viro lec 4
advertisement

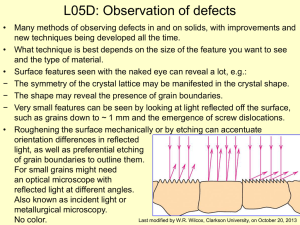
LECTURE 4: Methods used in Virology Viro100: Virology 3 Credit hours NUST Centre of Virology & Immunology 3. Centrifugation • After a virus has been propagated it is usually necessary to remove host cell debris and other contaminants before the virus particles can be used for laboratory studies, for incorporation into a vaccine, or for some other purpose. • Many virus purification procedures involve centrifugation; partial purification can be achieved by differential centrifugation and a higher degree of purity can be achieved by some form of density gradient centrifugation Partial Purification by Differential Centrifugation Purification of Virion by Density Gradient Centrifugation Rate zonal centrifugation involves layering the preparation on top of a pre-formed gradient. Equilibrium centrifugation can often be done starting with a suspension of the impure virus in a solution of the gradient material; the gradient is formed during centrifugation. 4. Structural investigation of cells and virion • Light Microscopy • Electron Microscopy • Transmission Electron Microscopy • Scanning Electron Microscopy • X-ray crystallography • Nuclear Magnetic Resonance • Atomic Force Microscopy Light Microscopy • Virions are beyond the limits of resolution of light microscopes • Light microscopy has useful applications in detecting virus infected cells • Cytopathic effects • Confocal microscopy • The principle of this technique is the use of a pinhole to exclude light from out of focus regions of the specimen. • Laser Electron Microscope • Structure of virions or of virus infected cells involve electron microscopy • Negative staining is carried out by using heavy metal containing compounds • Potassium phosphotungstate and ammonium molybdate • It generate contrast • Negative staining techniques have generated many high quality electron micrographs X-ray Crystallography • Detailed information about the three dimensional structures of virions (and DNA, proteins and DNA – protein complexes) • Crystal of the virions or molecules • crystal is placed in a beam of X-rays, which are diffracted by repeating arrangements of molecules/atoms in the crystal • Analysis of the diffraction pattern allows the relative positions of these molecules/atoms to be determined The diffraction information is fed into a computer, where 3-d coordinates can then be calculated based on electron densities that tend to diffract the x-rays more than anything else. The analysis integrates all of this information to yield a prediction of the complete 3-d structure 5. Electrophoretic techniques • to separate proteins by charge and or size • to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments • DNA Gel electrophoresis • SDS PAGE • Sodium dodecyl sulphate, Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis SDS PAGE DNA Gel Electrophoresis Thank You!