Document
advertisement

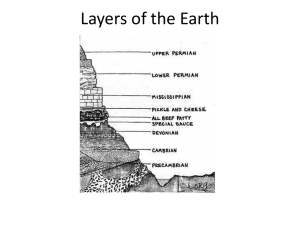
Paleontology The study of past life Paleontologist – scientist who studies fossils and plants from past life and other recontructed past ecosystems, study traces left behind by animals and piece together the conditions under which fossils were formed. Uniformitarianism – the idea that the same geologic processes shaping the Earth today have been at work throughout Earth’s history Relative vs. Absolute Dating I. Relative dating – determining whether an object or event is older or younger than other objects or events A. Superposition 1. Older rocks are under newer rock 2. Can only determine relative time B. Geologic column is an ideal sequence of rock layers that contains all the known fossils and rock formations on Earth arranged from oldest to youngest. II. Absolute Dating – the process of establishing the age of an object by determining the number of years it has existed. A. Radioactive decay – the process in which a radioactive isotope tends to break down into a stable isotope of the same element. 1. Radioactive atom has an unstable nucleus that decays a. Radiation is given off b. Decay is at a constant rate c. Decay material is formed d. Half-life is the amount of time for ½ of the radioactive element to decay 2. Radioactive carbon dating a. C-14 is present in all living things b. Used to date remains ***** Earth has been dated at 4.6 billion years Fossils III. Fossils – the remains or physical evidence of an organism preserved by geological processes. A. Trace Fossil – a fossilized mark that is formed in soft sediment by the movement of an animal. B. Index Fossil – a fossil that is found in the rock layers of only one geologic age and that is used to establish the age of the rock Measuring Geologic Time IV. Geologic Time A. Eras (largest divisions) 1. Precambrian – earliest, 4 billion years 2. Paleozoic – 345 million years 3. Mesozoic – 160 million years 4. Cenozoic – current, so far 65 million years B. Eras are divided into periods (except for Precambrian) C. Cenozoic periods are divided into epochs V. Geologic Eras A. Precambrian 1. Earth forms including seas & mountains 2. Few fossils of jellyfish, worms, bacteria, algae, & fungi B. Paleozoic – 6 periods 1. Invertebrates most common a. Trilobites b. Brachiopods 2. Vertebrates – fish and amphibians 3. Plants – ferns and trees in swampy areas Trilobite Trilobite Trilobite Brachiopods Brachiopods Brachiopods Eryops Eryops Eryops Eryops C. Mesozoic – 3 periods 1. Pangaea began to break apart 2. Cycads & conifers evolved 3. “Age of the Reptiles” 4. Dinosaurs became extinct Tyrannosaurus rex Cycads D. Cenozoic – 2 periods 1. “Age of Mammals” 2. At least 4 ice ages