Safety Data Sheet Trainging
advertisement

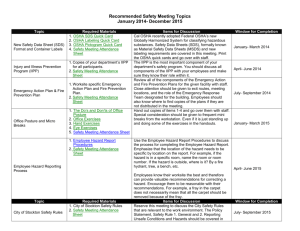
Safety Data Sheet and label Training Prepared by Gary Johnson October 2013 Background information • Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be provided by manufacturer/provider – required by the Hazard Communication Standard. • SDS and labels must conform to the Global harmonizing System (GHS) Background information • Safety data sheets must be provided by manufacturer/provider/importer – – These replace the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) • Labels and SDS must conform to the GHS standard – Both required by the Hazard Communication Standard. Format • SDS contains generally the same information as the MSDS. – SDS will be in a consistent 16 - section format Format • Section 1 – Identifies the chemical and other common names or synonyms – Contains the name , address, and phone number of the manufacturer/importer. – Describes briefly the recommended use of the chemical, and any restrictions on use. Format • Section 2 – Identifies the hazard classification of the chemical – Uses signal words (i.e. warning). – Gives hazard statements – Uses pictograms to identify the hazard – Precautionary statements – Description of hazards not otherwise classified – For a mixture gives the percent of each component. Format • Section 3 – substance( one ingredient ) – Chemical name – Synonyms – CAS number – Impurities and stabilizing additives which contribute to the classification of the chemical Format • Section 3 – Mixtures – Same information as required for Substances – Chemical name and concentration of all ingredients classified as health hazard and are • Present above their cut-off/ concentration limits • Present a health risk below the cut-off /concentration limits – A range may be used if the exact quantities are a trade secret – There is batch to batch variation – SDS is used for a group of substantially similar mixtures Format • Section 4 – first aid measures – First aid instructions by relevant routes of exposure (inhalation, skin and eye contact, and ingestion) – Description of symptoms – Recommendation of immediate medical care and special treatment , when necessary. Format • Section 5 - Fire-Fighting Measures – Recommend suitable extinguishing equipment, and information about what equipment that is not appropriate for a particular situation. – Advice on specific hazards that develop from the chemical during a fire – combustion products. – Recommendation on special protective equipment for fire fighters. Format • Section 6 – Accidental release measures – Advises appropriate response to spills – Use of precautions ( remove ignition source, provide sufficient ventilation) – Emergency procedures ( evacuation, consult experts, and PPE) – Methods and materials for containment – Cleanup procedures ( neutralize, decontaminate, adsorbent materials, equipment) Format • Section 7 – handling and storage – Precautions for safe handling including recommendations for handling incompatible chemicals, minimize environmental release, and general hygiene practices advise. – Recommendation on the conditions for safe storage including incompatibles, and special storage requirements (e.g. ventilation) Format • Section 8 - Exposure controls, Personal protective equipment – OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits(PELs), Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) and any other exposure limit used or recommended by the manufacturer. – Appropriate engineering controls – Recommendations for PPE (i.e. appropriate types of eye/face skin or respiratory protection needed based on hazards and potential exposure. – Specific special requirement for PPE (i.e. type of glove material, and breakthrough time of glove material) Format • Section 9 – Physical and chemical properties • • • • • • • • Appearance Odor, and odor threshold pH Melting point Boiling point and range Flash point Evaporation rate Flammability (solid, gas) • Upper/lower flammability or explosive limits • Vapor presure • Vapor density • Relative density • Solubilities • Partition coefficient • Auto ignition temperature • Decomposition temperature • Viscosity Format •Section 10 – Chemical stability and reactivity • Reactivity – Specific test data for the chemical(s) – Chemical stability • Indication of whether the chemical is stable or unstable under normal ambient temperature and conditions while in storage • Description of any stabilizers that may be needed to maintain chemical stabililty • Indication of any safety issues that may arise should the product change physical appearance. • Other – Indicate possible hazardous reactions, including polymerization or reaction that may produce heat, pressure, or other hazardous condition. – List of conditions to avoid – List of classes of incompabile materials – List of know or anticipated hazardous decomposition products that could be produced because of use, storage or heating Format • Section 11 - Toxicological information – Information on routes of exposure – Description of delayed, immediate, or chronic effect from short and long term exposure – Numerical measures of toxicity ( i.e. acute toxicity estimates LD50) – Description of symptoms. Form lowest to the most severe exposure – National Toxicology Program (NTP) listing as carcinogen, or International Agency for Research on Cancer(IARC) monographs or potential carcinogen by OSHA Format • Section 12, 13, 14, 15 – non mandatory – Ecological information – not regulated by OSHA – but by DEQ – Disposal considerations – not regulated by OSHA – but by DEQ – Transport information – not regulated by OSHA – but by DOT – Regulatory information • National or regional regulatory information Format • Section 16 – When the SDS was prepared or the last known revision was made. – Any other useful information provided by manufacturer/supplier. Labels • Must contain hazard pictograms / hazard statements • Must contain signal words • As of June 1, 2015 all containers will be required to have GHS compliant labels – All secondary containers must have these labels also! Pictograms • Flame Over Circle • Oxidizer • Flame • flammable Pictograms • Exploding Bomb • Explosives • Skull and Crossbones • Poisonous Pictograms • Corrosion • Gas Cylinder Pictograms • Health Hazard • Environment Pictograms • Exclamation Mark Pictograms Categories • Categories range from 1-5 for health hazards – The larger the number the lower the hazard. • Full information at • https://www.osha.gov/dsg/hazcom/ghs.html#4.6 • Categories range from 1-6 for explosive hazard • Different span dependent on hazard see site above for specifics. References • OSHA, 29 CFR 1910.1200(g) and Appendix D. United Nations Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), third revised edition, United Nations, 2009. These references and other information related to the revised Hazard Communication Standard can be found on OSHA's Hazard Communication Safety and Health Topics page, located at: http://www.osha.gov/dsg/hazcom/index.html. • https://www.osha.gov/Publications/HazComm_QuickCard_ SafetyData.html • https://www.osha.gov/Publications/OSHA3636.pdf • https://www.osha.gov/dsg/hazcom/ghs.html • Insert a link to the quiz choice url here