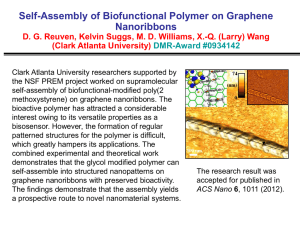
1: Introductory words
advertisement

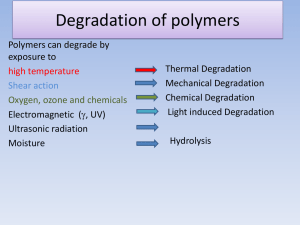
ADVANCED BIO-FRIENDLY POLYMERS Jaroslav Mosnáček What is degradation of polymers? • Any change of the polymer properties relative to the initial, desirable properties. • In this sense, "degradation" is a generic term for any number of reactions which are possible in a polymer. • These reactions, in turn, lead to a change in the physical and optical properties of the polymer. • It is accompanied with change in molar mass of the polymers Mode of initiation of degradation Thermal* Photo (light induced)* Biological* Chemical (Hydrolytic)* Mechanical High Energy Radiation *Will be discussed MECHANISTIC ASPECT OF POLYMER DEGRADATION Mode of Initiation Chain scission Random Chain scission (Hydrocarbons) Thermal Norrish Type (I, II) chain scission (SSR) Photochemical Enzymatic or hydrolytic attack of esters, amides and glucosides (SSR) Biological/hydrolytic Norrish I and II Random scisson .+ . + + Alkanes Alkenes Alkadienes SSR= Single step reaction MECHANISTIC ASPECT OF POLYMER DEGRADATION Mode of Initiation Side Chain elimination Solvolysis (Hydrolysis) of ester linkage (SSR) Chemical (hydrolytic) Thermal Elimination of HCl (PVC) (CR) Side Chain Elimination Hydrolysis of ester linkages H H Cl Cl H Cl H Cl H PVC Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl - HCl Polyene Aromatics SSR= Single step reaction CR = Chain reaction MECHANISTIC ASPECT OF POLYMER DEGRADATION Mode of Initiation Thermal Depolymerization COOR COOR COOR COOR COOR COOR COOR . COOR COOR .+ COO COOR COOR COOR Cross-linking COOR Typical for Poly(methyl methacrylate and mainly for other acrylate based polymers Monomer Thermal, Photochemical, Mechanical, Chemical Oxidation PP with Oxygen Beta-scission of tertiary alkoxy radicals