CHAPTER 5
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
“You are what you eat!”
Standards
•Distinguish among proteins, carbohydrates,
lipids, and nucleic acids.
Objectives
•Identify the major structural components and
functions of the four major macromolecules
Shoulder Partners
Flip Books
Take out your flip books for
notes
Turn to last page – it should be
open for notes about definitions
and reactions
Building Macromolecules
Take out the pieces of
macromolecules that you
colored and cut out last class
period
You also need one sheet of
construction paper
What is a MACROmolecule?
A Large molecule with a complex
structure
A polymer built from monomers
“little” molecule
Macromolecule
Poly - mer
Many
Parts
• A long molecule made of monomers
bonded together
Mono - mer
One
Part
The “building blocks” of polymers
A monomer is a sub-unit of a
polymer.
Three of life’s organic macromolecules are
polymers
• Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids
EXAMPLES
Think – Pair – Share
Explain to your partner how these
Lego structures are like Polymers
How are Polymers made?
How do monomers bind to form
polymers?
• condensation reactions called
dehydration synthesis (removal of
water)
How do polymers break down?
Hydrolysis reaction
• Hydro – lysis
Water
To Break
• Water is added to break the bonds
that hold the polymer together.
Hydrolysis
Think – Pair – Share
Why would polymers need to be “broken
down”?
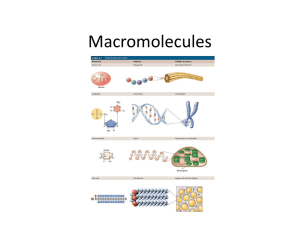
Classes of Organic
Macromolecules:
•
•
•
•
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
CARBOHYDRATES
Carbo - hydrate
Carbon
Water
Monomer
• Monosaccharide
• (“mono” = one; “saccharide” = sugar)
Polymers
• Disaccharides (di = two)
• Polysaccharides (poly = many)
Think – Pair – Share
What are some functions of
carbohydrates?
Functions of Carbohydrates in living
things:
• Major fuel/energy source
• Energy storage
• Can be used as raw materials for
other Macromolecules
• Structural/building material in plants
Structure of Monosaccharides
Contain only C, H, O
All have the
molecular formula (CH2O)n
In aqueous solutions many
monosaccharides form rings:
Structure of Disaccharides
Consists of two monosaccharides
The monosaccharides are joined by a
glycosidic linkage (bond)
Polar Bears
What reaction forms the glycosidic
linkage (bond) between the
monosaccharides to become a
disaccharide?
• Dehydration synthesis
Build a Carbohydrate
Assemble a disaccharide sugar.
• The building block/monomers of
simple sugars
carbohydrates are ____________.
2
• Place ________of
these into a chain
• Use the triangle water to point to the
bond site. Draw an arrow to show if
water is being added or released during
this reaction.
Label as a dissaccharide
Build a Carbohydrate
H2O
Polysaccharides
Structure: Polymers of a few hundred
or a few thousand monosaccharides.
Functions:
• energy storage molecules
• structural support
Examples of Carbs:
Starch - plant storage form for energy
• easily broken down into glucose units
Cellulose - fiber-like structural
material made of glucose monomers
• used in plant cell walls
Why is Cellulose so strong?
Glucose monomers are flipped to expose equal
Hydroxyl groups on either side of the chain
When Cellulose chains are lined up next to each
other, they Hydrogen Bond making a strong
material that’s difficult to break!
Glycogen is the animal short-term
storage form of energy
• Glucose monomers
Penguins
What reaction breaks the glycosidic
linkage (bond) between the glucose
molecules in glycogen so the
monomers can be used for fuel?
• Hydrolysis
Chitin is a polysaccharide used as a
structural material in arthropod
exoskeleton and fungal cell walls.
Build a Carbohydrate
Assemble the remaining carbohydrate
monomers into a polysaccharide
sugar.
Place the remaining carbohydrate
monomers into a chain.
Use the triangle water to point to the bond
site. Draw an arrow to show if water is
being added or released during this
reaction.
Standards
Distinguish among proteins, carbohydrates,
lipids, and nucleic acids.
Objectives
Identify the major structural components and
functions of the four major macromolecules
PROTEINS
Proteins
Monomer
• amino acids
• connected by peptide bonds
• Have a 3 dimensional globular shape
Amino Acids
• Molecules with carboxyl and amino
groups
• Differ in their properties due to
differing side chains, called R groups
20 different
amino acids
•The sequence of
amino acids
determine the
shape of the
protein
Did you know?
•Our body can only synthesize 12 of the
20 amino acids.
Think – Pair – Share
Where do we get the other 8 amino
acids?
Polymers =
polypeptides
Peptide bonds
connect amino
acids to form
polypeptide
chains
Examples of Protein Functions
Immune System
• Antibodies (proteins) bind to foreign
substances
Transport
• Membrane transport proteins - move
substances across cell membranes
• Hemoglobin carries oxygen, iron, and
other substances through the body.
Muscle Contractions
Signaling - Hormones such as insulin
regulate sugar levels in blood.
Proteins are very complex! Their specific
structure determines their function.
HEMOGLOBIN: Transport of
gases and iron in blood
ACTIN: Filament involved in
muscle contraction
Four Levels of Protein Structure
Primary
structure
• Is the unique
sequence of
amino acids
in a
polypeptide
+H N
3
Amino end
Gly ProThr Gly
Thr
Amino acid
subunits
Gly
Glu
Cys LysSeu
LeuPro
Met
Val
Lys
Val
Leu
Asp
AlaVal Arg Gly
Ser
Pro
Ala
Glu Lle
Leu Ala
Gly
Asp
Thr
Lys
Ser
Lys Trp Tyr
lle
Ser
ProPhe
His Glu
Ala Thr PheVal
Asn
His
Ala
Glu
Val
Asp
Tyr
Arg
Ser
Arg
Gly Pro
Thr Ser
Tyr
Thr
lle
Ala
Ala
Leu
Leu
Ser
Pro
SerTyr
Thr
Ala
Val
Val
LysGlu
Thr
AsnPro
Figure 5.20
o
c –
o
Carboxyl end
Secondary structure
• Is the folding of the polypeptide one time
• Forms an a helix or a b pleated sheet
pleated sheet
O H
H
H
H
R
R
C C N
C C N
N
N
C
C C
C
C
R
R
O
O
H
H
H
H
R
R
O
C
O
C
H
H
N
C
C N H C N H C N
H
O
C
C
O
H
H
O
Amino acid
subunits
R
R
R
C H
C H
O C
O C
N H
N H
N H
N H
O C
O C
C
H C R H C R
H C R H
R
N H O C
N H
O C
O C
C
O
N
N H
H
C
C
R
R
helix
O
O H
H H
H
R
C C N
C C N
N
N
C C
C C
R
R
O
O
H
H
H
R
O
H C
C
R
O
C
H
N
H
C N
C
H
C
O
H
R
R
C
N
H
H
H
C N
O C
Tertiary structure
• Is the overall three-dimensional
shape of a polypeptide
CH2
CH
2
Hydrogen
bond
O
H
O
CH
H3C
CH3
H3C
CH3
Hydrophobic
interactions and
van der Waals
interactions
CH
HO C
CH2
CH2 S S CH2
Disulfide bridge
O
CH2 NH3+ -O C CH2
Ionic bond
Polypeptide
backbone
Quaternary structure
• Is the overall protein structure that results
from the combination of two or more
polypeptide subunits
Polar Bears
Explain the four
levels of protein
structure to your
penguin
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease: A simple change in Primary Structure
Enzymes
proteins that act as a catalyst
Penguins
List at least 2
factors that
effect protein
structure
Environmental Factors That Effect Protein
Shape
pH
Temperature
Salinity
Denatured protein is biologically inactive
Can sometimes “renature” if primary
structure is unchanged.
Build a Protein
Assemble a 4-monomer polypeptide.
• The building block/monomers of
Amino Acids
proteins are ____________.
• Place 4 of these into a chain
• Use the triangle water to point to the
bond site. Draw an arrow to show if
water is being added or released
during this reaction.
Label as a 4-monomer polypeptide
Build a Protein
Assemble the remaining monomers into
a polypeptide.
• Use the triangle water to point to the
bond site. Draw an arrow to show if
water is being added or released
during this reaction.
?
Label as a ___-monomer
polypeptide
Standards
Distinguish among proteins, carbohydrates,
lipids, and nucleic acids.
Objectives
Identify the major structural components and
functions of the four major macromolecules
LIPIDS
•
•
•
•
What are Lipids?
Fats, phospholipids, steroids, waxes, pigments
Hydrophobic (“hydro”=water; “phobic” = fearing)
Consist mostly of hydrocarbons
Do NOT consist of polymers
Monomers
• The building blocks of all lipids are
called
• Fatty Acids
Functions of Lipids in living things:
• Energy storage
• Cell membrane structure
• Protecting against desiccation
(drying out).
• Insulating against cold.
• Absorbing shocks.
• Regulating cell activities by
hormone actions.
Structure of Common Fats - Triglycerides
Consist of a single glycerol and usually three fatty
acids
Glycerol – an alcohol with three carbons
Fatty Acid - Long Hydrocarbon chains with a
Carboxyl group at one end.
Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats :
• one or more double
bonds between
carbons in the fatty
acids allows for “kinks”
in the tails
• liquid at room temp
• most plant fats
Saturated fats:
• No double bonds in
fatty acid tails
• solid at room temp
• most animal fats
Oleic acid
cis double bond
(b) Unsaturated fat and fatty acid
causes bending
Stearic acid
(a) Saturated fat and fatty acid
Saturated fatty
acid
Saturated fatty
acid
Unsaturated
fatty acid
Build a Lipid
Assemble a triglyceride.
• The building block/monomers of lipids
Fatty Acids
are ____________.
• Use your notes to assemble w/ correct
structure/components
• Use the triangle water to point to the
bond site. Draw an arrow to show if
water is being added or released
during this reaction.
Label as a triglyceride
Phospholipids
Structure: Glycerol + 2 fatty acids +
phosphate group.
Function: Main structural component of
membranes, where they arrange in bilayers.
Phospholipids in Water
Draw a Phospholipid
Next to your triglyceride, draw a
phospholipid
Label the parts/components
Label the drawing as a phospholipid
Waxes
Function:
• Lipids that serve as coatings for plant
parts and as animal coverings.
Steroids
Structure: Four carbon rings with no fatty
acid tails
Functions:
• Component of animal cell membranes
(Ex: Cholesterol)
• Modified to form sex hormones
Standards
Distinguish among proteins, carbohydrates,
lipids, and nucleic acids.
Objectives
Identify the major structural components and
functions of the four major macromolecules
NUCLEIC
ACIDS
Nucleic Acid Monomers = Nucleotides
Nucleotide = 5 carbon sugar,
phosphate, and nitrogenous base
Deoxyribose in DNA
Ribose in RNA
Two Types of Nucleic Acids Polymers
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
• double stranded
• can self replicate
• makes up genes which code
for proteins is passed from
one generation to another
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
• single stranded
• functions in actual synthesis
of proteins coded for by DNA
• is made from the DNA
template molecule
Function of Nucleic Acids :
The stuff of Genes
Nucleic acids store and transmit
hereditary information
Genes
• Are the units of inheritance
• Code for the sequence of
amino acids(making
polypeptides)
• Made of nucleic acids
Both
polymers
function
together
for
protein
synthesis
Building the Polymer
Phosphate group of one nucleotide
forms strong covalent bond with the
#3 carbon of the sugar of the other
nucleotide.
DNA:
• Double helix
• 2 polynucleotide chains wound
into the double helix
• Base pairing between chains
with H bonds
•A-T
•C-G
Building DNA
The building block/monomers of lipids
nucleotides
are ____________.
• Build 2 nucleotides
• Use your notes to assemble w/
correct structure/components
• Link the 2 nucleotides together
• The phosphate group of one
nucleotide binds to the pentose
sugar of the next
Label as DNA
Building DNA
Use your notes to assemble w/ correct
structure/components
• Use the triangle water to point to the
bond site. Draw an arrow to show if
water is being added or released
during this reaction.
Label as a triglyceride
Summary of the Organic
Molecules: