Secretion of small intestine
advertisement

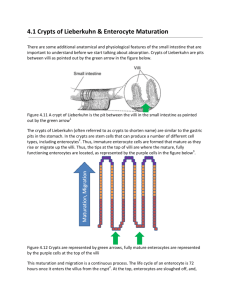
Secretion of small intestine: Extensive array of compound mucous secreting glands located in the 1st few centimeters of duodenum , these glands secrete mainly alkaline mucous in response to : 1- tectile or irritating stimulus of the overlying mucosa 2- vagal stimulation 3- gastrointestinal hormones especially secretin The function of mucous secreted by the glands is to protect the duodenal wall from digestion by gastric juice ., their rappid & intense response to irritating stimuli is especially geared to this purpose , in addition , the secretin stimulated secretion by glands contains a large excess of bicarbonate ion which add to the bicarbonate ion from pancreatic secretion &bile in neutralizing acid entering duodenum from stomach . bruner´s gland is inhibited by sympathetic stimulation , therefore , such stimulation is likely to leave duodenal bulb unprotected &is perhaps one one of the factors that cause this area to be site for peptivc ulcer in abou 50% of cases Secretion of intestinal digestive juice by crypts of leiberkuhn: crypts of leiberkuhn are small pits located on the entire surface of small intestine between the villi , the intestinal surface of both the crypt &villi are covered by an epithelium composed of 2 types of cell : amoderate number of goblet cells which secrete mucus that lubricate &protect the intestinal surface , & largre number of enterocytes which in the crypts secrete large quantity of water &electrolytes &over the surface of the villi reabsorbe water &electrolytes ,the intestinal secretions are formed by the enterocytes of the crypt at rate about 1800ml/ day , have slightly alkaline PH(7.5- 8), this circulation of fluid from the crypt to the villi supplies a watery veichle for absorption of substances from the crypt as it come in contact with villi which is the primary function of S.I.in addition to the watery secretion , the goblet cells in the epithelium secrete moderate amount of mucus which provide its usual function of lubrication &protection of intestinal mucosa . Mechanism of secretion of watery fluid: The exact mechanism that cause the marked secretion of watery fluid by the crypts of leiberkun is not known, it is believed to involve at least 2 active secretory processees:1active secretion of bicarbonate ion &2-active secretion of chloride ion . Finally all these ions together osmotic movement of water . Enzyme in the secretion of S.I.” When secretion of S.I.are collected without cellular debris they have almost no enzyme , howevere, the the enterocytes of the mucosa , especoially those that cover the villi , contain digestive enzyme that digest specific food substances while they are being absorbed through the epithelium .. These enzymes are 1-several peptidase (for splitting peptides in to amino acids ) 2- some enzymes for splitting disacharides in to monosacharides 3- intestinal lipase splitt neutral fat in to glycerole &fatty acids . Most if not all of these enzymes are mainly in the brush border , yhey are believed to hydrolysis of food on the outside surface of the microvilli before absorption of the end products . Regulation of small intestinal secretion : 1- local stimuli: the various local nervous reflexes in response to the presence of chyme in the intestine especially reflexes intiated by tactile or irritative stimuli &by increase enteric nervous activity associated with gastrointestinal movements , therefore,the greater amount of chyme the greater secretion . 2- hormonal secretions:some of hormones that promote GITsecretion also increase S.I. secretion , especially secretin &cholecystokinin in general , the local enteric reflex mechanism play the dominant role. Secretion of large intestine : 1-mucus secretion :the mucosa of the large intestine has many crypts of lieberkun but unlike that of S.I.there are no villi ,also the epithelial cells contain no enzymes , they consist mainly of mucous cells that secrete only mucus , therefore, the great secretion in the large intestine is mucus , this mucus containe large amount of bicarbonate ion caused by active transporte through other epithelial cells that lie between epithelial cells that secret mucus . The rate of secretion regulated by: 1- tactile stimulation 2- local nervous reflex 3- stimulation of pelvic nerves which carry parasympathetic innervation to cause marked increase in mucus scretion . Mucus in large intestine 1- protect the wall against excoriation 2- provide the adherant medium for holding fecal matter together . 3- protect the intestinal wall from bacterial activity 4 it plus the alkalinity of secretion . 2- secretion of water &electrolytes :when the L.I. becomes irritated like in bacterial infection , the mucosa secretes large quantities of water &electrolytes in addition to the normal viscid solution of alkaline mucus this act to dilute the irritating factors &cause rappid movements of fluid results in diarrhea,also washes away irritant facters