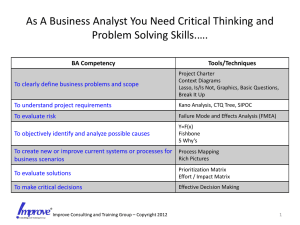
FMEA and SPC - CDTA Employee Portal
advertisement
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) XONITEK Corporation 1 FMEA… A way to conduct a “reliability analysis” of a product or service A systematic look for: Function Failure causes Failure modes Failure consequences XONITEK Corporation 2 Types of FMEA activities… DFMEA – Design analysis of: Components Subsystems Main systems PFMEA – Process analysis of: Equipment Scheduling Workstations Gages Procurement Employee training Tests XONITEK Corporation 3 FMEA Core Criteria… Relies on valid data on either the output or process for assessments to be valid Documented procedures that can be validated as part of the process help identify the source of variability… Random approaches to a process by employees can inject variability and create the different outcomes. Most effective when operating within the framework of a sound quality system XONITEK Corporation 4 FMEA Benefits… Improved Service Quality and Robustness… Reduced Customer Service Costs… Reduced Delivery Problems… Improved Service Implementation… Improved Safety… XONITEK Corporation 5 Creating the FMEA Team… Keep the team small so contribution and focus are most important in the ultimate success of the project. Both the “process experts” and those “unfamiliar” with the process will drive insight. Don’t forget to “walk the walk” when possible to get first hand knowledge for each member of the team. XONITEK Corporation 6 FMEA Reference Form… Sample FMEA form… XONITEK Corporation 7 FMEA Header Data… FMEA Title – Name of the System, Subsystem, Component or Process… FMEA Type – Circle or otherwise highlight if this is a Design or Process project. Project Leader – Person responsible for the FMEA overall… Prepared By – Individual maintaining updates on the project. Project Description – Concise and easy to understand description of the function… Include any additional technical parameters to help define the failure modes… XONITEK Corporation 8 FMEA Header Data… Dates: Original Date – the date the FMEA was created. Revised Date – this is the date the input from various persons was added to the file. Key Date – the targeted completion date of the project. Core Team – Members of the team responsible for the development of the FMEA and various aspects of its completion. XONITEK Corporation 9 Current State Section… Item or Function – Identifies the various parts, processes or subsystems that may fail. Use Brainstorming to begin to identify these elements of the FMEA. Can be a list of separate failure modes for the same functions May reference the upper or lower assembly impacts… Potential Effects Mode – Describes the impact of the failure with regards to the customer (internal or external)… Fishbone Diagrams may be useful to “get to” the root causes. Potential Failure Mode – Describes how the process or design may fail to perform with regard to design or process parameters… Man, materials, design, process, environment. “If – Then” consequential statements. Classification – Optional information, used when Govt. Regs., Safety Considerations or Engr. Specs exist for the product or process… Use a key for this field and add to the FMEA form to clarify symbols. XONITEK Corporation 10 Severity Rating Scale.. Severity Rating – Scale of 1 to 10 created by the team… with 10 as the most severe. Rating Description Definition of Failure Result: 10 Hazardous Failure could cause bodily injury to the customer or an employee. 9 High Major Failure defined as noncompliance with federal, state or local regulations. 8 Major The unit becomes inoperable when failure occurs. 7 Low Major Failure results in a high degree of customer dissatisfaction. 6 High Moderate The failure exists in a subsystem or partial malfunction of the product. 5 Moderate Failure is noticeable by the customer and may result in warranty or customer complaint. 4 Low Moderate Customer can overcome failure loss with no impact to the product or process. 3 High Minor Failure results in minor performance loss in the customers process. Customer can over come loss by process change. 2 Minor Failure may not be readily apparent to the customer, but would have minor affects on the customer’s process or product. 1 Low Minor No impact to the customer or loss of process/product capability. XONITEK Corporation 11 Current State Section… Potential Causes of Failure – Descriptive and comprehensive list of all “root” causes of failure… Reference “Fishbone” diagram as one of the tools to find this cause… Each “potential failure mode” may have more than one cause of failure. Occurrence Rating – An estimate of the frequency of the failure… derived from a team created table… Occurrence ranking shown on next slide… XONITEK Corporation 12 Occurrence Rating Scale… Rating Description Failure Rate Metrics 10 Imminent Failure Persistent failures, >= 100,000 ppm. 9 High Major >= 50,000 ppm < 100,000 ppm 8 Major >= 20,000 ppm < 50,000 ppm 7 Low Major Occurrence about 1/month or >= 10,000 ppm < 20,000 ppm 6 High Moderate Occasional Failure of about 1 every 3 months or >= 5,000ppm < 10,000ppm 5 Moderate Occurrence about every 6 to 12 months or >= 2,000 ppm < 5,000 ppm 4 Low Moderate Process capable 1.33 Cpk 3 High Minor Few failures or approaching1.67 Cpk 2 Minor Random failure or 10 ppm or approaching 2.0 Cpk 1 Low Minor Failure very unlikely, Cpk >2.0 XONITEK Corporation 13 Current State Section… Current Controls Prevention – Identify the methods and testing parameters that exist to find this failure... Current Controls Detection – Defines the manner that the defect is identified… Preference is detection by use of SPC or other testing methods. Discovery by failure is NOT preferred… Detection Rating – User defined table with assigned probabilities and associated rankings… Ranking table guide in next slide… XONITEK Corporation 14 Detection Ranking… Rating Potential of Detection Definition 10 No Detection Detection not possible with current systems. 9 Very Remote Problem may occur without notice using current sampling plan. 8 Remote Defect can be accepted in the normal inspection criteria sampling plan of “no defects allowed” 7 Low Product is 100% inspected for defect during the process. 6 Moderately Low Product is 100% inspected using “go – no go” gages. Process has been Poka Yoked for error elimination. 5 Moderate SPC process in place during the process and product is also inspected off line… 4 Low Probable SPC used and immediate response to out of tolerance conditions. 3 Probable Process capability has been demonstrated at 1.33 Cpk and SPC program in place. 2 High Probability Product 100% inspected by an automation process. 1 Absolute Detection Methodologies created to make the failure obvious and 100% automated inspection utilized. XONITEK Corporation 15 Current State Section… Risk Priority Number (RPN) – A value to rank the concerns calculated from the multiplication of the other rankings … RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection (the product of these three values) Use this value to prioritize the actions and resources of the organization. Do not overstep your resource capabilities… set a threshold of items for action and focus on those items first. Items with lower numbers but still have high severity must be addressed… Recommended Actions – Actions taken to lower the RPN… includes Cause and Effect diagrams, control charts or other actions necessary to reduce the risk tied to the RPN… XONITEK Corporation 16 Actions to RPN… Develop a strategy of what items to address in what order… Look for “synergy” of activities, where multiple problems may overlap. If you can’t eliminate the issue find ways to make it easily detectable when it occurs. Reduction of “severity” or “occurrence” is preferred over making the failure more detectable. Document all process or design changes and their impacts as part of the report out methodology. Recalculate the RPN as improvements are made to re-establish priorities. XONITEK Corporation 17 Details of filling out the FMEA… Person Responsible and Due Date – Enter the name of the person who has the lead action and target date of completion… Actions Taken – Describe the action and implementation date… Severity/Occurrence/Detection – The revised values based on actions taken… RPN – Revised RPN recalculated (multiply the three values: Severity, Detection and Occurrence) from the values above… XONITEK Corporation 18 Sample Completed FMEA… XONITEK Corporation 19 FMEA – Interactive Example XONITEK Corporation 20