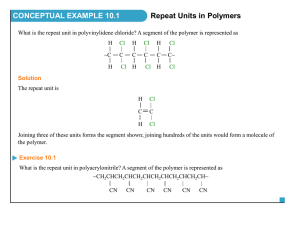
Functional Groups
advertisement

Organic Structure • Among neutral (uncharged) organic compounds – – – – – carbon: four covalent bonds and no unshared pairs of electrons hydrogen: one covalent bond and no unshared pairs of electrons nitrogen: three covalent bonds and one unshared pair of electrons oxygen: two covalent bonds and two unshared pairs of electrons a halogen: one covalent bond and three unshared pairs of electrons Models • Draw a lewis structure, make the model, draw ther 3-D structure, and decribe the bond angles for the following: • C2H6 • C2H4 • C2H2 • C2H5Cl • C2H4O • CH2O • CH5N Alcohols • Alcohol: contains an OH (hydroxyl) group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom : R R-C-O-H R Functional group (R = H or carbon goup : HH H-C-C-O-H HH Structural formula CH3 CH2 OH Condensed structural formula – may be primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) H CH3 -C-OH H CH3 -C-OH CH3 CH3 -C-OH H A 1° alcohol CH3 A 2° alcohol CH3 A 3° alcoh ol Alcohols • Problem: Draw Lewis structures, make the model, and describe the geometry and polarity for the two alcohols of molecular formula C3H8O Alcohols • Problem: draw Lewis structures and condensed structural formulas for the two alcohols of molecular formula C3H8O • Solution: : : Lew is stuctu res HH H H-C-C-C-O-H HH H Cond ensed stru ctural formulas CH3 CH2 CH2 OH A p rimary alcohol H H:O: H OH H C-C-C-H HH H CH3 CHCH3 A secon dary alcohol Amines • Amine: a compound containing an amino group – the amino group may be primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) CH3 NH2 CH3 NH or (CH3 ) 2 NH Methylamin e (a 1° amine) CH3 D imethylamin e (a 2° amine) CH3 NCH3 or (CH3 ) 3 N CH3 Trimethylamin e (a 3° amine) Amines – Problem: Draw Lewis structures, make the model, and describe the geometry and polarity for the two primary amines of molecular formula C3H9N Amines – Problem: draw condensed structural formulas for the two primary amines of molecular formula C3H9N – Solution: NH2 C-C-C-NH2 C-C-C Th e three carbon s may be bond ed to n itrogen in tw o w ays NH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 NH2 CH3 CHCH3 Add s even hydrogens to give each carbon four b on ds an d give the correct molecu lar formula Aldehydes and Ketones • Both contain a C=O (carbonyl) group – aldehyde: contains a carbonyl group bonded to a hydrogen; in formaldehyde, the simplest aldehyde, the carbonyl group is bonded to two hydrogens – ketone: contains a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms RO R C-C-H O CH3 CH R Fun ctional A cetaldeh yde grou p (an aldehyde) RO R O R C-C-C R CH3 CCH3 R R Functional group Acetone (a ketone) Aldehydes and Ketones – Problem: Draw Lewis structures, make the model, and describe the geometry and polarity for the two aldehydes of molecular formula C4H8O Aldehydes and Ketones – Problem: draw condensed structural formulas for the two aldehydes of molecular formula C4H8O • Solution: O CH3 CH2 CH2 CH O CH3 CHCH CH3 or or CH3 CH2 CH2 CHO CH3 CHCHO CH3 Carboxylic Acids • Carboxylic acid: a compound containing a -COOH (carboxyl: carbonyl + hydroxyl) group • in a condensed structural formula, a carboxyl group may also be written -CO2H. O O CH3 COH RCOH Fu nctional Acetic acid group (a carb oxylic acid ) Carboxylic Acids – Problem: Draw Lewis structures, make the model, and describe the geometry and polarity for the single carboxylic acid of molecular formula C3H6O2 Carboxylic Acids – Problem: draw a condensed structural formula for the single carboxylic acid of molecular formula C3H6O2 • Solution: the only way the carbon atoms can be written is three in a chain; the -COOH group must be on an end carbon of the chain O CH3 CH2 COH or CH3 CH2 COOH