Chapter 5 and 6 The Rock Cycle
advertisement

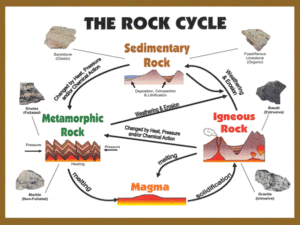
Chapter 5 and 6 The Rock Cycle Rocks • A ______ is a naturally occurring, _______ __________________ of _____________. Fig 4.1 Rock Cycle • A process in which rocks are ____________on Earth. • The cycle goes through a series of _________. – ______________ Rock – ______________ Rock – ______________ Rock The ________ _________ is a group of changes, this change does not necessarily have to be a ____________ change. _________ rock can change into _____________ rock or into _________________________ rock. _________________ rock can change into _____________________ rock or into ______________ rock. ____________________ rock can change into ____________________ or ___________________ rock. Almost all of rock today that we have on earth is made up of all the same stuff as the rocks that _____________ and other __________ life forms walked, crawled, or _____________ over While the stuff that ________ are made of has ___________ the same, the __________ themselves, have _______. Over time rocks are _______________ into other rocks Moving _____________ plates are responsible for _______________ and _____________ many types of rocks When _______________ a rock sample ______________ observe the rock’s color and _________ and determine its mineral _______________. ___________: the ______, _________, and pattern of the rock’s _________. ___________: the apparent color of the rock, on the inside and the outside. ____________ __________: The minerals that make up the different parts of a rock. _____________ Rocks What are They? • Fire Rocks • Formed ____________ by trapped, cooled ___________________ • Formed ____________ ground when ______________ erupt and ________ cools What are igneous rocks? • ____________ rocks are rocks that are formed from the _____________of _____________or ___________________. • _____________ is _________ that flows out onto ____________ surface. ___________ is _____________ material that is located __________ the earth’s surface. Composition of Magma ____________ is often a ____________ mix of molten rock, gases, and mineral crystals. • The ____________ found in ___________ are the same ___________ __________ found in ________ crust: ___________ (O), ___________ (Si), aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), potassium (K), and sodium (Na). _________ of Igneous Rocks • ____________ igneous rocks are ___________grained igneous rocks that __________ ___________ on Earth’s surface. These are the rocks that are formed from ____________. • ________________________ igneous rocks are ___________-grained igneous rocks that cool ________ beneath Earth’s surface. Extrusive Igneous Rocks • _______________________= SMALL CRYSTALS/ FINE GRAINED!!!!! • Basalt Obsidian ______________Rocks • Where Intrusive Rocks Are Found? Under Ground ________Covers _________of Earth’s Crust Intrusive Igneous Rocks • ____________________________________= SLOW COOLING, BIGGER CYSTALS AND COARSE. • Granite Types of Igneous Rocks Scoria-________ Granite-________ Pumice - _________ Obsidian-________ Examples of Igneous Rocks __________ __________ is a very important Igneous rock. The ________ _______is primarily composed of Basalt. Basalt is an _________igneous rock that contains little___________. Basalt is __________colored because it has more ____________and __________in it compared to___________. Hot Spot __________ and spreading ridges have a lot of basalt. Examples are the ___________ _______________ and__________. Granite The most famous igneous rock is_________. Granite primarily makes up most of the __________ _________. You mostly likely know granite from people’s countertops. Granite is usually _______colored than _______because it contains a lot of__________. Granite is an__________ rock. Granite is formed from the __________ of __________and ___________ crusts. Granite usually contains some form of ________ and______________. Pumice _________ is another _________igneous rock. You know _________as the stone that you girls use to smooth your feet. Pumice had a unique property, it _________in water. The _________why it ________is because pumice is formed as a __________ ______ erupts and _________is ___________from _________into the _____ very rapidly and as is _________is _________there are _________that get __________in the rock and as it cools, the rock obtains a lot of __________in it, making it very-very__________. Pumice is primarly made from______________. Obsidian _______ is known as _________ _______, it is very shiny and very smooth. It is also usually black. Obsidian is an _______igneous rock, it cools very__________, allowing for _____ _______ growth. It has A LOT of ______in it, that is why it is so shiny and ______like. ________________ Rocks How They are Made • ___________and _________break down the earth • Bits of earth settle in lakes and rivers • __________are formed and build up • ___________and _________turn the________ to rock Formation of __________ Rocks • Much of Earth’s __________is covered with____________. • ___________are pieces of________ material that have been __________on Earth’s surface by________,________,__________, gravity, or ___________precipitation. • When ____________ become ________ together, they form _________ rocks. • The _________ of sedimentary rocks begins when ___________ and ___________ produce _______________. Formation of Sedimentary Rocks • ___________= _______ moves ________. Layers of sediment build up. ______ from the upper ______ pushes down on ______ and is ________ in to rock. • _________= Large ________, pressure cannot make them stick together. So _______ sediments are _________ together. • __________ rocks often form as layers. Thus, why would older layers be on the _________ of the rock? TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • _______ Rock= Made from _____-_______ rocks. These fragments can either be ________ or _________- together. • The ______ and ________ of sediments determine the name for that rock. • SANDSTONE ____________________ • _________would be considered a _________ sedimentary rock. • Sandstone has _________grains, so the sand sediments are _________together. • These rocks contain a lot of ______and _________. • Sandstone tends to be___________. Shale • ________is another example of a __________sedimentary rock. • However, the __________that make shale are much ________ than__________. The __________that make up shale tends to be_______, _________and________-. Thus shale forms from_________-, not cementation. • Shale can help _________ locate________ reserves. These are called_________ ______________. __________________________ • Conglomerate rocks are_____________________. They are made up of large _____________________ sediments like sand and pebbles. The sediment is so large that pressure alone cannot hold the rock together; it is also cemented together with dissolved minerals. • It forms in many different environments and settings where the energy of _______________________ enough to move large grains. Usually rivers, floods or glaciers do the moving of this type of sediment. TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • ___________ Sedimentary=These rocks are formed from ________ _________________. • The ______________that are left behind after a ___________ __________________. • Those sediments will then form into sedimentary rocks. ____________ is a good example. TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • ____________Sedimentary Rocks=Rocks that form from __________ remains. These are the remains from once living organisms. Can be both _________ and _________ remains. COAL • ________ is a _________ ________ created from the remains of plants that lived and died about _____ to _____ million years ago when parts of the earth were covered with huge _______ forests. Coal is classified as a ______________ energy source because it takes _________ of years to form. What is Coal? • Coal: – A sedimentary rock _______________________ – Mineralized _______________________material deposited over a long period of time (although miniscule geologically) – altered chemical composition – Formed by increased T and P – Partial decay resulting from restricted access to oxygen ________________________? • Peat ≠ coal, but is the _______________stage in coal formation • A dark colored, brown to black,____________ substance formed from partial ____________ of marsh vegetation by moisture and bacteria _______________of Coal formation • • • • • ____________________________ peat lands Upper delta and alluvial plain swamps ________________________________ Bogs Limnic environments Coal Formation • Sediment burial, subsidence of peat bogs – Completely cuts off contact with atmospheric ______________________________________ – Overburden: compaction and subsidence – Increase pressure, temperature The Standard Geologic Time Scale ____________ Period (354 – 290 Ma) Mississippian (354-323 Ma) Pennsylvanian (323-290 Ma) locations of significant deposition of organic matter in what is now North America ____________________Limestone • The accumulation of ________or shell ___________in___________, a sedimentary rock, provides geologists with a record of the ___________of the animals that used to live in the ancient oceans. ____________that contains large shell or coral fragments is called______________. Types of Sedimentary Rocks ____________ ______________ Conglomerate Halite- Chemical Shale Limestone _________ is a tricky sedimentary rock. It is primarily made from ________ _____________. It can be formed from______ living ___________, like shells and such, thus this type of limestone would be classified as an ______ _________ ______. It can be _______ when water_______, or the _________ _________ out of _______ and ______, with other minerals form limestone, thus it would be classified as a _________ _________ rock. Limestone Limestone is the rock that is most ________ rock in the state of__________. The reason why is because the state of Florida was __________for the majority of its life, a lot of ___________built up the state in addition to ___________ ___________out of water. Remember that limestone is made primarily from __________ ___________, thus it is a.___________ This really important to a lot of _____________the features in the state of____________. Florida Keys And The South Florida • As land masses go, all of__________ is a mere child, having___________ from the sea as recently as 20 to 30 million years ago. • For _________its_________ base lay beneath the warm waters of the _______ _________ __________. • Slowly it __________ ___________, building ____________deposits that would eventually rise above the surface. • The Florida ________lie on a thick layer of limestone. The rock is covered by an ancient ________ _____________. Florida Keys • So over many year dead _________animals( especially corals) with _________________ __________skeletons fell to the bottom of the ocean and was built up over time for form fossil _____________. • In addition _____ _______has dropped and exposed this___________, and poof- Florida Keys and the rest of Florida. __________ and________________ • ___________is a rock made up largely of _____________ ___________and is readily dissolved by rainwater. • Water __________through the rock picks up the __________ ____________and the evaporation of the laden drops of water leaves a deposit that, over a great period of time, creates the beautiful stalagmites and stalactites. What Is The Difference? • Stalagmite - Stalactite = Ground and Ceiling • Stalactites drop from the ceiling and Stalagmites rise up from the ground. __________________ _________ It is hypothesized that the ___________of the ________started about ____million years ago when the area was under a warm _______ ______. While the area was covered in the______, _______ _________was readily being ___________by marine _____________. Over the course of many______, the ___________ __________the surface and the ____________started to get eroded by________ _________ in the rainwater and_________, forming the __________ and the famous _________ features. Marianna Caverns On the floor of the cave, are the____________, these are also ____________ ____________structures formed from calcium carbonate being ______________out from the_________. _________ _________are small, thin,_______, pipe deposits of ______that form around the water (containing dissolved___________ _________) dripping from the_________, as the water_________ from the ceiling, it will leave the _______ _________behind. Over time, the hollow _______fills up with __________ ______and becomes more stable and a__________ is created. When a __________and a ___________meet each other in the middle, a ______________is created ______________ • ___________ are common where the rock below the land surface is_____________. • As the rock____________, spaces and ___________develop underground. • Sinkholes are dramatic because the land usually stays intact for a while until the underground spaces just get too big. • If there is not enough support for the land above the spaces then a sudden ____________of the land surface can occur. Sinkholes • The most ___________from sinkholes tends to occur in__________, Texas, Alabama, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, __________and Pennsylvania. • ___________HAS MORE SINKHOLES than any other state in the nation. • Sinkholes provide a primary pathway for rainwater to replenish subsurface______________; they are an important part of the __________ system that supplies _______of Florida's drinking water. ______ ___________ State Park • Falling Waters State Park is right here in ____________Florida. First, this state park houses the_________ ____________ in the state. • The _______ from the fall goes directly into an_____________ _____________. • The waterfall is in a_______________. • You can walk to the ________and into the sinkhole, you can see that there is____ water that piles up at the bottom of the waterfall, it all goes______________. Falling Waters State Park • There is a _________path that takes you around________ sinkholes, some are rather deep and lead to the ___________cave _____________ down below. ___________Rocks What are They? • Rocks that have____________ • They were once _________or____________ • ____________and _________changed the rocks Causes of Metamorphism • Metamorphic rock forms when high _____________and ___________combine to alter the______________, mineralogy, or chemical composition of a rock without ______________it. • The high temperatures ultimately are derived from Earth’s _________ _______________. • The high _____________can be generated in two ways: – From___________ pressure caused by the ____________of _______________rock – From the _____________ forces generated as rocks are deformed during ___________building Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic Textures • Metamorphic rocks are classified into___________ textural groups: __________and________________. – ____________metamorphic rocks are characterized by __________ ___________and __________of minerals. – High pressure during metamorphism causes minerals with______ or ___________crystals to form with their long axes ___________ to the pressure. Foliated Metamorphic Rocks • _____________-Foliated Metamorphic Rock Metamorphic Textures • __________= Rocks that have ___________________. These rocks do not have a sheet like structure. • No matter how much_________ is applied, the grains will not__________. Under Pressure • Metamorphism Summary Of Metamorphic Rocks • Below is a summary of the major characteristics of metamorphic rocks. • Classified by ________and_____________ • Rarely has fossils • May react with acid • May have alternate bands of light and dark minerals • May be composed of only one mineral, ex. ________&____________- Types of Metamorphic Rocks Schist Gneiss Metamorphic Rock Pictures Granite, Gneiss, Shale, Slate, Sandstone, and Quartzite are good examples of metamorphic rocks.