Rock Cycle Identify the agents of change*
advertisement
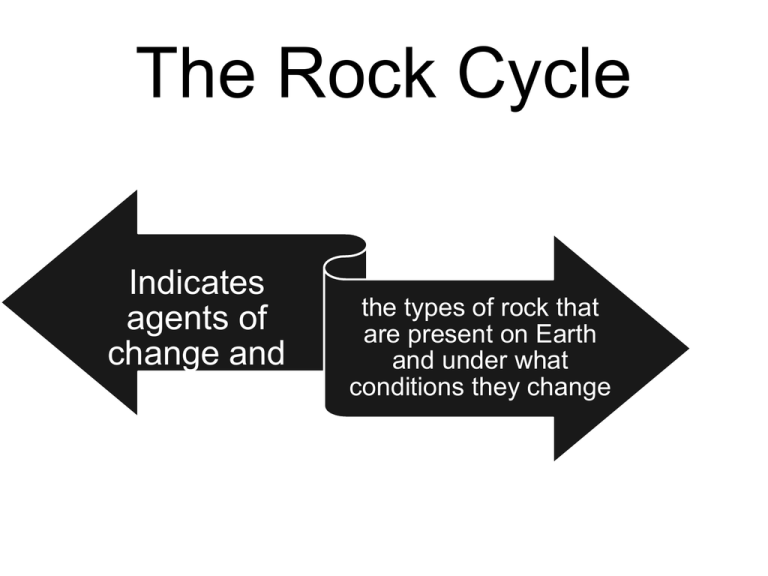
The Rock Cycle Indicates agents of change and the types of rock that are present on Earth and under what conditions they change Rock Cycle Identify the agents of change… Sedimentary Metamorphic Igneous Rock cycle processes Cooing and hardening Solidiification lithification Weathering and erosion Sedimentation lithification Heat and pressure from internal and tectonic forces Litho- prefix meaning stone or rock Lithification Igneous Cooling Solidification rapid Cooling Solidification slow Sedimentation & Deposition Cementation of sediments Igneous rocks • From fire… • Intrusive ; formed inside Earth • Extrusive; formed outside Earth (surface) • Mafic or felsic • Magnesium and aluminum rich or quartz rich… Igneous Rock Mafic & Extrusive Igneous Rock, Basalt Columns Sedimentary rock • Formed from weathered and eroded rock particles • Could not be the original rocks • WHY or why not? Layers in Sedimentary Rock How does it form? Grand Canyon • If Grand Canyon consists of layers of millions of years of sedimentary rock, how did it form? • When did the layers form? • When did the weathering and erosion take place? • Were the rocks or the canyon, original rocks on Earth? Why or why not? Is this the first rock on Earth? Sandstone Desert Geysers eject many minerals, heat and water Metamorphic Rock • Formed from heat and pressure • Formed from tectonic pressures • Re-crystallization • Banding • Distortion Word meaning? •Meta means change, transformation •Morphic means referring to the form or structure of an object How does metamorphic rock form? • Igneous rock that has weathered and eroded over time • Note the globs of volcanic rock that solidified • Dark colors due to elements such as magnesium, aluminum, (iron maybe) Volcanic rock weathered by water and wind. Iron deposits • Sedimentary rock • Sandstone; made from particles of other rock, finely weathered and compacted; • Glued with calcite mineral • On sea floor • Seas contain abundance of calcite • Shelled organisms are made of calcite Extrusive Igneous Rock Basalt Columns • Basalt hexagonal shapes • Devil’s Tower; national monument in Wyoming Basalt is extrusive mafic igneous rock Contains abudance of magnesium sandstone granite • Granite • The most common intrusive felsic igneous rock on Earth • Most common rock of continental crust • Mostly quartz, horneblende and feldspar • Chalk is a type of limestone • Formed on seafloor • Limestone metamorphosed becomes marble Where would we find marble? Why? Weathered by wind and water Rock type? Why? The Giant’s Causeway Ireland Stone Mountain, GA A natural pluton intrusive igneous rock Ancient volcanic necks • Beautiful sandstone landscapes • Iron oxidized is iron oxide • • Fe2 O3(rust) • Hence the coloring • • • • • • The Palisades in Northern New Jersey Overlooking the Hudson River Diabase; extrusive igneous (mafic) Similar to basalt This region was once overrun by volcanic fields Prior to the volcanic action, rock was subjected to tectonic, subduction forces • What type of rock lies below the Palisades? The Palisades in NJ overlooking the Hudson River Metamorphic folds- bands • • • • • Classic metamorphic rock Re-crystallization of minerals due to heat Pressure distorts Bands of minerals evident Pressure creates friction that aids in heat production • Deep in Earth Rock Type? Clastic rock Rock type? Name for ‘glue’? Giant’s Causeway, Ireland Basaltic Hexagonal Columns Why aren’t fossils found in metamorphic or igneous rock? Striations of layered sandstone • • • • • Sedimentation forms layers What forms the shape of this rock? Where is the oldest rock in this rock? The youngest rock? WHY? Volcanic – Igneous Large or small crystals? • Desert Geysers in the black rock canyon of Nevada • Note the colors of nature • Orangy red due to oxidized iron • Yellow- sulfur • Green is mold/algae • Water and Hydrogen sulfide and Carbon dioxide – gases released Minerals from Earth interior may combine to form rock Green Italian Marble - Metamorphic Marble shows classic re-crystallization • Distortion • Hard, dense rock due to pressurization • Used for government buildings, monuments,businesses, schools • Flooring- lasts forever • Pink, white, green- high polish possible • Beautiful, functional-valued quarries There’s no place like home.