Data Encryption with SQL Server
advertisement

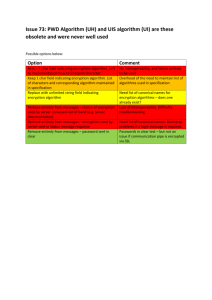
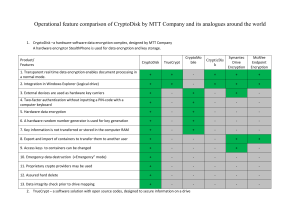
Protect Your Data's Privacy! Data Encryption with SQL Server Joe Kuemerle @jkuemerle www.kuemerle.com Background of Joe Kuemerle • Lead Developer at BookingBuilder Technologies • Over 15 years of development experience with a broad range of technologies • Focused on application and data security, coding best practices and regulatory compliance • Presenter at community, regional and national events. What Is Encryption What Is Encryption Encryption is the process of mathematically altering data in a consistent, reversible fashion. It should be used to store sensitive information that will need to be retrieved later. Encryption relies on a secret that is the only viable way to reverse the mathematical process • Encryption can be Symmetric where a single value (the encryption key) is used to both encrypt and decrypt the data • Or Encryption can be Asymmetric where there are two values in that data encrypted with Value 1 can only be decrypted with Value 2 and vice versa. This is also know as Public Key Encryption • What Is Encryption “Encryption is the process of substituting a small secret in place of a large secret” Symmetric Encryption Asymmetric Encryption Certificates • Certificates are used to store asymmetric keys and consist of a private key and public key. • SQL Server provides built in management of certificates • Do not use use certificates to encrypt data, it is slow and can be vulnerable when storing lengthy values. Use a symmetric key to encrypt the data and a certificate to encrypt the symmetric key. Hashes • Hashes are not an encryption method. A hash takes an input value and transforms it to a unique value that is infeasible to convert back to the original value. • Hashes are not for storing data that needs to be reread but are for proving knowledge of a secret without the actual secret being revealed. • Hashes are ideal for verifying passwords. The actual password is unimportant we just need to have the user prove that they know the password. Hashes • Best practices call for the use of SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 or higher functions • Bcrypt is a “Future-Adaptable” open source hashing algorithm • Do not use MD5 or SHA1as there are proven methods for undermining the hash results. • SQL Server 2005/2008 only support MD5 & SHA1, Denali supports SHA256 SHA384 and SHA512 Demos • Yay! No more bullet points. All source code is available on CodePlex: http://sqlcrypto.codeplex.com/ References Laurentiu Christofor: http://blogs.msdn.com/lcris/ Raul Garcia: http://blogs.msdn.com/raulga Bruce Schneier: http://www.schneier.com/ http://blogs.msdn.com/b/sqlsecurity/archive/2010/06/14 /database-encryption-key-dek-management.aspx • Cryptography: • • • • o http://www.garykessler.net/library/crypto.html o http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac/ • BCrypt: o http://chargen.matasano.com/chargen/2007/9/7/enough-with-the-rainbowtables-what-you-need-to-know-about-s.html o http://codahale.com/how-to-safely-store-a-password/ o http://derekslager.com/blog/posts/2007/10/bcrypt-dotnet-strong-passwordhashing-for-dotnet-and-mono.ashx • Demo source: http://sqlcrypto.codeplex.com @jkuemerle / joe at kuemerle.com http://www.speakerrate.com/jkuemerle Photo Credits • http://www.flickr.com/photos/wwworks/4612188594 • http://www.flickr.com/photos/joyosity/3358614462 • http://www.flickr.com/photos/jmrosenfeld/31582581 5 • http://www.flickr.com/photos/23258385@N04/22258 09637 • http://www.flickr.com/photos/chelseamcnamara/4 058966236 • http://xkcd.com/538/