Force Protection Call 4
A-0938-RT-GC
EUSAS
European Urban Simulation for Asymmetric Scenarios
Scalarm: Massively Self-Scalable Platform
for Data Farming
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
Agenda
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Introduction to Data Farming in the EUSAS project
The problem of Data Farming scale
Overview of Scalarm
Architecture of Scalarm
Resource management
Scalarm applications
Conclusions
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
2
Goals of data farming in EUSAS
However,
As
Result
During
Each
Agents
Moreover,
a result,
agent
of
training
can
the
ifgroups
we
many
also
can
mission
look
sessions
be
be
scenarios
may
parameterized!
divided
closer,
cannot
have
soldiers
the
into
of
leaders.
bemission
simulation
groups!
predicted
perform
areaprocess
simply
possible
mission
on
is(scenario).
but
the
more
soldiers
basis
complicated
of are
the able
fewthan
serious
to it
seems.
execute
game
executions
mission only
of the
a few
scenario.
times during the training session.
Data farming allows analysis of missions that have several different parameter
combinations (possibly billions).
1. group that loots:
Leader of group 1:
•radius of influence - 10,
•prestige - 30,
•…
•group size - 30,
•aggression of members Agent 1:
10,
•readiness for
for aggression
•readiness
ofaggression
members -- 510,
•anger - 3,
2.
group
•fear
- 12, that is prone
to
•….violence
•group2:size - 12,
Agent
•aggressionforof members •readiness
10,
aggression - 10,
•readiness
•anger - 10,for aggression
of members
- 25
•fear
- 2,
•….
In EUSAS project data farming provides:
•
Identification of dependences between input parameters and simulation result
(described by measures of effectiveness).
•
Comparison of behaviour models/soldiers strategies.
•
Selection of input parameters for training sessions
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
3
Introduction to Data Farming in the EUSAS project
• Data Farming, in general, enables discovery of useful
insights in studied phenomena by providing large
amounts of data for analysis.
• In the context of EUSAS, Data Farming is utilized to
study agents’ behaviour in various scenarios in order
to verify different engagement strategies.
• EUSAS developed a novel system, called Scalarm, to
facilitate conducting large Data Farming experiments
with heterogeneous computational infrastructure.
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
4
The problem of Data Farming scale – simple
scenario
•
Two groups:
1. Looters group
1
2. Group that is prone to violence
•
Two informal leaders:
•
•
2
Many input parameters:
•
•
soldiers do not know who they
are
group sizes, leader prestige,
readiness for aggression…
Many monitored MoEs:
•
•
escalation, anger, number of
killed or injured agents…
Presented application of data farming system:
•
Identification of dependencies between input parameters and simulation results
(described by Measures of Effectiveness).
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
5
The problem of Data Farming scale
•
Simple simulated scenario can include:
• 2 individual agents representing group leaders (each with 22
parameters)
• 2 groups of agents (each group with 24 parameters)
•
•
•
•
=> 92 different parameters for a single scenario
Let’s suppose we want to check only 2 values for each
parameter => 2^92 different simulations
Let’s suppose a single simulation runs only for 1 second on
average => 157,019,284,536,451,074,949 compute years
We need to filter input parameter combinations even more
and have a lot of computing power at the backend.
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
6
Scalarm goals
•
•
•
•
•
Simulating complex phenomena with multiple input
parameters by running various types of simulation
applications, e.g. multi-agent, optimization, etc.
Self-scalable platform adapting to particular problem size
and different simulation types
Exploratory approach for conducting Data Farming
experiments
Supporting online analysis of experiment partial results
Running on Cloud, Grid and private cluster infrastructures
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
7
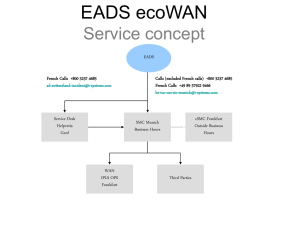
Scalarm architecture
Small experiment
Large
experiment
Standard
Very
largeexperiment
experiment
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
8
Resource management
Client
Client
Workload change:
shorter simulations =>
Platform
increase
of
management
management
resources
overhead
More
workload
Free resources
Experiment
conducting
EM
SiM
EM
SM
EM
EM
SM
SM
SiM
SM
SiM
SM
SiM
SiM
SiM
SiM
SiM
SiM
SiM
SiM
Computational
resources
- worker node
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
EM – Experiment Manager SM – Storage Manager SiM – simulation manager
9
Scalarm applications - TODO
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
Comparison of behaviour models/soldiers strategies
•
Crowd behaviour depends on
many input parameters:
•
•
Behaviour model/strategy
that works well for one
parameters’ set may
work badly for another.
Example:
Soldiers model created with MASDA:
escalation mean: 72.22
Different strategies may be compared in 3 steps:
1. Multiple execution of mission by soldiers
(using different strategies).
2. Behaviour cloning.
3. Executing data farming experiment for each
cloned strategy.
First implementation of soldiers model
escalation mean: 153.53
Conclusion: MASDA helped to choose strategies that work well in different conditions.
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
11
Conclusions
1. To enhance soldiers’ training, a large number of analysis of
soldiers’ behaviour in different scenarios is required, thus
Data Farming is a crucial module of the project.
1. EUSAS Data Farming module (implemented as Scalarm)
constitutes a complete virtual platform for executing
interactive Data Farming experiments.
1. Scalarm enables analysts to generate and analyze large
amount of data with computer simulation in order to gain
useful insight into simulated scenarios.
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved
12
Thank you for your attention !
© EADS 2010 – All rights reserved