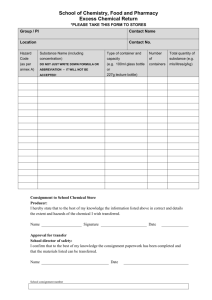
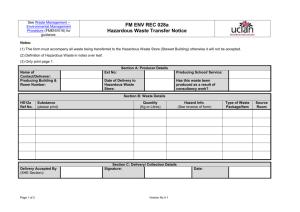
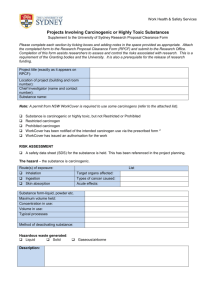
Almac_CHEMICAL_AWARENESS_COURSE_Master
advertisement

An Introduction to Chemical Awareness An Introduction to Chemical Awareness An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Aims and Objectives • • • • • Current legislation Hazards and symbols of chemicals Types of chemicals and what they do PPE Risk assessment An Introduction to Chemical Awareness EXAMPLES • • • • • • • • Legionnaires disease Blood borne viruses MRSA Latex gloves Respiratory Sensitizers Cyotoxic drugs Clinical Waste Glutaraldehyde • • • • • • • • Bleach Paints Glues Lubricating oils Wood dust Pesticides Ozone (Photocopying) Toilet cleaners • Chlorohexidine An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Current legislation An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions • Very toxic or toxic substances and preparations cause death or acute or chronic damage to health when inhaled, swallowed or absorbed via the skin, even in small quantities. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions • Harmful substances may cause death or acute or chronic damage to health when inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through the skin. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions • Corrosive substances and preparations may destroy living tissues on contact and include: Acids – Sulphuric Acid Alkalis – Sodium Hydroxide An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions • Irritant substances and preparations are non-corrosive but may cause inflammation through immediate, prolonged or repeated contact with skin or mucous membranes An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Sensitising substances and preparations may cause an allergic reaction. (Inhalation and Skin contact) Di-Isocyanates, Flour/Grain Dust, Crustaceans/Fish An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Carcinogenic substances and preparations may induce cancer or increase its incidence if inhaled or ingested or absorbed by the skin. Mustard gas, hardwood dusts, coal soots An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Mutagen substances or preparations which cause a permanent change in the amount or structure of the genetic material in an organism, resulting in a genetic change or the characteristics of the organism. Eg Ethidium Bromide (dye) An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Teratogenic substances which are capable of disturbing the growth and development of an embryo or foetus. Eg Ethanol An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Solvent is a liquid or gas that dissolves a solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution. In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Oil a colloquial term used to refer to certain diverse and unrelated compounds sharing the same physical properties (such as viscosity and a hydrophobic nature), while ignoring related compounds. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Oxidisers a chemical compound that readily transfers oxygen atoms. Eg Hydrogen Peroxide An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Flammable or Highly Flammable or Extremely Flammable is the ease with which a substance will ignite, causing fire or combustion. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Explosion is a sudden increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner, usually with the generation of high temperatures and the release of gases. Eg Chemical An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Definitions Dangerous when wet substance is one that spontaneously undergoes a chemical reaction with water. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness “Substance Hazardous to Health ?” An Introduction to Chemical Awareness “Substance Hazardous to Health ?” An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Other signs An Introduction to Chemical Awareness EVALUATING THE RISK • • • • FIND OUT The likelihood of exposure What level of exposure could occur Potential duration of exposure Potential for recurring exposure CONCLUDE Whether existing or potential exposure is significant or not? An Introduction to Chemical Awareness “Substance Hazardous to Health” • • • • very toxic, toxic, harmful, corrosive, irritant WELs Biological agent Any substance creating a comparable hazard An Introduction to Chemical Awareness FACTORS FOR ASSESSMENT • • • • • • Routes of entry Health effects Chemical reactions Engineering controls Safety data sheets Personal protective equipment An Introduction to Chemical Awareness ROUTES OF ENTRY • INHALATION • INGESTION • SKIN ABSORPTION • INJECTION An Introduction to Chemical Awareness TOXIC EFFECTS THE EFFECTS OF A CHEMICAL ON THE BODY ARE DTERMINED BY: THE AMOUNT TAKEN INTO THE BODY THE EXPOSURE TIME An Introduction to Chemical Awareness TOXIC DOSES • ONE GRAM OF SALT CAN KILL A RAT • SIX GRAMS OF CAFFEINE CAN KILL A HUMAN • ONE TABLET OF PENICILLAN CAN KILL A PERSON WHO IS ALLERGIC TO IT An Introduction to Chemical Awareness ACUTE EFFECTS • Usually results from short exposures to high doses • Very often short lived, and usually followed by permanent damage or complete recovery • Effects are usually very visible so cause is easily found • Wide variation in effects from simple irritation to death An Introduction to Chemical Awareness CHRONIC EFFECTS (1) • Health Effects - from exposures over a “long” period of time. • Cause and effect difficult to identify An Introduction to Chemical Awareness CHRONIC EFFECTS (2) • CARCINOGENIC • TERATOGENIC • MUTAGENIC An Introduction to Chemical Awareness CHRONIC EFFECTS (3) • REPRODUCTIVE TOXINS These chemicals, unlike teratogens, can affect the male and female reproductive systems. As a result the ability to have children may be impaired. • SPECIFIC ORGAN TOXICITY Chronic overexposure to some substances can damage specific organs e.g. Carbon Tetrachloride can cause liver damage. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness WELs ( 1) • Workplace Exposure Limit (WELs):- Is the concentration of airborne substance, averaged over a reference period(e.g. 8 hour long term) to which employees may be exposed by inhalation under the circumstances. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness WELs ( 2) The concentration of an airborne substance, averaged over a reference period at which, according to current knowledge, there is no evidence that it is likely to be injurious to employees if they are exposed by inhalation, day after day, to that concentration An Introduction to Chemical Awareness WELs Cumulative effects of different chemicals. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness MAINTAINING CONTROL • Health questionnaires • Monitoring exposure -WELs • Emergency plans • Auditing procedures • Health surveillance An Introduction to Chemical Awareness SAFETY DATA SHEET 1 • • • • • • • • Identification of the substance/preparation Identification of the company or undertaking Composition/information on ingredients Hazard identification First Aid measurements Fire-fighting measurements Accidental release measures Handling and storage An Introduction to Chemical Awareness SAFETY DATA SHEET 2 • • • • • • • • • Exposure controls/personal protection Physical & chemical properties Stability & reactivity Toxicological information Ecological information Disposal information Transport information Regulatory information Other information An Introduction to Chemical Awareness ABBREVIATIONS • TWA = Time Weighted Average • STEL = Short term exposure limit (15 mins) • LTEL = Long term exposure limit (8 hours) (TWA) • WELs = Workplace Exposure Limit An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Skin Absorption • SK = Can be absorbed through the skin Exposure via the dermal route may: Make a substantial contribution to the body load. Cause systemic effects so conclusions based on airborne concentration limits may be invalid. • SEN = Causes respiratory sensitization (Asthmagen) An Introduction to Chemical Awareness COSHH Essentials Skin Care: Body’s largest organ. Protection against the environment. First line of defence against harmful bacteria. Without its sensory organs we would have no warning of dangerous contact. Wash hands regularly. Apply a moisturiser. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness CONTROL MEASURES “HEIRARCHY OF CONTROL” ELIMINATION SUBSTITUTION CONTROL AT SOURCE ENGINEERING CONTROLS : ( Total / Partial Enclosure / Isolation / LEV ) MAINTAIN DISTANCE REDUCE CONTACT TIME : (Rotation) PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT OPERATING PROCEDURES •SUPERVISION •TRAINING DISCIPLINE An Introduction to Chemical Awareness PRACTICAL CONTROLS • Limit volumes being handled /stored. • Review type, size, shape, weight of containers used. • Store incompatible substances separately. • Implement spillage /emergency procedures. • Transport substance in closed/sealed containers. • Use substances in less volatile states /forms. • Restrict access. An Introduction to Chemical Awareness PRE-INFORMATION, TRAINING & INSTRUCTION • Inform the employee about the risks • Give the employee information on PPE • Provide instruction on use • Arrange for training An Introduction to Chemical Awareness HEALTH SURVEILLANCE • • • • • • • Reactions / behaviour Skin examination Lung function test Breath sample Saliva sample Blood sample Urine sample An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Risk Assessment 1. Identify hazards 2. Decide who may be harmed and how 3. Evaluate the risks and decide on precautions 4. Record findings and implement them 5. Review your assessment update, if necessary An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Myth: Risk assessment is too complicated for me to do! Source: H and S Myths An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Myth: Graduates are banned from throwing mortar boards Source: H and S Myths An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Good schools need to focus on turning out people who are risk savvy, not risk averse petty bureaucrats equipped with tick-box clipboards. Safety needs to be a core value in schools just like everywhere else - not the first excuse of choice when things get a bit difficult. Source: Judith Hackett (Chair of HSE) An Introduction to Chemical Awareness Conclusions An Introduction to Chemical Awareness