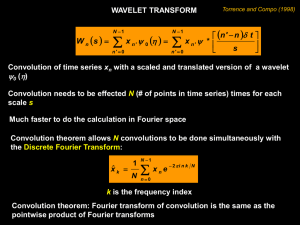
Wavelet phase determination without accurate time
advertisement
WAVELET PHASE ESTIMATION WITHOUT ACCURATE TIME-DEPTH CONVERSION JIANGBO YU ADVISOR: DR. JOHN CASTAGNA AGL UPDATE MEETING MAY 2, 2012 CONTENT • Introduction • Theory • Results • Conclusion INTRODUCTIONSEISMIC-TO-WELL-TIE CONVOLUTION Statistical wavelet from seismic Reflectivity series from well logs Phase rotate wavelet until maximum correlation is found QC initial tie Final tie Edgar and van der Baan, 2009 PROBLEMS OF SONIC LOG CALIBRATION • P-wave velocity from sonic log is different with seismic velocity • Short logging runs, or gaps in sonic log coverage • Inaccurate time-depth conversion • Aggressively forcing a well tie will affect the estimated wavelet THEORY-HISTOGRAM MATCHING PHASE ESTIMATION 1. Zero-phase wavelet estimation Zero-phase wavelet from seismic Normalized Amplitude Spectrum 0.3 Normalized spectral amplitude 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 -50 0 50 0 20 40 60 Frequency (Hz) 80 THEORY – HISTOGRAM MATCHING 2. Frequency domain deconvolution Deconvolution output Narrow-band reflectivity 0 0 500 500 1000 1000 1500 1500 2000 2000 Amplitude spectrum Normalized spectral amplitude Normalized spectral amplitude Amplitude spectrum 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 20 40 60 Frequency (Hz) 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 80 0 20 40 60 Frequency (Hz) 80 Amplitude histogram of narrow-band reflectivity Amplitude histogram of inverted reflectivity 2.5 2 2 Density Density 1.5 1.5 1 0.5 0.5 0 1 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 Data 0.4 0.6 0 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 Data 0.4 0.6 THEORY – HISTOGRAM MATCHING True phase 90degree 32 30 28 Misfit 26 24 22 20 97 -150 -100 -50 0 Phase Rotation Estimated Estimated wavelet Wavelet 50 100 True wavelet Phase rotated wavelet -60 -60 -40 -40 -20 -20 Time (ms) Time (ms) 18 -200 0 0 20 20 40 40 60 60 13-Oct-2011 10:26:46 13-Oct-2011 10:26:46 150 200 THEORY – HISTOGRAM MATCHING Assumption: Major part of the difference between inverted reflectivity amplitude distribution with well log derived reflectivity amplitude distribution is caused by the incorrect phase of wavelet Advantage: Will not be affected by inaccurate time-depth conversion REAL DATA Correlation: 0.924 REAL DATA 7 1.615 x 10 1.61 1.605 Misfit 1.6 1.595 1.59 1.585 -89 1.58 -200 -150 -100 -50 Estimated from seismic-to-well tie (-86 degree) 0 Phase rotation 50 100 150 200 Estimated from histogram matching (-89 degree) RESULT– REAL REFLECTIVITY RESULT– ACCURATE TIME-DEPTH CONVERSION Histogram matching Estimated Wavelet Wiener filter Wiener Filter -60 -40 -40 -40 -20 -20 -20 0 Time (ms) -60 Time (ms) Time (ms) True wavelet Phase rotated wavelet -60 0 0 20 20 20 40 40 40 60 60 60 13-Oct-2011 10:26:46 13-Oct-2011 10:26:46 07-Mar-2012 17:41:13 RESULT– BULK SHIFT Synthetic trace (black) vs. Bulk shifted synthetic trace (w) 100 Time (ms) 200 300 400 500 600 TrueTrue wavelet wavelet Histogram matching Estimated Wavelet -60 -40 -40 -20 0 -20 Time (ms) Time (ms) Time (ms) -60 -40 -20 0 Wiener filter Wiener Filter -60 0 20 20 20 40 40 40 60 60 60 RESULT– DYNAMIC SHIFT Synthetic trace (black) vs. Dynamic shifted synthetic trace (w) 100 Time (ms) 200 300 400 500 600 Histogram matching Estimated Wavelet Wiener filter Wiener Filter -60 -40 -40 -40 -20 -20 -20 0 0 20 20 40 40 60 60 Time (ms) -60 Time (ms) Time (ms) TrueTrue wavelet wavelet -60 0 20 40 60 CONCLUSION • Inaccurate time-depth conversion will affect seismic wavelet estimation through well-tie • Histogram matching could estimate wavelet phase correctly even with a wrong time-depth conversion