digestive_systems
advertisement
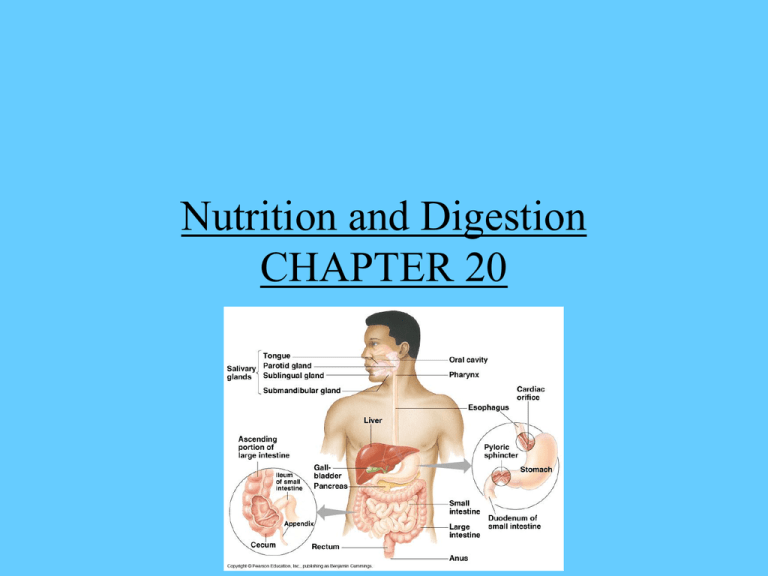
Nutrition and Digestion CHAPTER 20 • Everything that lives needs food, in order to carry out all of life’s functions. • Food contains complex organic and simple molecules that can supply both energy and raw materials. Nutrients The complex substances and simpler substances that are used in life processes. Nutrients • Food is composed of 3 major organic molecules & their building blocks. • Polymer-Large molecule (ex. Protein) • Monomer-Smallest building block (ex. Amino Acids) 1. Carbohydrates • Polysaccharides( Starch) are digested into monosaccharides. 2. Proteins • Proteins are digested into Amino Acids. 3. Lipids (Fats) • Fats are digested into fatty acids & glycerol. Human nutrition Do water, vitamins and minerals need to be digested? Why not? Digestion • Digestion is the process of converting complex organic molecules (Polymers) into smaller ones (Monomers) so they can be absorbed through the cell membrane. Autotrophs • produce their organic molecules in the process of photosynthesis. • Do plants carry out digestion? _______ • Why or why not? • Do plants carry out digestion? __NO_____ • Why or why not? They build their own organic substances by using water, carbon dioxide, and minerals absorbed from surrounding. Photosynthesis- makes sugars Sugars can be built into more complex sugar molecules or combined with minerals to form lipids and amino acids. Heterotrophs • obtain their organic molecules by eating. • Do heterotrophs carry out digestion? _YES____ • Why or why not? Chunks of food have to be broken down into smaller particles until in form of molecules small enough to pass through cell membrane. Do all nutrients need to be digested before entering the blood stream? NO! • Water, Vitamins, and Minerals readily pass across cell membrane with little or no need for digestion. DIGESTION IN HETEROTROPHS • Intracellular digestion Digestion that takes place inside a cell. • Protozoans use food vacuoles & lysosomes to digest the food. Food Vacuoles in Paramecium Intra or Extracellular? • Sponges have flagella that draw the water (containing plankton) in & digest the food in individual cells Extracellular Digestion • Digestion that takes place in a cavity surrounded by cells. • Hydra is a chunkfeeder, taking in large particles & digesting them in its gastrovascular cavity. • 2-Way traffic-1 opening! Filter Feeding-Pass food thru a part of their body that strains out microscopic plankton. • Sessile or slow moving animals like sponges & bivalves filter the water. • Sponges have flagella that draw the water in & digest the food intracellular. 1-Way Traffic A complete mouth-anus digestive tract is present in many animals. Much more efficient as digestive is divided into stages. Earthworm digestion • Complete digestive tract-Mouth-Anus Bivalves • Filter Feeders • Have a true digestive tract-strain food on mucus covered gills. • Incurrent & Excurrent siphons. http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=bFpblBf1dfE&safety_mode=tr ue&persist_safety_mode=1&safe =active http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=uO4lkvjLRs&feature=channel&safety_ mode=true&persist_safety_mode =1&safe=active Pharynx Muscular-helps to “suck in” soil Crop Stores the food Gizzard An organ filled with sand that grinds the food. Intestine Chemical digestion and absorbs nutrients. • Intestine Human Digestive System Video of digestive system http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uFX-MOLSGaU Beginning of Digestion • Mechanical & Enzymatic digestion begin in the mouth• Food is masticated to increase surface area for Enzymatic digestion . Human Salivary glands Secrete Saliva-Water, Salivary amylase that digests starch (enzymatic) Peristalsis • Peristaltic waves of esophagus muscles move food along the digestive tract stimulating the opening of the cardiac sphincter. 3 layers of muscle in stomach Stomach • The stomach’s rugae continue to churn (mechanical) the food, acts as a storage area for the food and.. • Chemical digestion also takes place… Gastric Juice • Gastric juice is secreted which contains HCL, mucus & Pepsin which will digest proteins. • Chyme then leaves the stomach thru the pyloric sphincter. Small Intestine-Several organs secrete digestive juices into the duodenum thru various ducts.The gall bladder adds bile-stored from the liver Pancreas • The Pancreas adds enzymes to digest all 4 groups of organic molecules. • Intestinal Juice acts on the disaccharides in the small intestine. Enzymes in digestion Final steps in Digestion The complete breakdown & absorption of organic molecules occurs in the jejunum & ileum. Villi & Microvilli • The lining of the small intestine is folded to increase the surface area to absorb the max amount of nutrients. • The absorbed nutrients travel in the blood to the liver to be sorted out by the Liver. Large Intestine (Colon) Water is absorbed as solid feces are formed until they exit through the rectum Large intestine What occurs in the large intestine? Why should you eat yogurt when you take antibiotics? What can be dangerous about having diarrhea? Colonoscopy /http://www.insidestory.iop.org/insidestory_fl ash1.html A- Salivary Glands/Mouth B- Esophagus C- Stomach D- Pancreas E- Large Intestine (Colon) F- Appendix G- Small Intestine H- Gallbladder I- Liver J- Rectum/Anus Vestigial structure, once used to aid in carbohydrate digestion APPENDIX Releases bile into small intestine- helps digest fats GALL BLADDER Adds enzymes like trypsin to digest organic molecules (proteins amino acids) into small intestine PANCREAS Mechanical and chemical digestion (amylase break down carbs). Chew up food to increase surface area for enzymes to digest Mouth/Salivary Glands Produces bile (helps digest fats) and sorts out nutrients. LIVER Water reabsorption LARGE INTESTINE Mechanical (churning and mixing) and chemical digestion. Gastric Juices- HCl, pepsin, mucus start to break down proteins changing food into chyme. SMALL INTESTINE tubular passageway leading into stomach peristalsis- toothpaste squeezing movement of food. ESOPHAGUS Where solid feces are stored and then released. RECTUM/ANUS Complete breakdown and absorption of organic molecules. Villi (and microvilli) increases the surface area so the max. amount of nutrients can be absorbed into the bloodstream to be transported to liver. SMALL INTESTINE Digestive disorders • • • • • • • Gall bladder disease Lactose intolerance Irritable bowel syndrome Crohn’s Disease Heartburn/esophageal reflux disease Diabetes Hyper/hypoglycemia Importance of good nutrition • Why the saying “you are what you eat?” • What should you eat before a game or a run? • What should you eat after weight-lifting? • What foods should you avoid? • What is the best way to maintain a healthy body composition (lean/fat balance, weight)? Which type of organism do you think would have a longer digestive tract? An herbivore or a carnivore…. Hmmmmm……. Carnivores vs Herbivores Why?









