Kock_2012_HumanComConf_SEMwWarpPLS
advertisement

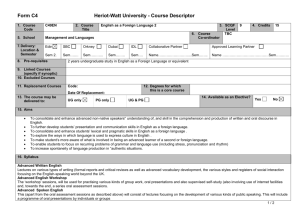
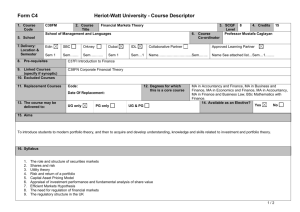
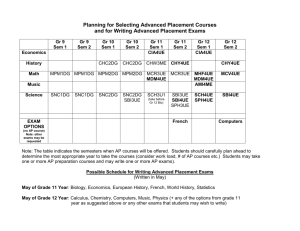
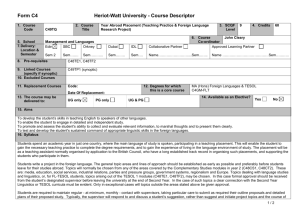
Structural Equation Modeling in Human-centric Computing Research: A Study of Electronic Communication in Virtual Teams Using WarpPLS Ned Kock Texas A&M International University Outline of presentation • • • • • • Fundamental problem with tech research Types of models, including SEM models Challenges in SEM analyses WarpPLS Electronic communication in virtual teams YouTube video and WarpPLS resources Fundamental problem with tech research • A technology research team develops a new technology • They say: We developed a new technology, and it works! • But often they cannot answer these questions: – Is the technology associated with an increase in performance in a given task? – If yes, how much? Two-variable model Coefficient of association (beta) and related P value (probability that the association is due to chance) Variable reflecting degree of use of a technology by a team Variable reflecting performance in a given team task Two-variable model: Measurement Variables frequently measured as columns on a table where each row refers to an individual or team Multiple regression model Variables Tech and Effic “compete” with one another for the explained variance in Perf Variable reflecting the efficiency of a team, in terms of speed and cost Similar to multiple regression model, but indirect effects are also included Path model SEM model SEM = structural equation modeling Similar to path model, but variables are measured through other variables Latent variable (LV) with 8 indicators, hence “8i” The 8 indicators that make up LV SEM model with results P values < 0.05 suggest significant associations among LVs Generality of SEM • Two-variable models and tests, such as ANOVA, are special cases of multiple regression models and tests • Multiple regression models are special cases of path models • Path models are special cases of SEM models • SEM models and tests are very general and can be employed in most technology studies Challenges in classic SEM analyses • Classic SEM is also known as covariancebased SEM • Multivariate normality is assumed, but frequently not the case • Linearity is assumed, but frequently not the case • Usually indirect and total effects, with respective P values, are not calculated Nonlinearity among variables • Most relationships among variables describing natural and behavioral phenomena are nonlinear • Particularly common are noncyclical nonlinear relationships, such as logarithmic, hyperbolic decay, exponential decay, exponential, and quadratic relationships • Trying to force-model nonlinear relationships as linear may cause false positives (type I error) and false negatives (type II error) in multivariate analyses Force-modeling as linear J-curve pattern modeled as a linear relationship (R = .582; Variance explained = 33.9%) Nonlinear modeling J-curve pattern modeled as a nonlinear relationship (R = .983; Variance explained = 96.7%) WarpPLS as a solution • Uses resampling techniques (e.g., bootstrapping) for calculation of P values, therefore not requiring multivariate normality • Takes nonlinearity among latent variables into consideration in the calculation of coefficients of association • Indirect and total effects, with respective P values, are calculated automatically E-communication in virtual teams • Study of 290 new product development teams • New product development examples – Develop a new car part – Develop a new chemical • The teams were geographically distributed • The teams used a variety of e-communication technologies (e.g., email and videoconferencing) SEM model to be tested Prjmgt = degree to which project management techniques were used by team ECM = degree of electronic communication media use by team Effic = efficiency of team, in terms of speed and cost Success= success of team, in terms of new product sales and profits Test results: Direct effects More electronic communication media used by team -> more project management techniques used Test results: Direct effects (2) More project management techniques used -> more team efficiency in terms of speed and cost Test results: Direct effects (3) More team efficiency in terms of speed and cost -> more team success in terms of new product sales and profits Test results: Direct effects (4) More project management techniques used -> more team success in terms of new product sales and profits Test results: Direct effects (5) More electronic communication media used by team -> no more or less success in terms of new product sales and profits; when Prjmgt and Effic are controlled for Test results: Direct effects (6) More electronic communication media used by team -> no more or less success in terms of new product sales and profits; when Prjmgt and Effic are controlled for This suggests that electronic communication media use exerts its effects in indirect ways Test results: Total effect of ECM β=0.15 (P=0.01) More electronic communication media used by team -> more success in terms of new product sales and profits Test results: Total effect of ECM (2) β=0.15 (P=0.01) Each 3-point increment in use of electronic communication media on a 0-10 scale (one standard deviation), is associated with a 15 % increase in Success Test results: Nonlinearity WarpPLS: YouTube videos • SEM Analysis with WarpPLS (all steps) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yUojJaV3jlA • Other YouTube video resources: – Perform SEM Analysis and View Results with WarpPLS (Step 5) • http://youtu.be/Srp9ewa1T8o – Various video clips • http://www.scriptwarp.com/warppls WarpPLS.com WarpPLS blog Acknowledgements: Resources used • • • • Mobilemadlibs.com Scriptwarp.com Warppls.blogspot.com WarpPLS.com Thank you!