Rubisco
advertisement

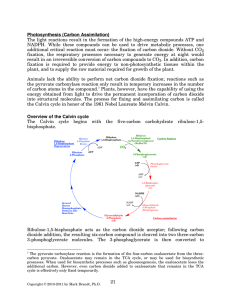
Calvin Cycle Calvin cycle cannot be called “dark reaction” because it is still lightdependent. Rubisco (1) Carbon fixation Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate + CO2 + 2(3-phosphoglycerate) Catalyzed by rubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase; RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase) Rubisco is the most abundant enzyme on the earth In stroma 50% of chloroplast protein is rubisco. One of the reasons why animals cannot photosynthesize because it lacks rubisco. Rubisco: 8 large subunits + 8 small subunits Large subunit is the catalytic subunit. (2). 3-phosphoglycerate glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (2). 3-phosphoglycerate glyceraldehyde 3phosphate包括了兩個步驟(為glycolysis的相反) 3-phosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate kinase 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Triose phosphate isomerase Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Carbohydrates can both synthesized in chloroplast and cytosol by utilizing fixed carbon from chloroplast. For cytosolic carbohydrate biosynthesis, triose phosphates needed are transported by Pi-triose phosphate antiporter (translocator) Most of the triose phosphates exported from chloroplast are dihydroxyactone phosphate. On the other hand, triose phosphates imported into chloroplast from cytosol are mostly 3phosphoglycerate. Pi-Triose phosphate antiporter This antiporter removes dihydroxyacetone phosphate from stroma into cytosol, importing Pi into stroma to ensure continuous supply of inorganic phosphate for photophosphorylation ATP synthesis. It will also move NADPH synthesized by photorespiration into cytosol. NADPH will be converted to NADH during this process. (3) Regeneration of ribulose 1,5bisphosphate from triose phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate is an important branchpoint. Cell can choose to synthesize starch or regenerate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate from F-6-P. Animals do not have these following enzymes so they can not perform photosynthesis: Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase ribulose 5-phosphate kinase rubisco For every triose phosphate synthesized, 9 ATP and 6 NADPH are consumed. One phosphate from ATP is exported with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Regulation of Carbon metabolism in plants is more complex than animals because of photosynthesis 1.thioredoxin system (photosystem I) 2.variation of H+ and Mg2+ concentration due to light exposure 3.Allosteric regulation by intermediates 4.covalent modification Regulation of rubisco: carbamylation of lysine residue Covalent modification Although carbamylation at lysine residue of rubisco will activate it, ribulose 1,5bisphosphate will inhibit this carbamylation at physiological pH. Rubisco activase will promote the ATPdependent release of ribulose 1,5bisphosphate, exposing lysine residue for carbamylation. Rubisco is activated after carbamylation activated rubisco will not be inhibited by ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. Nocturnal inhibitor also regulate photosynthesis • Some plants synthesize 2carboxyarabinitol 1phosphate in the dark, which is a potent inhibitor of carbamolyated rubisco. • It will be break down by rubisco activase or by light. Nocturnal inhibitor is similar to the b-keto acid intermediate of rubisco reaction Light reaction result in H+ transport into stroma. This causes stromal pH to rise. Mg2+ exported from thylakoid into stroma to balance charges. pH, [Mg2+] activate rubisco fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1) pH, [Mg2+] Light will cause disulfide bond reduction of these following enzymes through thioredoxin system : Ribulose 5-phosphate kinase Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Photorespiration •Aside from being an carboxylase, Rubisco is also an oxygenase. The oxygenation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate produces phosphoglycolate, a metabolically useless product. •Although rubisco does have higher affinity toward CO2 (9mM; O2 is 350mM), the concentration of O2 (20%) is much higher than CO2 (0.04%). •Rubisco requires aqueous solution of CO2. However, the solubility of CO2 decrease abruptly at higher temperature. •On average, one photorespiration happens for every three photophosphorylation. Phosphoglycolate is dephosphorylated in stroma. Similar to PDH and a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase C4 metabolism C4 metabolism • Because the initial trapping of CO2 in C4 metabolism involved PEP carboxylase and the production of oxaloacetate (a four carbon compound), it is called C4 metabolism. • PEP carboxylase utilizes HCO3-, which is structurally distinct from CO2 and O2. • Moving Calvin cycle to bundle sheath cell will shield rubisco from any possible exposure to oxygen. Bundle sheath cell is located in the center of the leaf Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) • Succulent plants such as cactus and pineapple grow in hot and very dry area have evolved a different strategy for carbon assimilation. • They also separate the initial trapping of CO2 from Calvin cycle like C4 plants, but the difference between CAM and C4 is CAM separated CO2 trapping and Calvin cycle over time, not space.