sedimentary rocks, metamorphic rocks, and age determination
advertisement

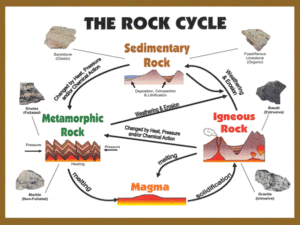
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS, METAMORPHIC ROCKS, AND AGE DETERMINATION SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Sedimentary rock family • Definition and Explanation • comprised of sediments • accumulated from physical and or chemical processes mostly in large bodies of water • consolidated through lithification SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Factors and concepts related to rock formation • weathering--”breaking down” of rock materials at or near surface of Earth • chemical--decomposition of materials and formation of new substances through removal of or additions to the weathered material • physical or mechanical--disintegration of materials with no new substances forming SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Erosion • removal or transportation of material by stream water, glacial ice, wind, and gravity • eroded materials may eventually accumulate in large amounts • Lithification • compaction and cementation of sediments to become rocks SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Stratification • accumulations in layers (strata or beds) and is the most common occurrence of this family of rock • Law of superposition • in a series of strata, each layer is older than the one above and younger than the one below--this reflects a relative age relationship between layers Stratification in Sedimentary Rocks SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Sedimentary rock types • three types based on the way they form; clastic (detrital), chemical inorganic, and organic • clastic • sediments accumulated primarily by physical processes as deposits from stream water, glacial ice, wind, etc. then lithified to rock SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Wentworth’s sediment size classification is used to name the specific clastic rock in the detrital class Wentworth’s Scale of Sedimentary Particles Different colors of beach sand in the world CLASTIC ROCKS Detrital (Clastic) Sedimentary Rocks Larger grained Conglomerate Breccia Detrital (clastic) Sedimentary Sandstones Graywacke Arkose Quartz Sandstone Detrital (clastic) Sedimentary Rocks Smaller Grained Claystone Siltstone Shale SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • biological (organic) rocks • accumulation of animal shells or plant material then lithified--particle size is not important in naming biological rocks SED-MET ROCKS-AGE BIOLOGICAL OR ORGANIC ROCKS SED-MET ROCKS-AGE White Cliffs of Dover COAL SERIES buried plants Peat bituminous lignite anthracite methane coal gas SED-MET ROCKS-AGE Biological (organic) formed chert SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • chemical (inorganic) rocks • formed from chemical reactions in the oceans or large bodies of water CHEMICAL OR INORGANIC ROCKS Lakes formed from Glaciation Lake Bonneville Evaporite deposits in Death Valley, California SED-MET ROCKS-AGE Chemically (inorganic) formed chert---nodules of chert caused by replacement of silica for bedrock—is present in the local Burlington limestone bedrock in this area SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Some special features in sedimentary rocks • cross bedding • relatively thin layers inclined at an angle to the main bedding • formed by currents in water or wind Cross bedding SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • graded bedding • a sedimentary layer characterized by a decrease in sediment size from bottom to top • ripple marks • small waves of sand that develop on surface of sedimentary layer by the action of moving water or wind Ripple marks SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Significance of sedimentary rocks • only family of rock containing an abundant record of life forms and the changes in life forms throughout geologic time • only family of rock in which natural gas, petroleum and coal are formed and found • used as building materials, tombstones and some limestones are used as a source of lime Groundwater Coal Petroleum and Natural Gas Cement from Limestone Uranium Salt SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Metamorphic rock family • Definition and explanation • formed primarily through action of temperature and/or pressure on preexisting rocks • little or no melting during process • time is also an important factor • rocks will loose evidence of fossils or other features present before the change SED-MET ROCKS- AGE • Types of metamorphism • contact or thermal • usually forms with intrusions of smaller rock bodies as stocks in country rocks • temperature associated with the intrusive body is the prime metamorphic agent—lower temperatures would form lower grade of metamorphic rocks SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • regional metamorphism • usually forms with intrusions of larger bodies like batholiths or laccoliths • temperature and pressure are equally important in the metamorphic process and includes a much larger area of metamorphism—higher temperatures would form a higher grade of metamorphic rock SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Kinds of metamorphic rocks • all but one rock is comprised of silicate minerals • foliated • minerals are aligned in a pattern Foliated metamorphic rocks Foliated or Lineated Metamorphic Rocks Gneiss Slate Schist Gneiss Phyllite Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks Non foliated Metamorphic Rocks Quartzite (from arkose) Marble SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Important uses • building materials and tombstones • marble can be used in art as a sculpturing material SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Age determination (geologic age) • important concepts used • relative age concepts • crosscutting and intrusive nature of igneous rocks • law of superposition pertaining to sedimentary rocks • absolute age dating • determination of amounts of radioactive parent and stable daughter Relative Age dating SED-MET ROCKS-AGE • Age determination method • relative and absolute age determination methods are used together to establish the absolute age of rocks which cannot themselves be dated • igneous rocks are the best rock family to use in absolute age determinations • Index fossils are used to facilitate the determination of the age of sedimentary rocks Determine the absolute age of sedimentary bed , B given: 1. igneous intrusive, V dated at 2.15 million years old 2. lava flow, P dated at 2.25 million years old (both V and P were dated using the absolute age determination method we discussed in the mineral section) Correlation of Index Fossils From 2 Different Areas