Igneous Rocks - Mrs. Plante Science
advertisement

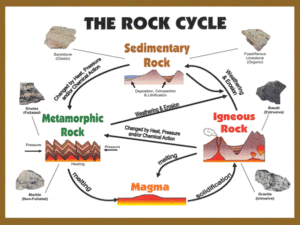
Igneous Rocks What are Igneous Rocks? • Igneous rocks: form when molten (liquid) rock material cools into a solid. How do Igneous Rocks Form? • All igneous rocks form during solidification. – Crystallization: when magma/lava cools and forms a solid composed of intergrown mineral crystals. Animation Compare the crystal sizes of these igneous rocks. basalt Small crystals granite pegmatite Large crystals Crystal Sizes • Crystal size depends on the length of time it takes the rock to cool. – Longer cooling = larger crystals Crystal size Time to Cool Large crystals indicate a slow cooling (days to 1000’s of years). Small crystals indicate a fast cooling (seconds to hours). What is the difference between extrusive and intrusive igneous rocks? • Extrusive – lava cools ON or ABOVE Earth’s surface – rocks have small or no crystals. • Intrusive – magma cools BELOW Earth’s surface – Rocks have large crystals. Devils Tower National Monument, Wyoming. An igneous intrusive body exposed by erosion. Palisades sill: A sill is a horizontal igneous intrusion. The Palisades sill is located on the west side of the Hudson river in NJ and lower NYS. Exposed by erosion, the Palisades are vertical cliffs seen in the photos (right) Extrusive (Volcanic) Textures Glassy (no crystals) (Obsidian) Fine crystals (Basalt) Intrusive (Plutonic) Textures Coarse crystals (Granite) Very Coarse Crystals (Pegmatite) Identification of Igneous Rocks 1. Texture: depends on: – Size of mineral crystals – Presence of glass – Gas bubbles (vesicles) Vesicular textures are full of bubbles Pumice Scoria Identification of Igneous Rocks 2. Color Light or Dark Identification of Igneous Rocks 3. Density Low Granite is a lower density igneous rock or High Peridotite is a higher density igneous rock Identification of Igneous Rocks 4. Composition • Mafic : contains Fe (iron) and Mg (magnesium) • Felsic : contains Al (Aluminum) Key Identifying Features of Igneous Rocks 1. Glassy Texture: No crystals 2. Intergrown mineral crystals: Interlocking (like puzzle pieces) 3. Vesicular: gas bubbles Intergrown Crystals Intergrown Crystals Intergrown Crystals NOT Intergrown Crystals Practice Name a light-colored, fine-grained rock with no bubbles. Name a coarse-grained, dense rock. Name a very light-colored, glassy, extrusive rock with bubbles. Finding The Minerals Identify the rock. Unless you have other information, work in the middle of the rock’s box. This is the amount of Potassium Feldspar in the rock. This is the amount of Quartz in the rock. This is the amount of Plagioclase Feldspar in the rock. Use tick marks on a scrap paper to measure the percentage. Potassium Feldspar 25% Quartz 40%