lightindependantphot..
advertisement

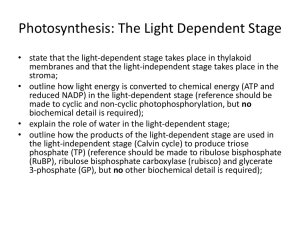
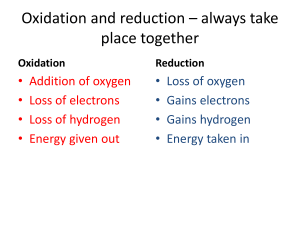
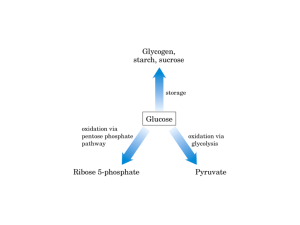
Light-independent reaction To be able to explain that: • Energy from the light-independent reaction is used to fix carbon dioxide. 1. Write a balanced equation for photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 2. Give reasons why photosynthesis is important. 3. 4. 5. Makes food, oxygen In which cycle does photosynthesis feature? carbon What is the waste product of photosynthesis? oxygen What is the splitting of water called? photolysis 6. What is made during the light dependent reaction? ATP, NADPH, oxygen The Light-Independent Reactions • The light-independent, or carbon-fixing reactions, of photosynthesis take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts • CO2 readily diffuses into the chloroplast where it is built up into sugars in another cyclic process called the Calvin cyclt Glossary • Ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) • glycerate 3phosphate (GP) • ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase • 5 carbon sugar • A 3 carbon compound (an acid) • An enzyme also known as RuBISCO • The fixation of Carbon Dioxide is light independent. • Carbon Dioxide combines with RuBP CO2 = 2 x glycerate 3 phosphate RuBP •CO2 is covalently bonded to RuBP catalysed by the enzyme RuBISCO •The product is two molecules of glycerate 3 phosphate •This process is called fixation • Energy and H+ ions are required to turn the Glycerate 3 phosphate into the 3 carbon sugar triose phosphate • Energy is provided by ATP and the H+ ion is provided by the NADPH from the light dependant reaction 2NADPH 2ADP + Pi 2NADP 2ATP CO2 = 2 x glycerate 3 phosphate RuBP 2 x Triose Phosphate • Two triose phosphate molecules join together to form one hexose sugar e.g. glucose • Glucose may be immediately respired, stored as starch or converted into other products • The bulk of triose phosphate is converted into more RuBP to enable the fixation of Carbon to continue • This uses the rest of the ATP produced in the light dependant reaction 2NADPH 2ADP + Pi 2NADP 2ATP CO2 2 x Triose Phosphate = 2 x glycerate 3 phosphate RuBP ADP + Pi ATP Hexose sugar • Plants can’t ingest proteins and fats • Calvin cycle is the starting point for all the substances a plant needs Product synthesis Hexose sugar Eg Glucose, Fructose Glycerol from Triose phosphate Fatty acids from glycerate 3 phosphate Amino acids synthesised from glycerate 3 phosphate Starch, Cellulose, Other Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins • 5 out of every 6 molecules of triose phosphate are used to regenerate RuBP Calvin cycle in summary • CO2 combines with ribulose bisphosphate • Glycerate phosphate is made • Glycerate phosphate is converted into triose phosphate • Triose phosphate is converted into glucose • RuBP is regenerated Questions 1. 5. Which compound is carboxylated? How is carbon dioxide fixed? What does GP stand for? Which compound is regenerated? What is ATP required for? 6. What is NADPH required for? 2. 3. 4. • RuBP • Joined to RuBP • Glycerate-3-phosphate • RuBP • Energy for reduction and regeneration of RuBP • Source of hydrogen for reduction What reaction converts GP into • triose phosphate? 8. What kind of sugar is RuBP? • 9. Which enzyme is important in • the Calvin Cycle? 10. How many carbon atoms in GP?• • 11. Where does the Calvin Cycle happen? 7. reduction pentose Rubisco 3 stroma