Intermolecular forces
advertisement

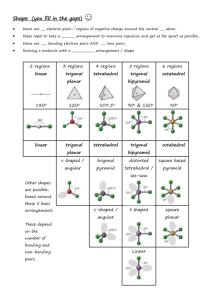
Forces in Solids and Liquids Types Strong forces – ionic bonds between ions (metal and non-metal atoms), covalent bonds (C and Si structures), metallic bonds (metal atoms only) Weak forces – between MOLECULES (non-metal atoms only) The nature of intermolecular forces Intermolecular forces are the forces that hold MOLECULES together in a MOLECULAR SOLID or LIQUID. The forces are WEAK in comparison to covalent, metallic and ionic bonds – this explains why molecular solids have LOW melting and boiling points The three types Hydrogen bonding Occurs only between molecules that contain a F, O or N bonded to a H Permanent dipole-permanent dipole Occurs between molecules which are polar Temporary dipole-temporary dipole Occurs between all molecules. Is significant for non-polar molecules and large molecules Questions: For each compound state the type of force holding the particles together. If molecular, draw its structure and state the most significant type of WIF Cobalt Methanol Tetrafluoromethane Hydrogen sulfide Magnesium fluoride Phosphine (PH3) Dichloromethane Hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen chloride Nickel Graphite Ammonia Helium Carbon dioxide Copper sulfate Answers: Cobalt Metallic bond Methanol Hydrogen bonding Tetrafluoromethane Temporary dipole Hydrogen sulfide Permanent dipole Magnesium fluoride Ionic bond Phosphine (PH3) Permanent dipole Dichloromethane Permanent dipole Hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen bonding Hydrogen chloride Permanent dipole Nickel Metallic bond Graphite Covalent bonds Ammonia Hydrogen bonding Helium Temporary dipole Carbon dioxide Temporary dipole Copper sulfate Ionic bond Question: Bromine melts at -7°C, and sodium bromide melts at 755°C. Explain why there is a big difference in their melting points. Answer: Bromine is a molecular solid with molecules composed of 2 covalently bonded bromine atoms. The molecules are held together by temporary dipoles as Br2 is a non-polar molecule. It is non-polar because the both Br atoms have identical electronegativity. Temporary dipoles are relatively weak, therefore little energy is required to break them and the melting point is low. NaBr is an ionic solid composed of Na+ and Br- ions in a 3D lattice. The ionic bonds holding the ions together are strong, requiring a lot of energy to break and therefore the melting point is high. Question: (complete and hand in for marking) Rank the following compounds from highest to lowest melting point. Explain your reasoning: Water diamond carbon dioxide sulfur dioxide sulfur trioxide iron Answer: Highest to lowest: Diamond - strong covalent bonds between C atoms Iron – strong metallic bonds between Fe atoms Water – WIF – hydrogen bonds between H2O molecules (contains O bonded to H) Sulfur dioxide – WIF – permanent dipoles between SO2 molecules (polar) Sulfur trioxide – WIF – temporary dipoles between SO3 molecules (non-polar) Carbon dioxide - WIF – temporary dipoles between CO2 molecules (non-polar and fewer electrons than SO3)