swiftly moving mixture of sand and water that occurs after an earthquake 1. creep 2. flow 3. slide 4. fall 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 0% fa id e ll 0% sl flo ee p cr 1 0% w 0% 16 17 18 19 20 a slump formed after a heavy rain 1. creep 2. flow 3. slide 4. fall 0% p ee cr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 0% flo 13 w 14 0% 0% e fa id sl 15 16 17 ll 18 19 20 solifluction in Antarctica 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% fa id e ll 0% flo ee p cr 1 0% w 0% sl 1. creep 2. flow 3. slide 4. fall 15 16 17 18 19 20 talus results at the base of a mountain 1. creep 2. flow 3. slide 4. fall 0% 0% p ee r c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 flo 13 w 0% sl 14 15 e id 0% fa 16 17 ll 18 19 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 15 16 0% 17 0% 0% F B 0% D 0% C A B C D E F A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. E hanging valley 18 19 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 15 16 17 0% 18 0% 0% F B 0% D 0% C A B C D E F A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. E waterfall 19 20 arete 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 0% 16 17 0% 18 19 0% F 0% E B 0% D 0% C A B C D E F A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 B 14 0% 15 16 0% 17 18 0% 0% F 0% D 0% C A B C D E F A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. E horn 19 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 15 16 0% 17 18 0% 0% F B 0% D 0% C A B C D E F A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. E U-shaped valley 19 20 cirque 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A B C D E F 0% A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 0% B 14 15 0% 0% C D 16 17 18 0% 0% E F 19 20 The slow, steady, downhill flow of loose, weathered earth materials 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. slump creep water mudflow landslide 0% s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 p m u l 0% p ee r c 0% w 0% er at m 13 14 15 16 flo ud 0% w 17 la sl nd 18 e id 19 20 Swiftly moving mixture of mud and water that causes many deaths 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. slump creep water mudflow landslide 0% u sl 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 p m 0% p ee r c 0% w 0% er at m 14 15 16 17 flo ud 0% w la 18 sl nd e id 19 20 A rapid, downslope slide of earth materials 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. slump creep water mudflow landslide 0% s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 p m lu 13 0% p ee cr 0% w 0% er at m 14 15 16 flo ud 17 0% w la 18 lid s nd 19 e 20 A landslide in which the material rotates and slides along a curved surface 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. slump creep water mudflow landslide 0% u sl 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 p m 0% cr p ee 0% w 0% er at m 14 15 16 f ud 17 0% w lo la 18 sl nd e id 19 20 This acts as a lubricant between grains of soils and sediments 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 nd sl la ud f 16 0% id e 0% lo w 0% m sl cr ee p 0% at er 0% w slump creep water mudflow landslide um p 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 17 18 19 20 A mass of ice that forms in mountainous areas 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 0% 0% 0% m as s ab ra si on m ud flo w 0% lo es s 0% ue dr um lin m ov em en t 0% ci rq 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r 0% tin continental glacier outwash plain valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement loess abrasion mudflow co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 15 16 17 18 19 20 A downslope movement of loose sediment and rock under gravity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% tin lo es s ab ra si on m ud flo w 0% ue dr um lin sl um p 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as m h as pl s ai m n ov em en t 0% ci rq continental glacier outwash plain mass movement cirque drumlin slump loess abrasion mudflow co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 A broad, continent-sized mass of ice 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 0% 0% 0% 0% 12 13 14 15 16 0% 0% 0% ab ra si en on ta lg la ci er 0% lo es s 0% sl um tw p as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r ci rq ue m dr as um s lin m ov em en t tin co n slump outwash plain valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement loess abrasion continental glacier ou 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 17 18 19 20 Windblown deposits composed of silt continental glacier loess valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement slump abrasion mudflow 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 12 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% gl ac ie r ci rq ue m dr as um s lin m ov em en t sl um p ab ra si on m ud flo w lo es s va lle tin 11 0% y en ta lg la ci er 0% co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 A deep depression carved out by an alpine glacier 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 0% 0% 0% ab ra si on m ud flo w lo es s 0% ue 0% ci rq 0% p dr um lin 0% sl um 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r 0% tin continental glacier outwash plain valley glacier slump drumlin cirque loess abrasion mudflow co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Occurs when sand particles rub against the surface of rocks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 tin 11 12 13 14 15 0% 0% 0% p ab ra si on 0% sl um 0% lo es s 0% ue dr um lin m ov em en t 0% m as s 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r 0% ci rq continental glacier outwash plain valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement loess slump abrasion co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 16 17 18 19 20 Where meltwater flows and deposits 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% ab ra si on m ud flo w 0% lo es s 0% sl um tw p as h pl ai n ci rq ue m dr as um s lin m ov em en t 0% ou en ta lg la ci er 0% tin continental glacier slump outwash plain cirque drumlin mass movement loess abrasion mudflow co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Swiftly moving mixture of mud and water sometimes triggered by an earthquake 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 tin 11 12 13 14 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% ue dr um lin m ov em en t m ud flo w ab ra si on sl um p 0% 15 m as s 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r 0% ci rq continental glacier outwash plain valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement mudflow abrasion slump co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 16 17 18 19 20 A landslide in which earth material rotates and slides along a curved surface 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 0% 0% n sl um p 0% m as s ab ra si o 0% lo es s 0% ue dr um lin m ov em en t 0% ci rq 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r 0% tin continental glacier outwash plain valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement loess abrasion slump co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 15 16 17 18 19 20 An elongated landform produced when glaciers move over older moraines 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 0% 0% 0% m as s ab ra si on m ud flo w 0% lo es s 0% ue dr um lin m ov em en t 0% ci rq 0% en ta lg la ou ci tw er as h pl va ai lle n y gl ac ie r 0% tin continental glacier outwash plain valley glacier cirque drumlin mass movement loess abrasion mudflow co n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 15 16 17 18 19 20 After weathering processes take place, mass movements may occur. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 A landslide in which layers of snow slide down a mountainside at speeds of up to 300km/hr is a(n) rockslide. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 Fa 14 15 16 e ls 17 18 19 20 Because a heavy saturation of water greatly increases the weight of soils, the force of friction is more likely to pull the material downhill. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 16 17 18 19 20 The best way to reduce the number of disasters related to mass movements is to relocate people. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 15 16 17 18 19 20 A method of transport by which strong winds cause particles to stay airborne for long distances is called saltation. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 The structure shown in the illustration below is shaped by wind-blown sediments and is called a(n) ventifact. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 16 17 18 19 20 Many parts of Earth’s surface are covered by thick layers of windblown silt that are called loess. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa 15 16 e ls 17 18 19 20