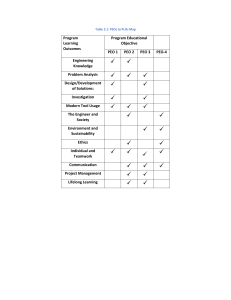
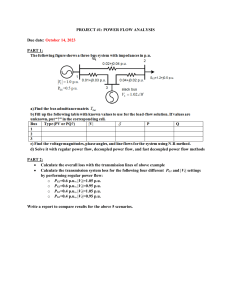
CH217-Redox.1.2012
advertisement

Review General Re action : (oxid) + e- = (red) (red) K= (oxid )(e-) é ù 2.303RT P(red) o ú E=E logê nF ë P(oxid) û Review II 1 é P(red ) ù pe = pe - log ê n ë P(oxid ) úû o 1 pe = log(Kredox ) Notice the sign! n o DG o RT 2. 203RT 2. 203RT o E == ln (K ) = log(K ) = pe nF nF nF F o where: F = Faraday constant = 23, 060cal / molV = 96, 490J / molV T = temperature o K n = number of electrons transfered R = 8.314J / mol K = 0. 082057 liter atm / deg mol 2. 303RT and = 0.05916 at 25o C F WHAT ABOUT NATURAL SYSTEMS? o pe E o + - O 2 + 4H + 4e Û 2H 2 O 20.75 1. 227 • Oxygen would like to be reduced. • If we can combine oxygen with a compound that wants to be oxidized we have an energy source! What wants to be oxidized? o pe E o + O 2 + 4H + 4e Û 2H 2 O o 2+ Hg + 2e Û Hg 20.75 1. 227 13.35 0. 789 o 2+ Cu + 2e Û Cu 5. 71 0.337 0 0 + - 2H + 2e Û H 2 (g) o 2+ Pb + 2e Û Pb - 2. 31 - 0.126 What about Natural systems? - CO 2 + 4e + 4H Û CH 2 O + H 2O + This is a general equation for the oxidation/reduction of organic material Relative to activity series o o pe E O 2 + 4H + + 4e - Û 2H 2 O 20.75 1. 227 Hg 2+ + 2e - Û Hg o 13.35 0. 789 Cu 2+ - + 2e Û Cu o + 2H + 2e Û H 2 (g) 5. 71 0.337 0 0 + CO2 + 4e + 4H Û CH2 O + H2 O -1. 20 Pb 2+ - + 2e Û Pb o - 0. 071 - 2. 31 - 0.126 Using the two half reactions + - - + O 2 + 4H + 4e Û 2H 2 O 20.75 1.227 CO 2 + 4e + 4H Û CH 2 O + H 2O -1. 20 - 0. 071 O 2 + CH 2 O Û H 2 O + CO 2 Eo = 1.227 + (0.07) = 1.297 V O 2 + CH 2 O Û H 2 O + CO 2 Eo = 1.227 + (0.07) = 1.297 V CH2O = 0.01 M, O2 = 0.2 atm CO2 = 1.0 atm ù 0.05916 é [1] E = 1.297 logê ú = 1.26 4 ë[0.2][0.01]û The negative G indicates that this reaction is spontaneous! What happens when we run out of oxygen? Other oxidants will take the place of oxygen. Most sediments are anoxic! Biologically Mediated reactions O2 (g) + 4H + + 4e - = 2H2 O peo = 20.8 MnO2(s) + H+ + e- = MnOOH(s) peo = 18.3 3 + - 2 NO + 2H + 2e = NO + H 2 O peo = 14.2 NO2- + 8H + + 6e - = NH4+ + 2 H2 O peo = 15.1 MnOOH(s) + 3H+ + e- = Mn2+ + 2H2O peo = 25.4 + - 2+ Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3H + e = Fe + 3H2 O peo = 17.1 SO42 - + 8H + + 6e - = S(s) + 4H2 O peo = 6.0 - + S(s) + 2e + 2H = H2 S (g) peo = 2.9 CO2 + 4H + + 4e - = CH 2 O + H2 O peo = -1.2 Sequence of Microbially Mediated redox processes http://www.chem1.com/acad/webtext/pdf/c3redox.pdf Redox / Nutrient Cycling CO2 Surface Water (CH2O)106(NH3) 16(H3PO4) Fe(OH)2PO 4 PO43- 2- Fe(II) + O2 Fe(OH)3 (s) Bottom Water Sediment CO2 PO43- Fe(II) + PO43Fe(OH)3 (s) S2FeS iron sink. Oxygen Demanding Substances CH2O + O2 = CO2 + H2O NH4+ + 2 O2 = 2H+ + NO3- + H2O 4Fe2+ + O2 + 10H2O = 4Fe(OH)3 (s) + 8H+ 2SO32- + O2 = 2SO42- Biological Oxygen Demand Quantity of oxygen utilized by a suitable aquatic microorganism in five days. Why five days? Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) oxygen utilized by a specific chemical titration. 3CH2O + 16H+ + 2 Cr2O72- = 4 Cr3+ + 3CO2 + 11 H2O